Digital Patient Intake and Clinical Workflow Software Sector M&A Transactions and Valuations

From Q1 2021 through Q4 2025, sustained investment in healthcare digitization, rising administrative complexity across provider organizations, and increasing pressure to improve operational efficiency drove robust M&A activity within the digital patient intake and clinical workflow software sector. As healthcare providers faced staffing shortages, reimbursement pressure, and heightened patient access expectations, software platforms embedded at patient access points and within day-to-day clinical workflows became increasingly mission-critical, driving sustained investor and acquirer interest.
Strategic acquirers and financial sponsors targeted software platforms that digitize patient access, intake, scheduling, and clinical workflows, viewing control of patient flow and operational data as foundational to long-term platform value. Acquisition strategies centered on scaling workflow-critical platforms, expanding functionality across intake, engagement, and clinical operations, and building integrated software ecosystems characterized by recurring revenue, high switching costs, and deep customer embeddedness.
This report analyzes M&A activity and valuation dynamics across the sector, including capital deployment trends, acquirer priorities, and valuation benchmarks such as enterprise value to revenue and enterprise value to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization multiples, while highlighting transactions that underscore continued consolidation, capability expansion, and the emergence of scaled, multi-product software platforms embedded across the patient access and clinical workflow lifecycle.
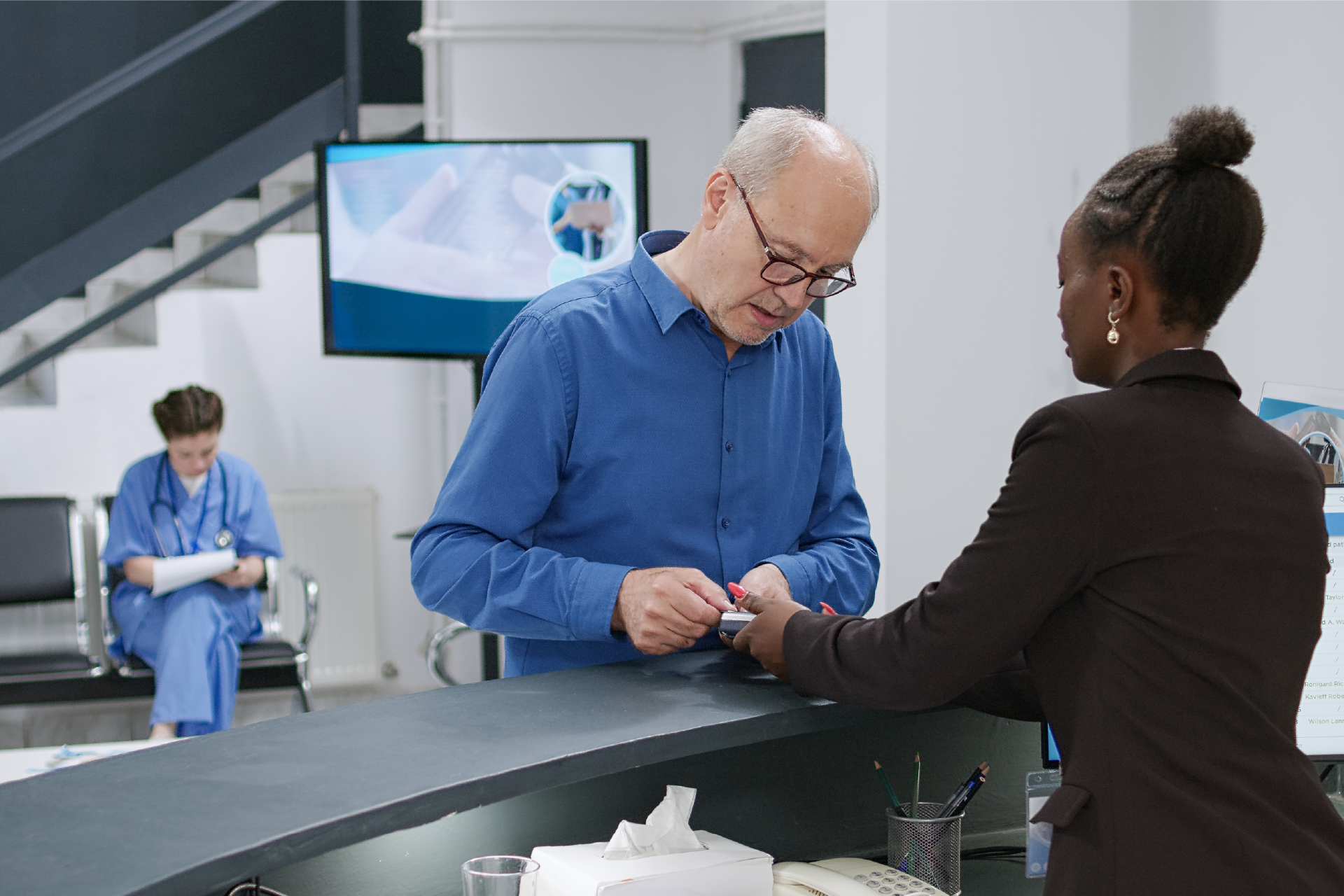

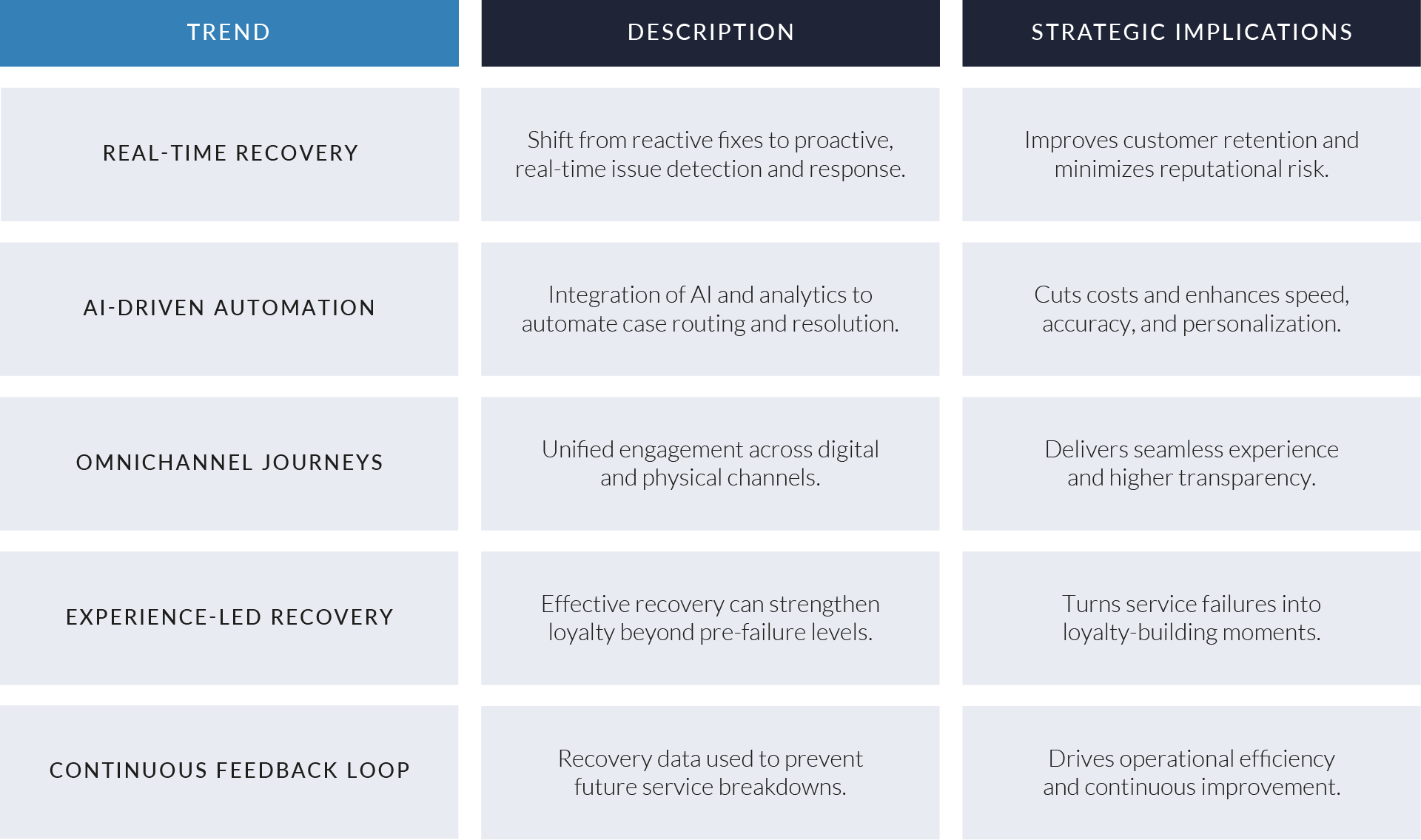
EXHIBIT 1
Digital Patient Intake and Clinical Workflow Software — Sector Overview

Source: PitchBook healthcare IT market research; NextGen Healthcare corporate and product disclosures; U.S. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) interoperability guidance; Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) patient access and interoperability rules; HL7 FHIR standards documentation; Health Journalism and Becker’s Healthcare digital front door coverage.
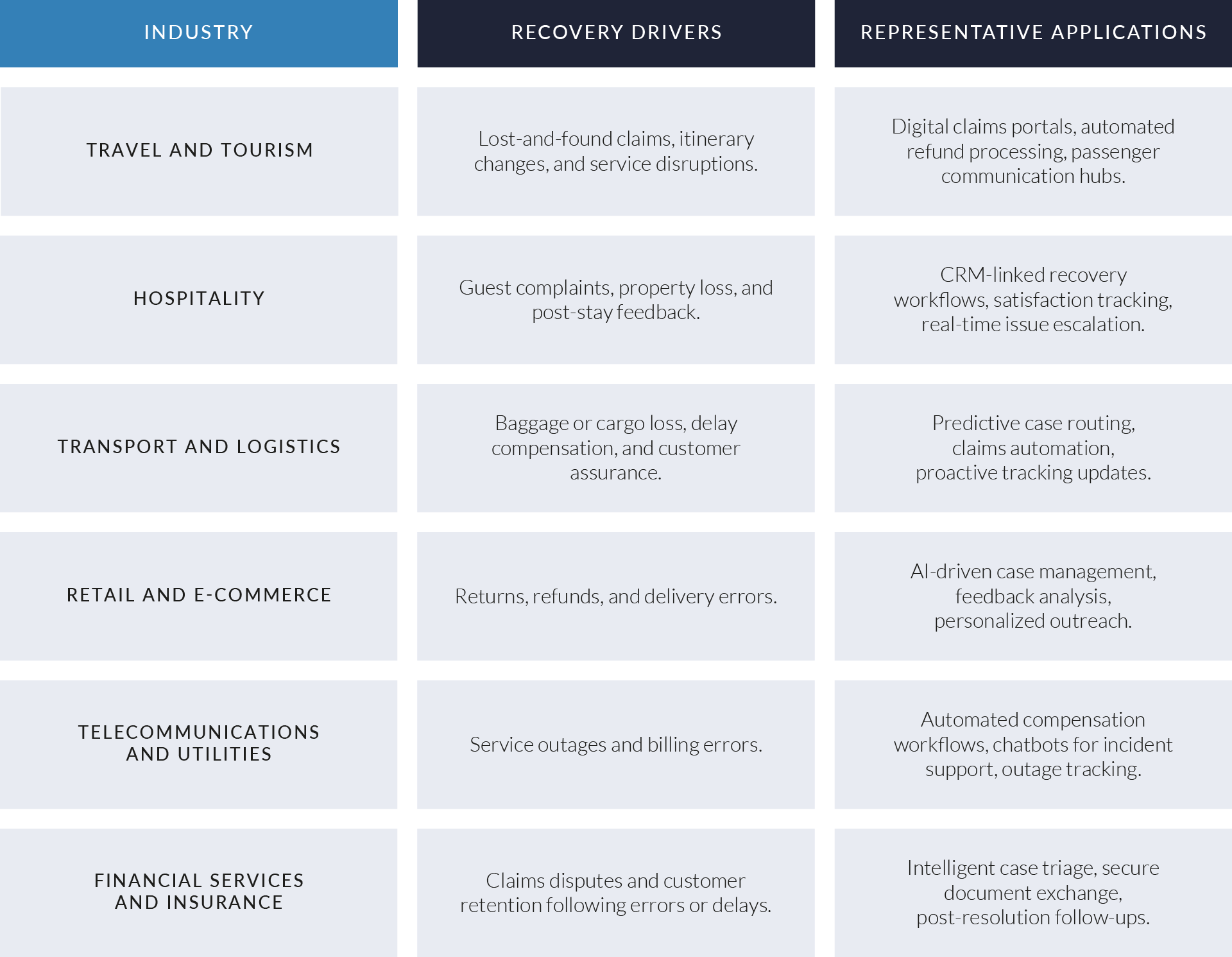
EXHIBIT 2
Key Trends Shaping the Digital Patient Intake and Clinical Workflow Software Sector

Source: PitchBook healthcare IT market research; NextGen Healthcare corporate and product disclosures; U.S. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) interoperability guidance; Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) patient access and interoperability rules; HL7 FHIR standards documentation; Health Journalism and Becker’s Healthcare digital front door coverage.
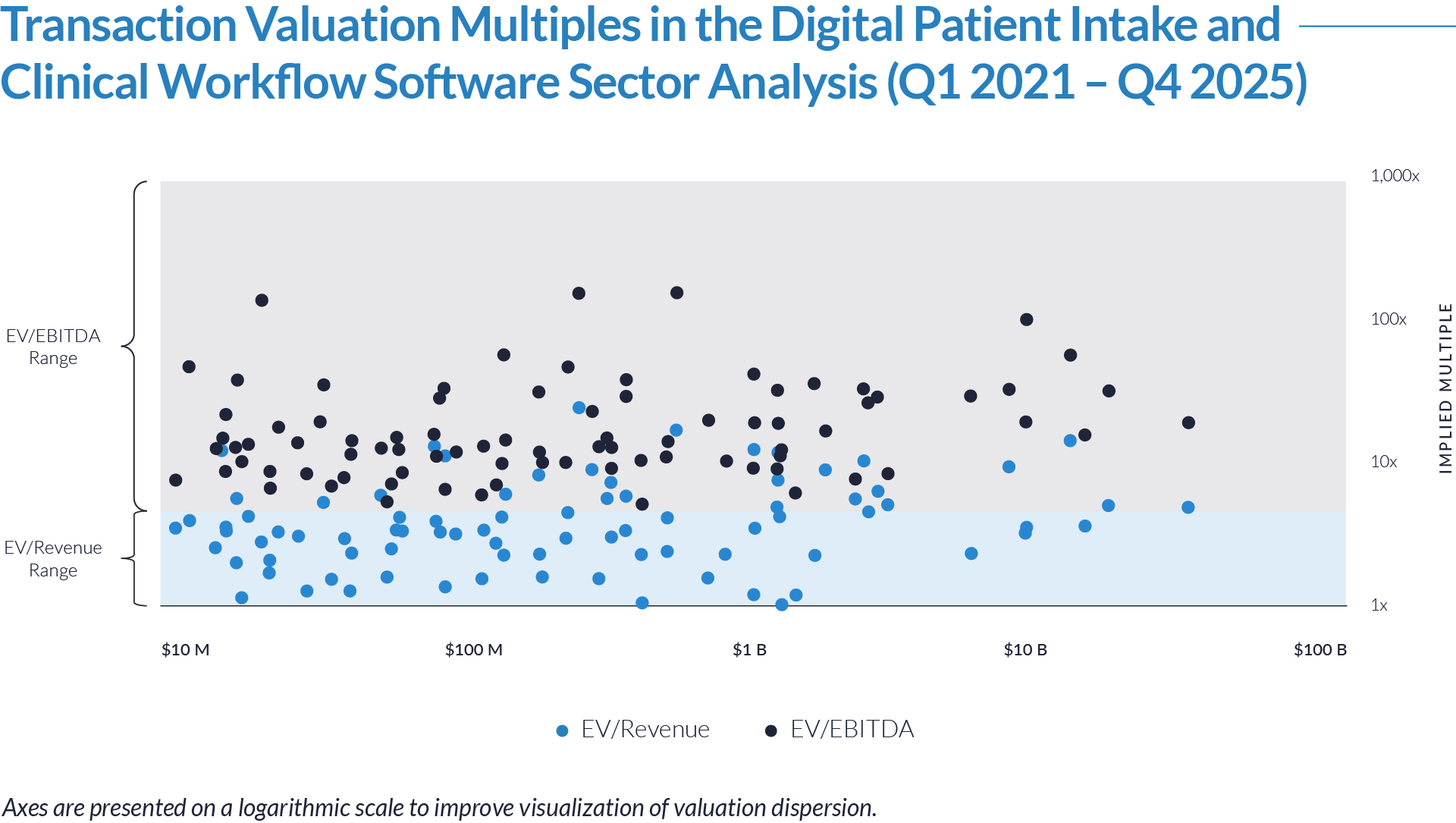
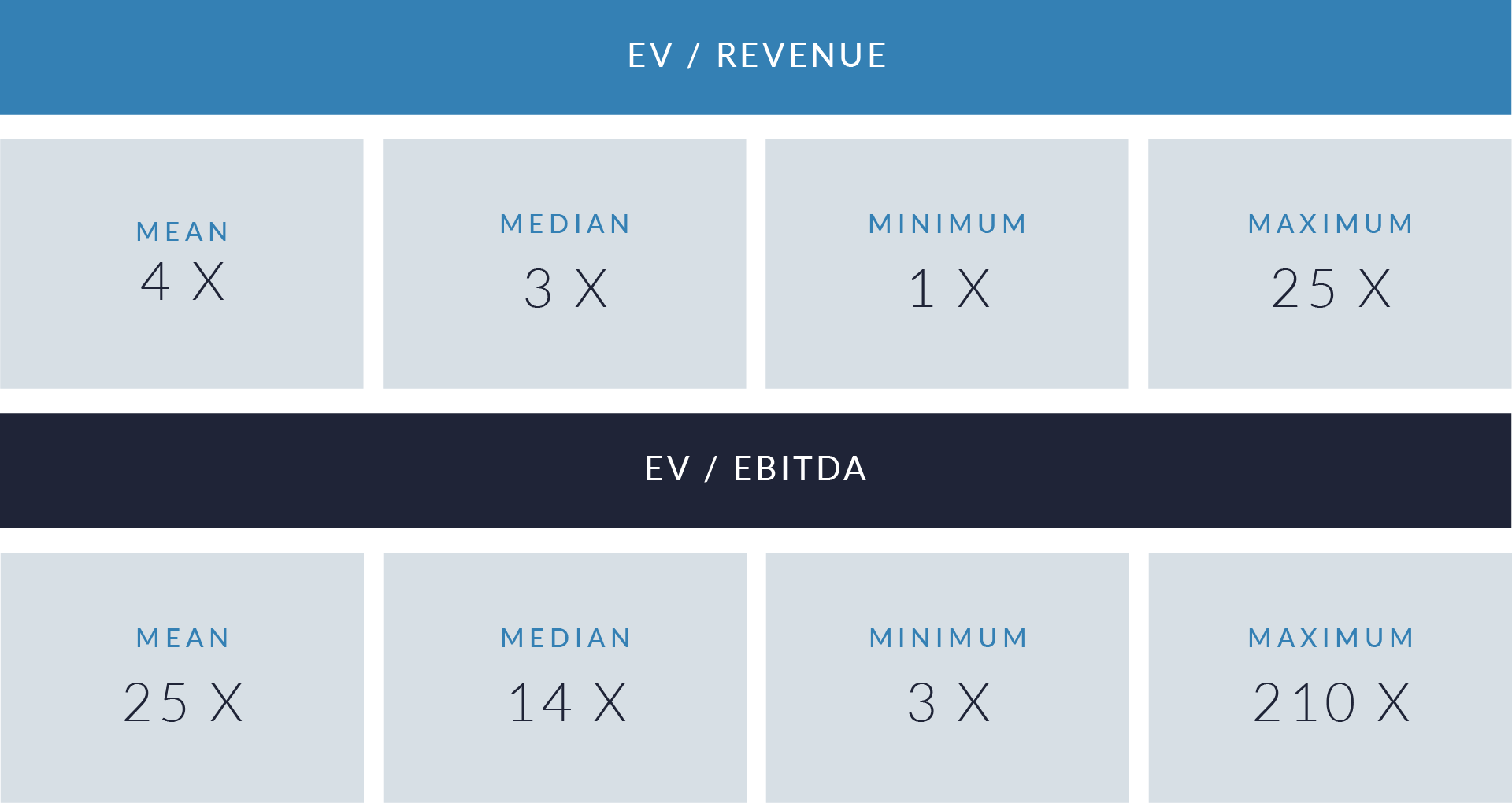
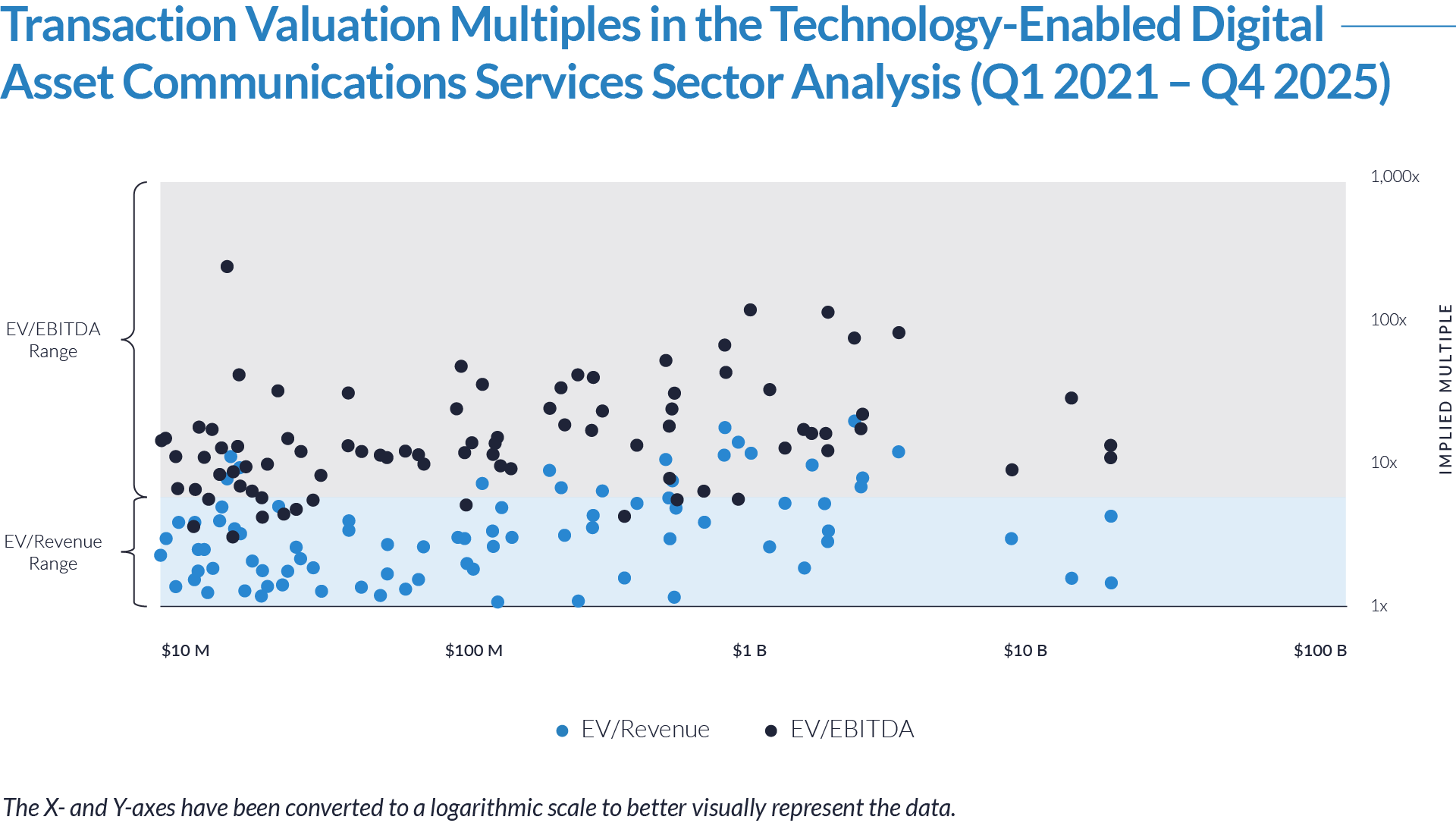
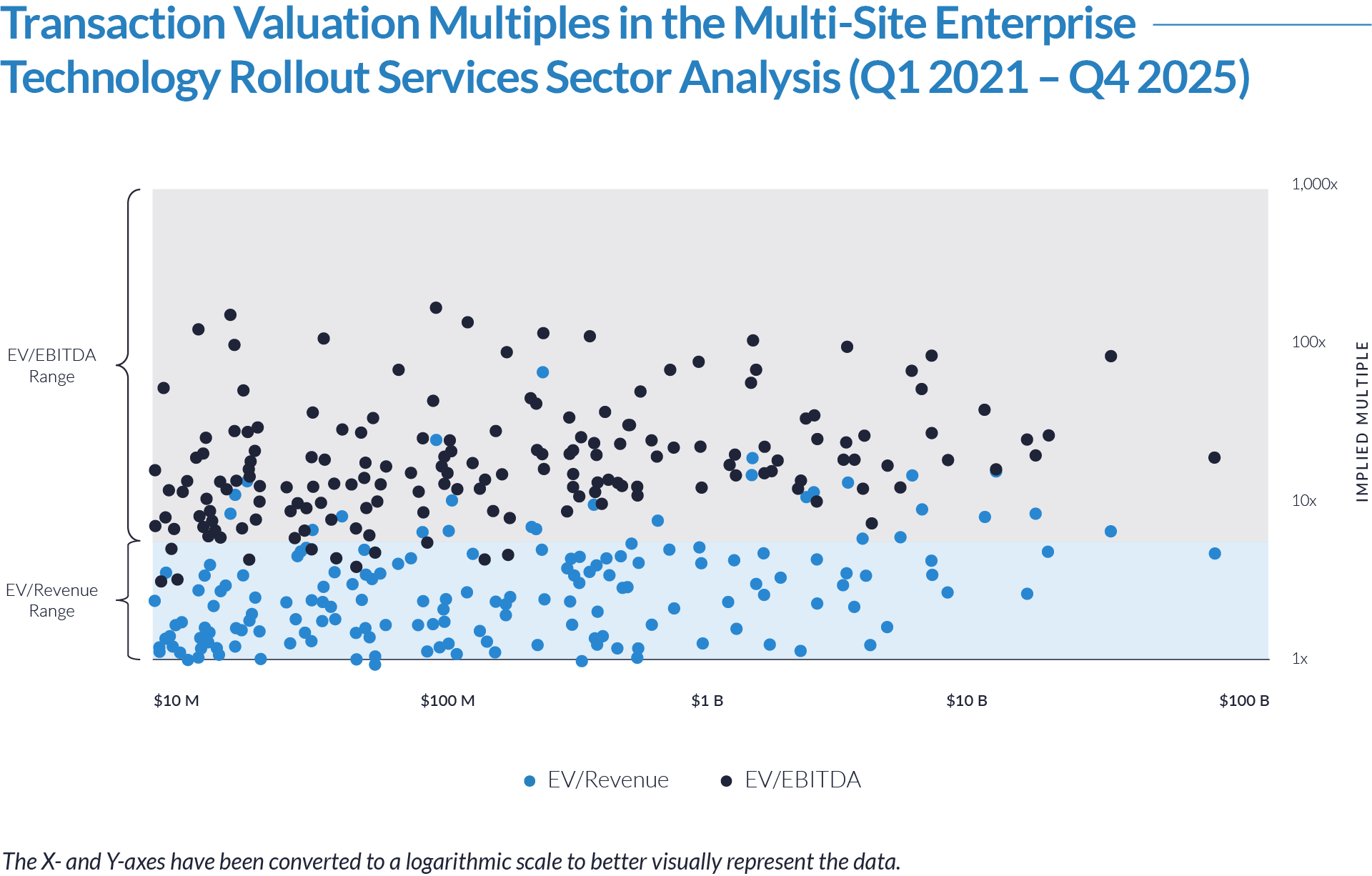
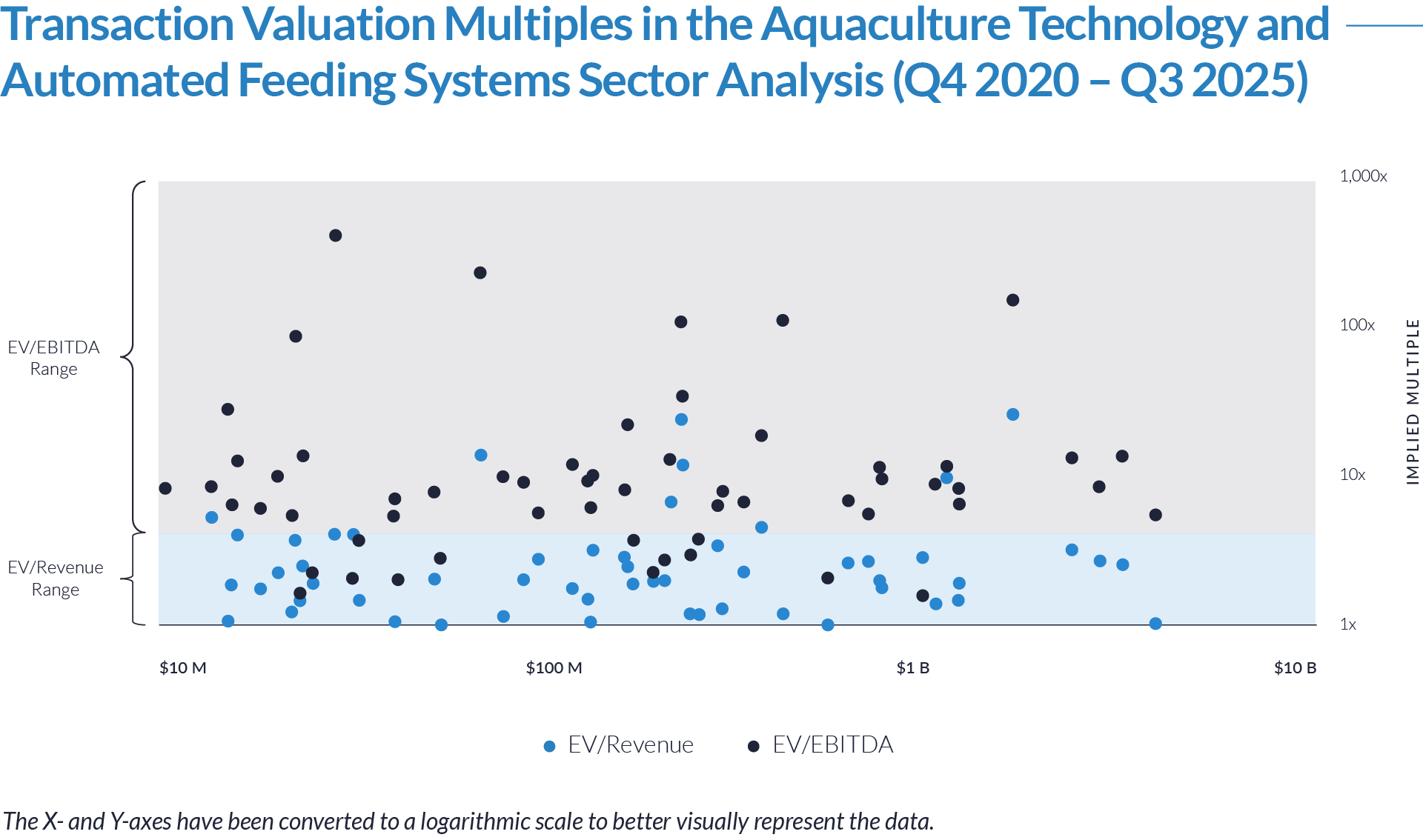
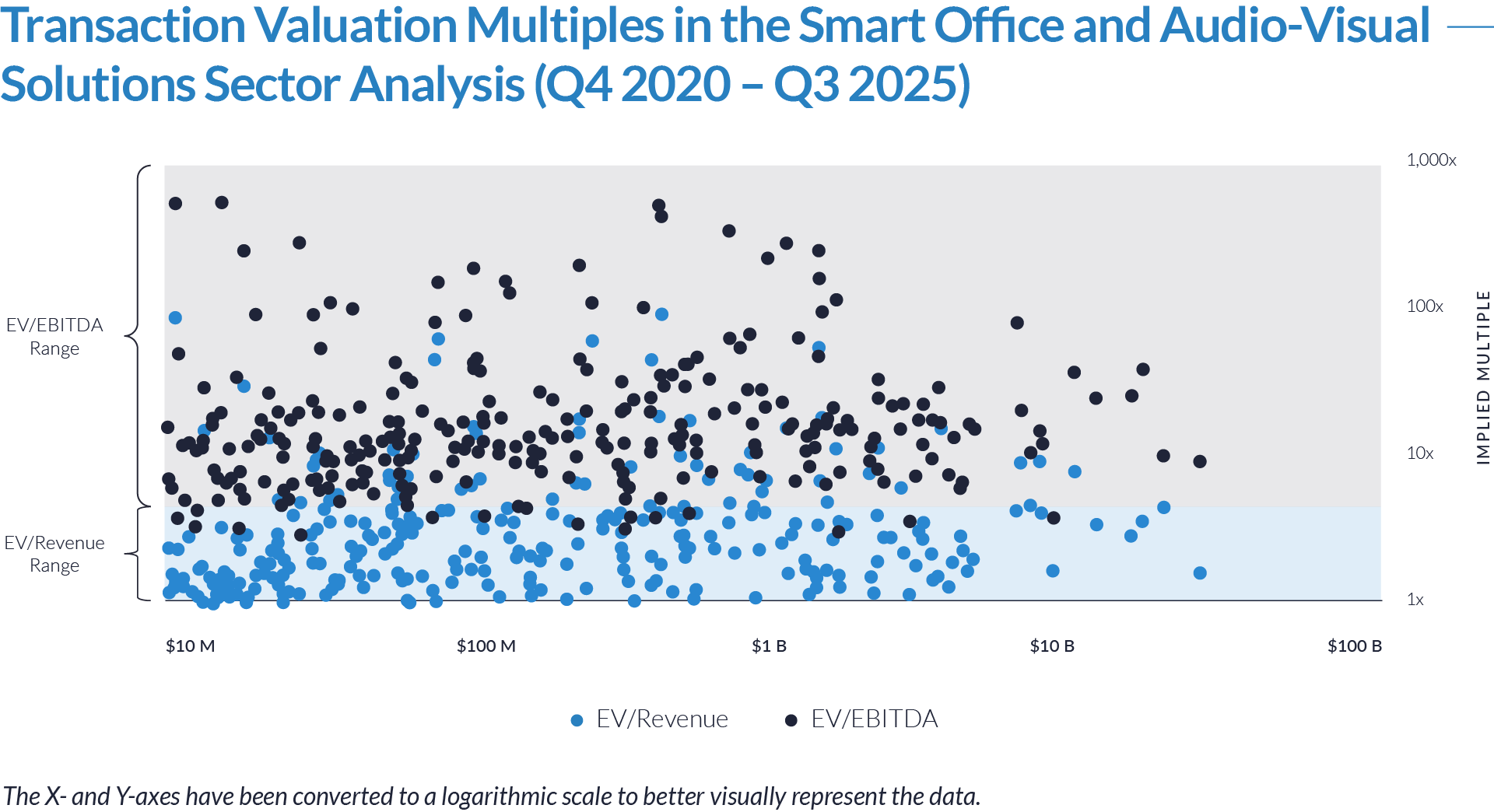
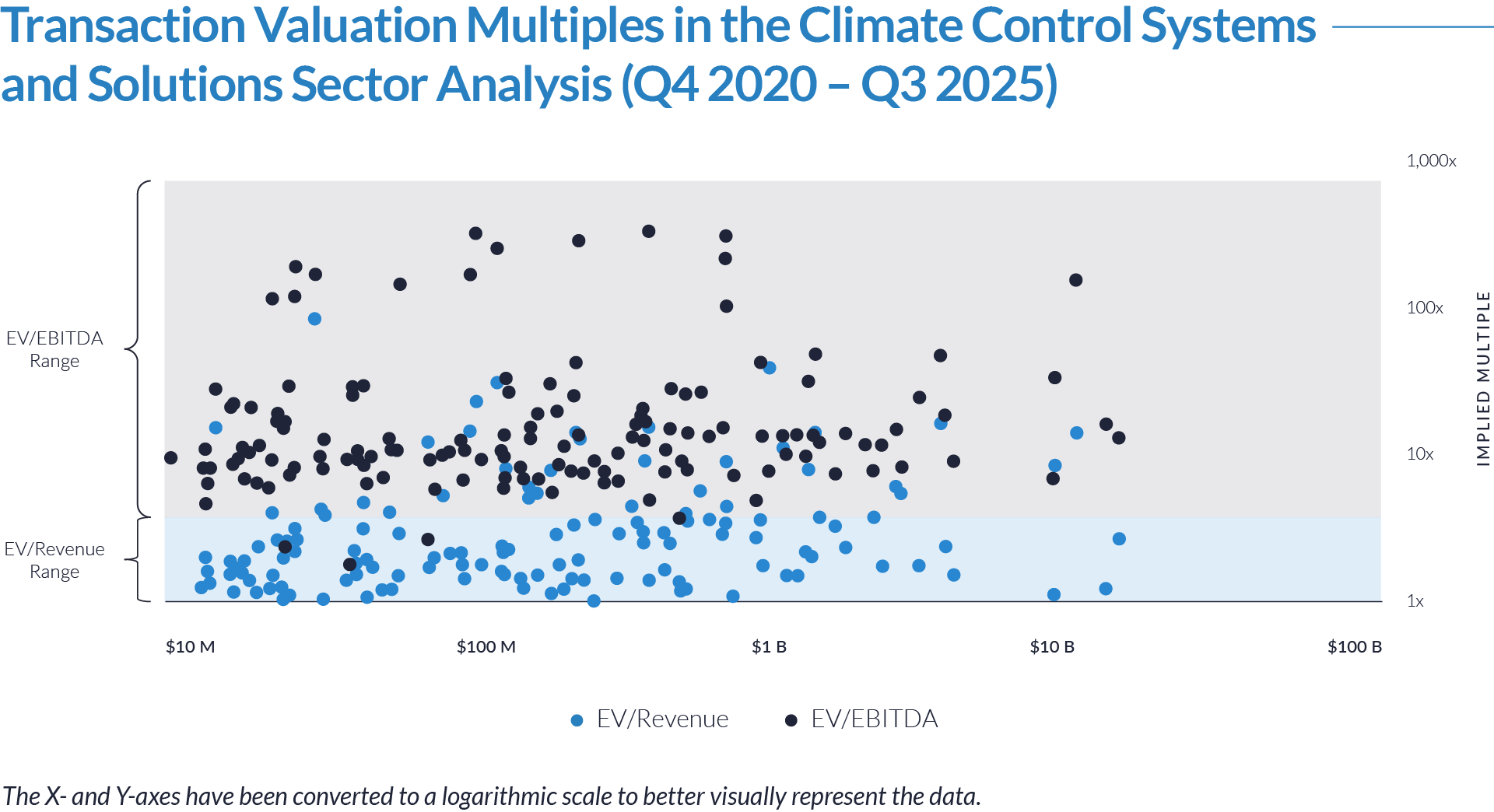
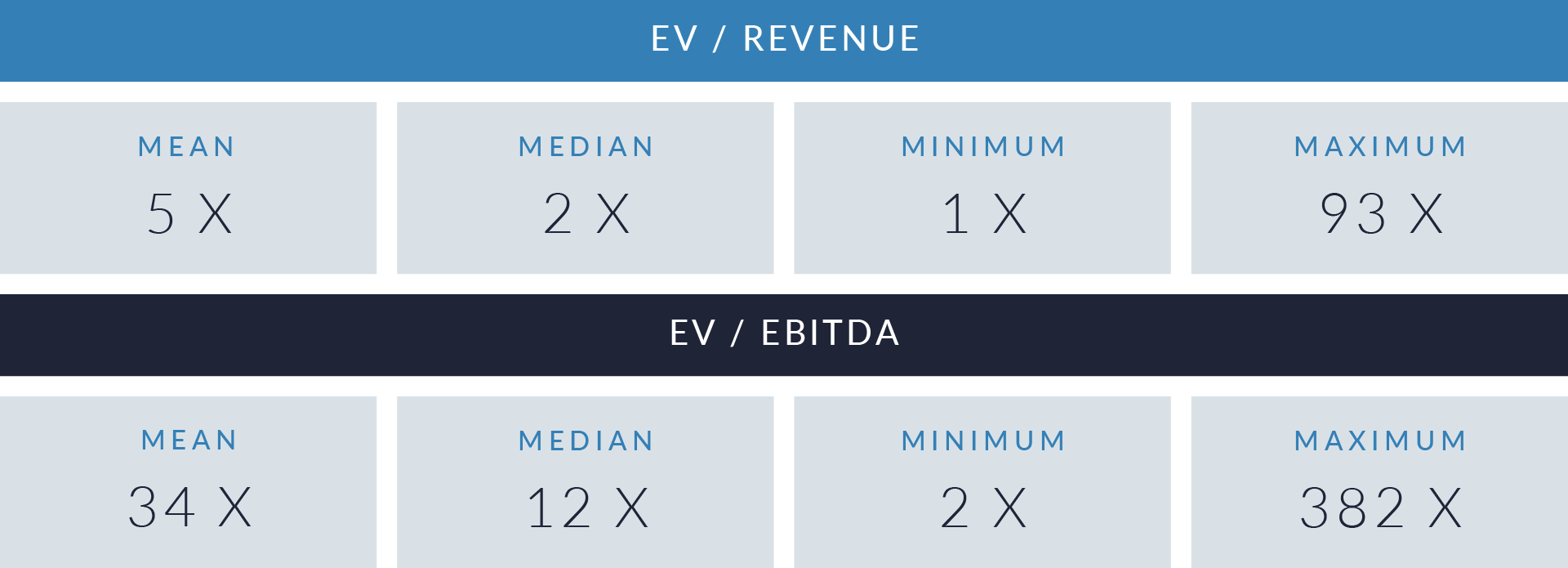
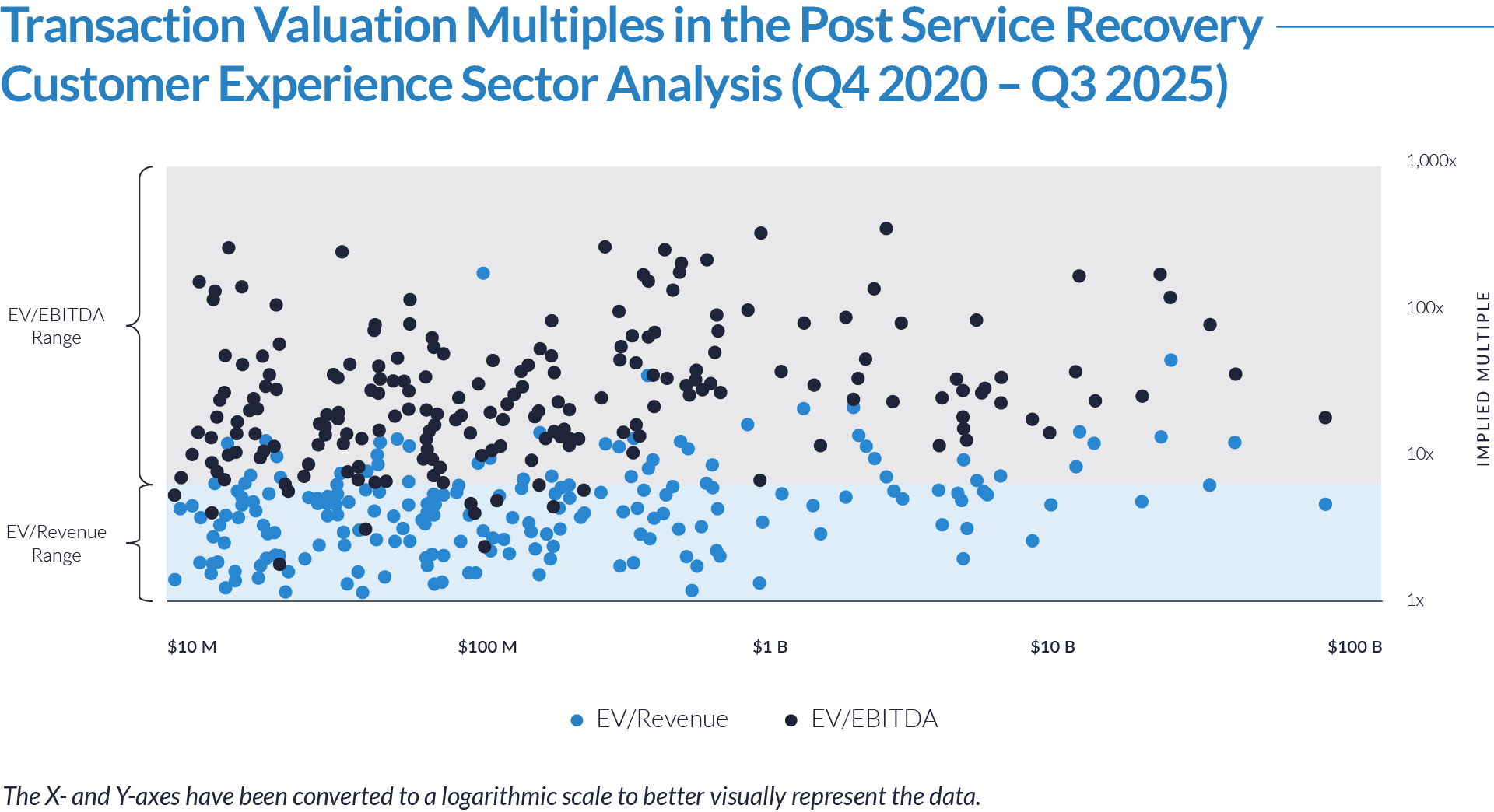
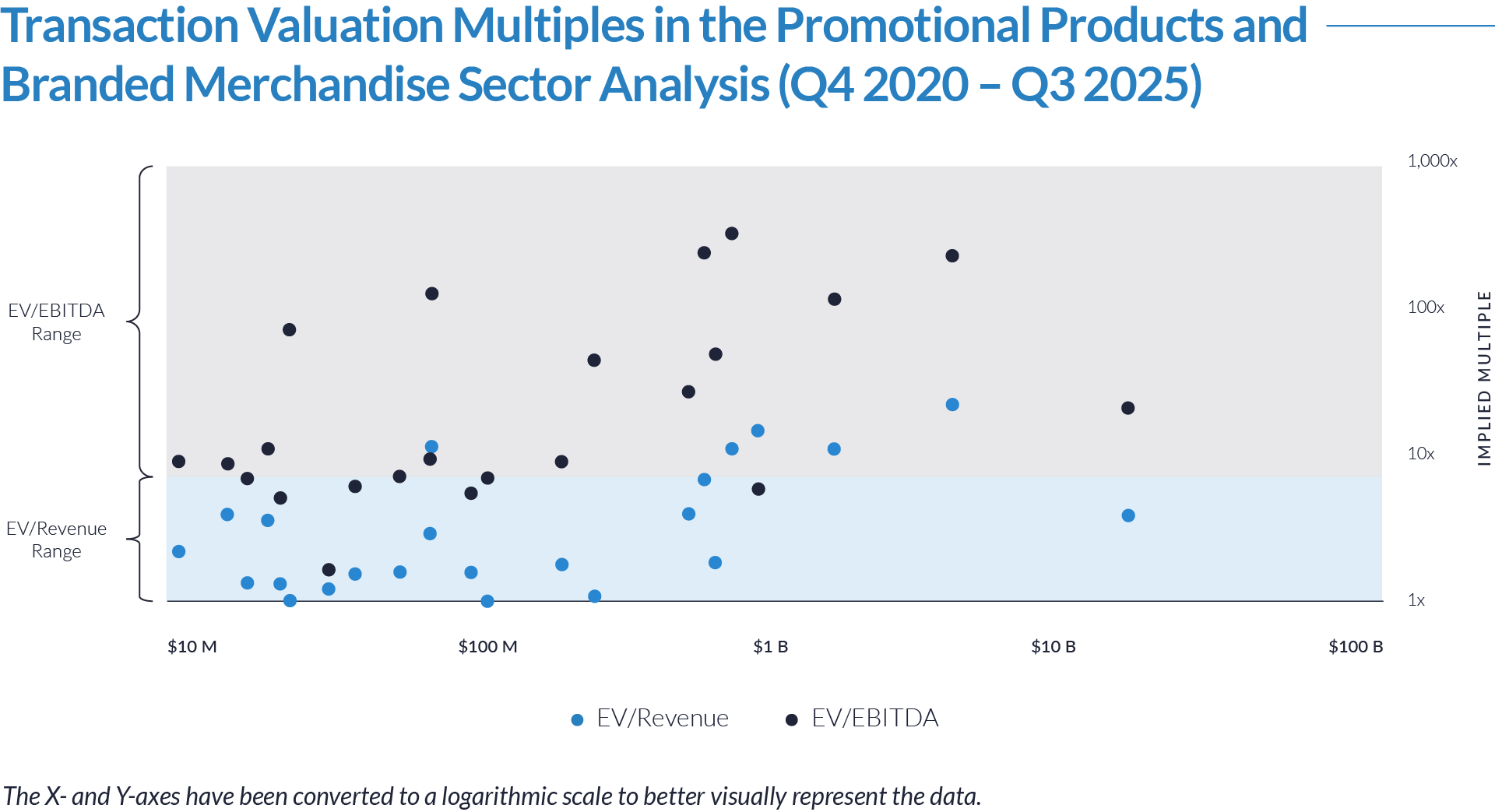
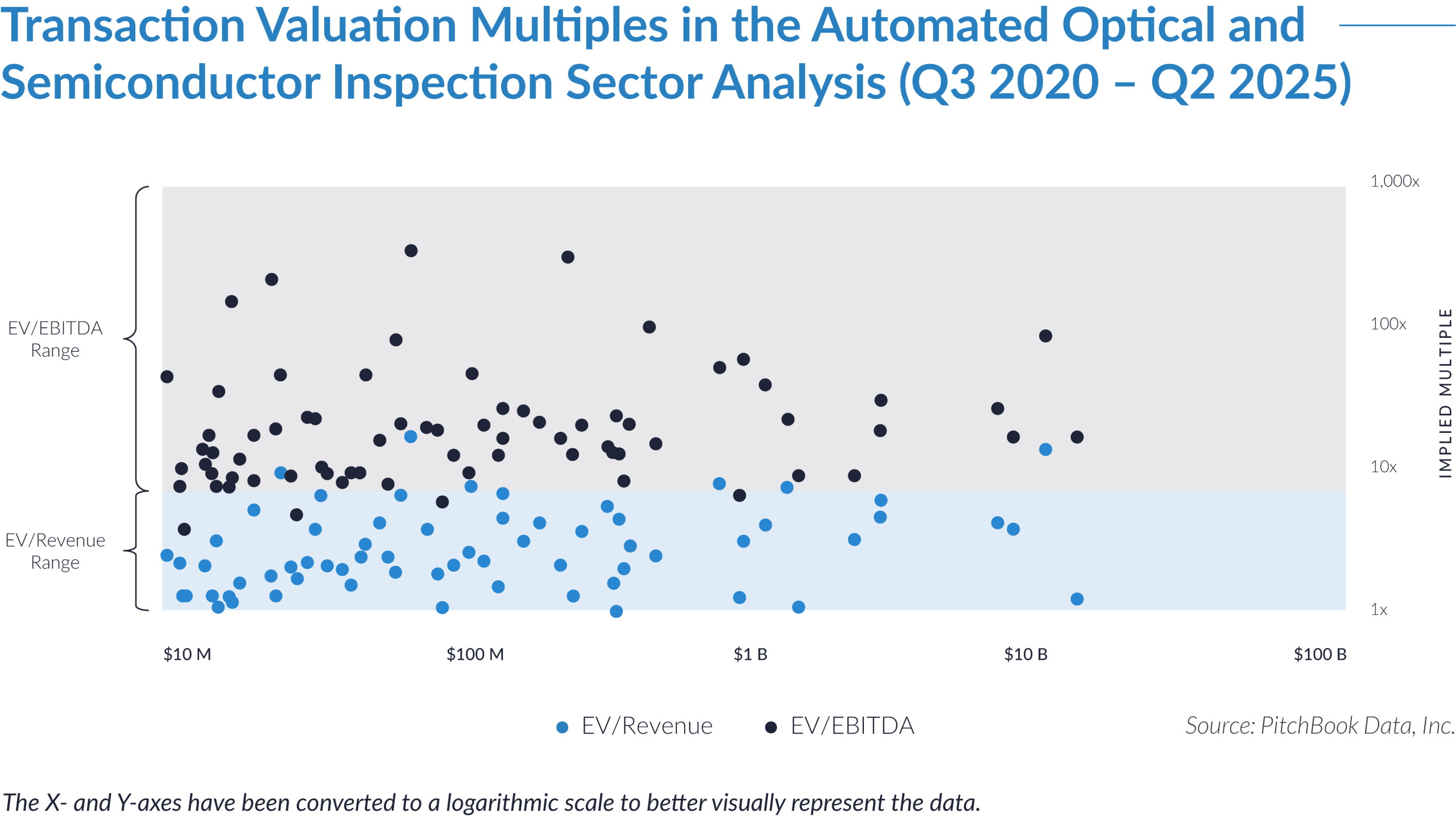
- Valuation multiples are based on a sample set of M&A transactions in the digital patient intake and clinical workflow software sector using data collected as of January 29, 2026.
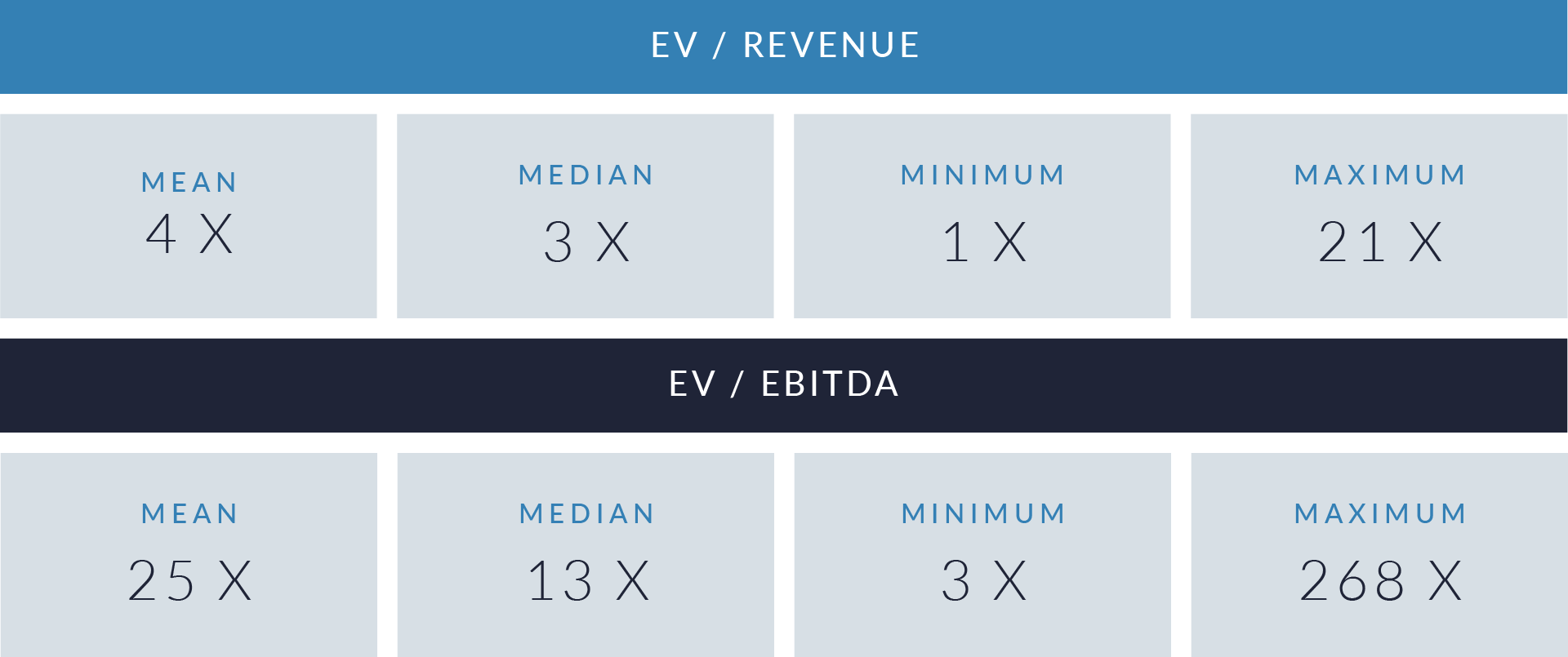
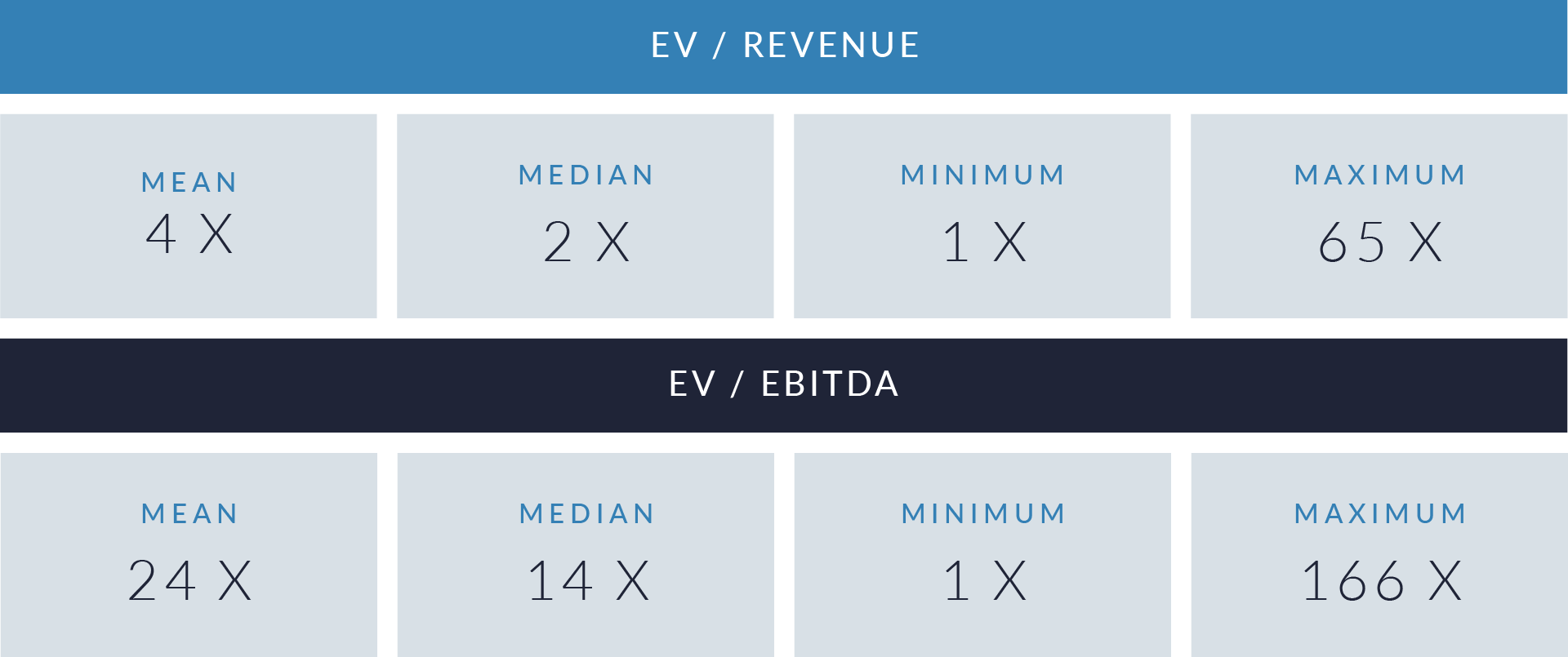
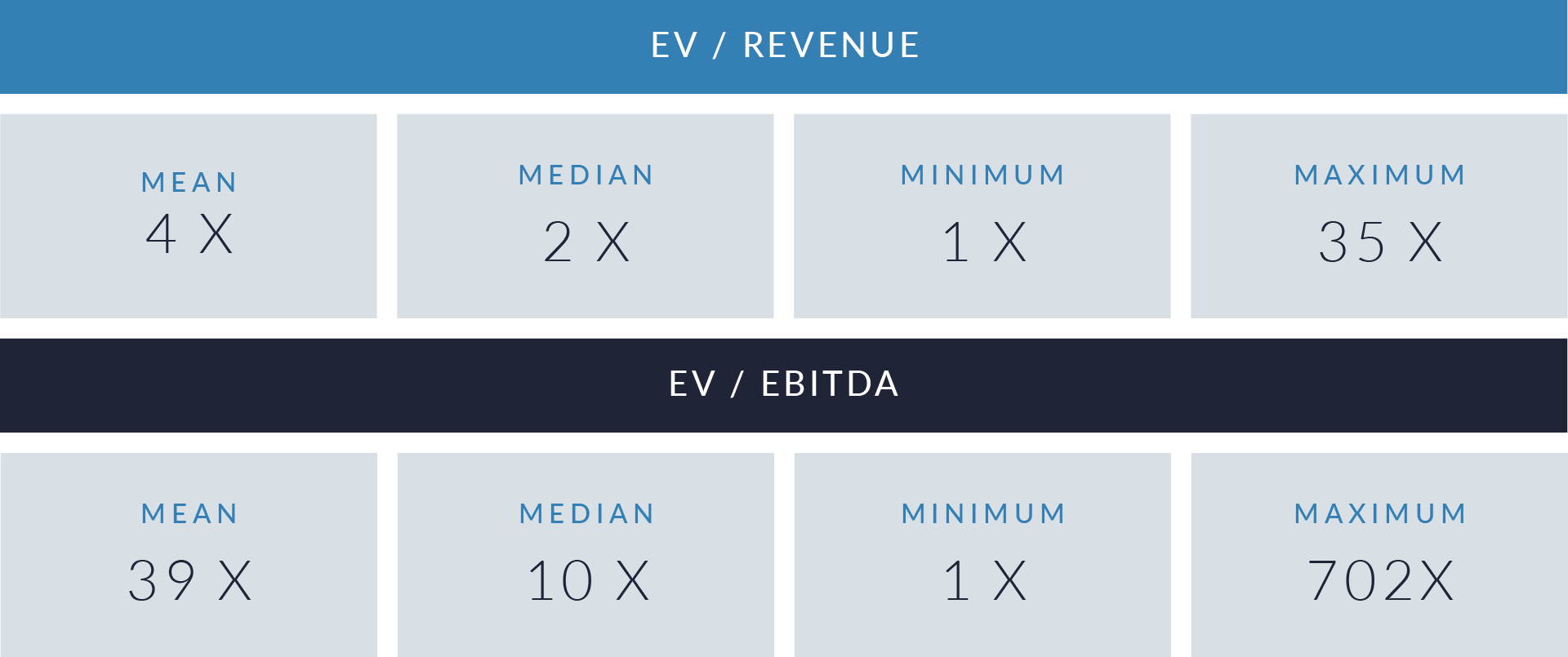
- Wide valuation dispersion reflects platform criticality and growth differentiation. Enterprise values range from sub-$1 billion transactions to mega-cap buyouts exceeding $15 billion, with EV/revenue multiples spanning approximately 1x to >25x and EV/EBITDA multiples exceeding 150x at the high end, often reflecting reinvestment-heavy or near-breakeven operating profiles rather than mature profitability. Premium multiples concentrate among high-growth, workflow-critical platforms.
- Companies trading at double-digit EV/revenue multiples (10x–25x) and elevated EV/EBITDA multiples (30x–100x+) are typically characterized by recurring SaaS revenue, deep integration into patient intake and clinical workflows, and system-of-record or front-door positioning, reinforcing investor willingness to underwrite long-term value creation over near-term profitability.
- Lower-multiple cohort highlights consolidation opportunity within the sector. A meaningful portion of the dataset trades at 1x–4x EV/revenue and <15x EV/EBITDA, reflecting smaller scale, limited product breadth, or lower growth profiles. This valuation gap underscores continued M&A and roll-up potential, as financial sponsors and strategic acquirers seek to acquire under-scaled platforms and drive value through expanded functionality, broader customer reach, and enhanced monetization through integration.

Capital Markets Activities
The data highlights transaction activity, capital deployment, and geographic concentration trends within the digital patient intake and clinical workflow software sector. Ongoing healthcare digitization, rising administrative complexity, and pressure to improve operational efficiency continue to drive M&A across patient access, intake, and workflow software providers. Acquirers increasingly target scaled, workflow-critical platforms embedded at the front end of care delivery, prioritizing businesses with deep electronic health record integration, recurring software revenue, and broad functionality across intake, engagement, and clinical operations.
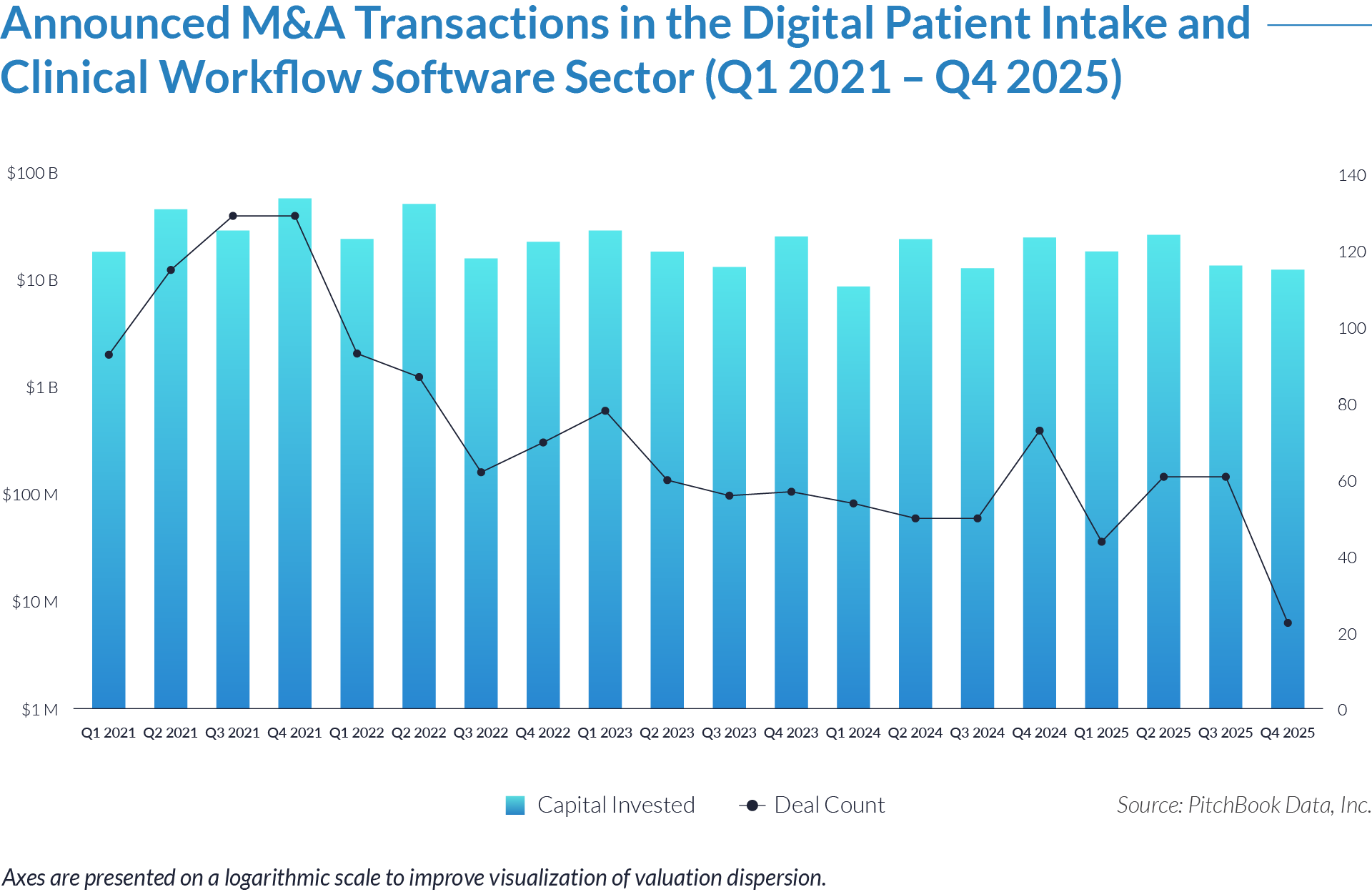
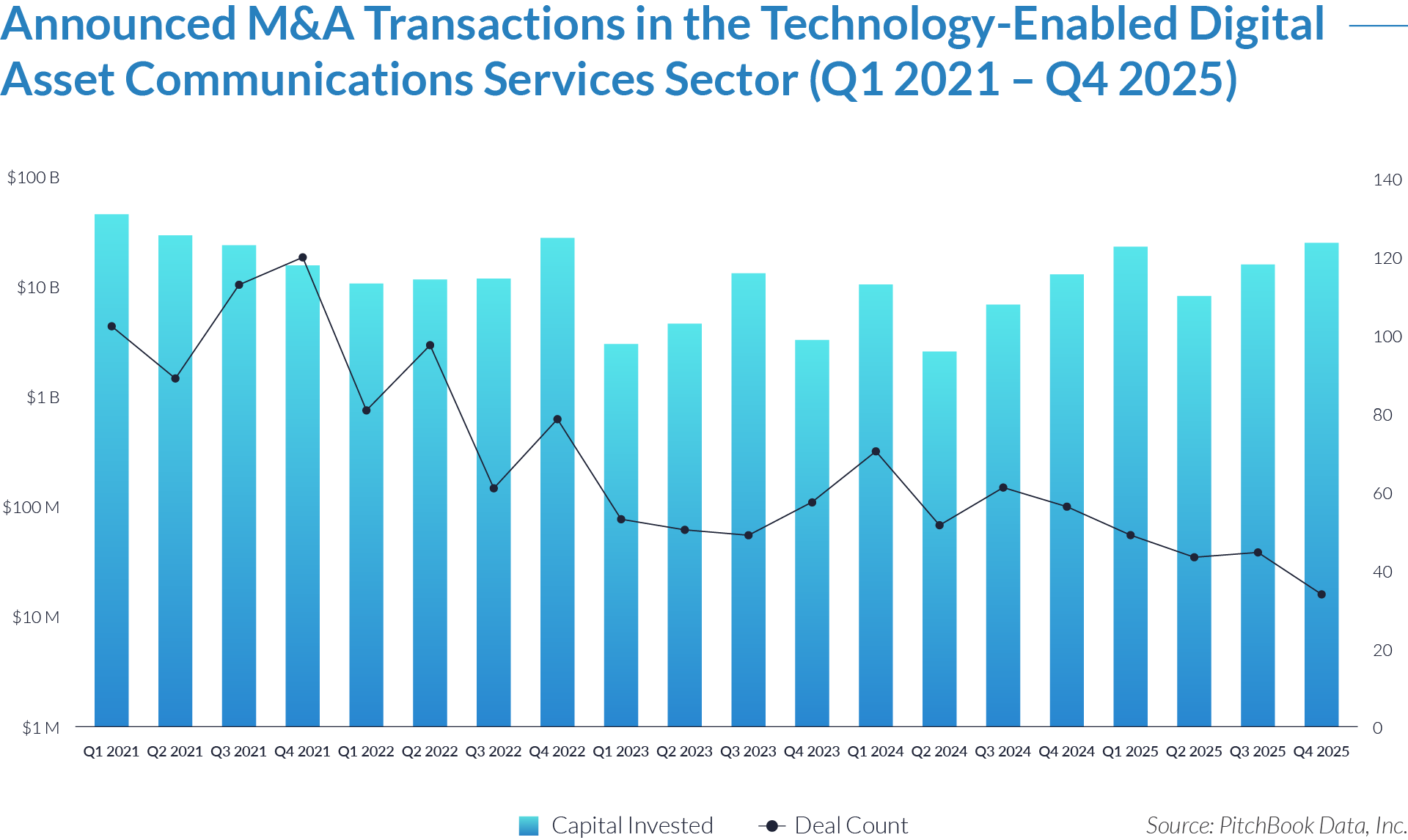
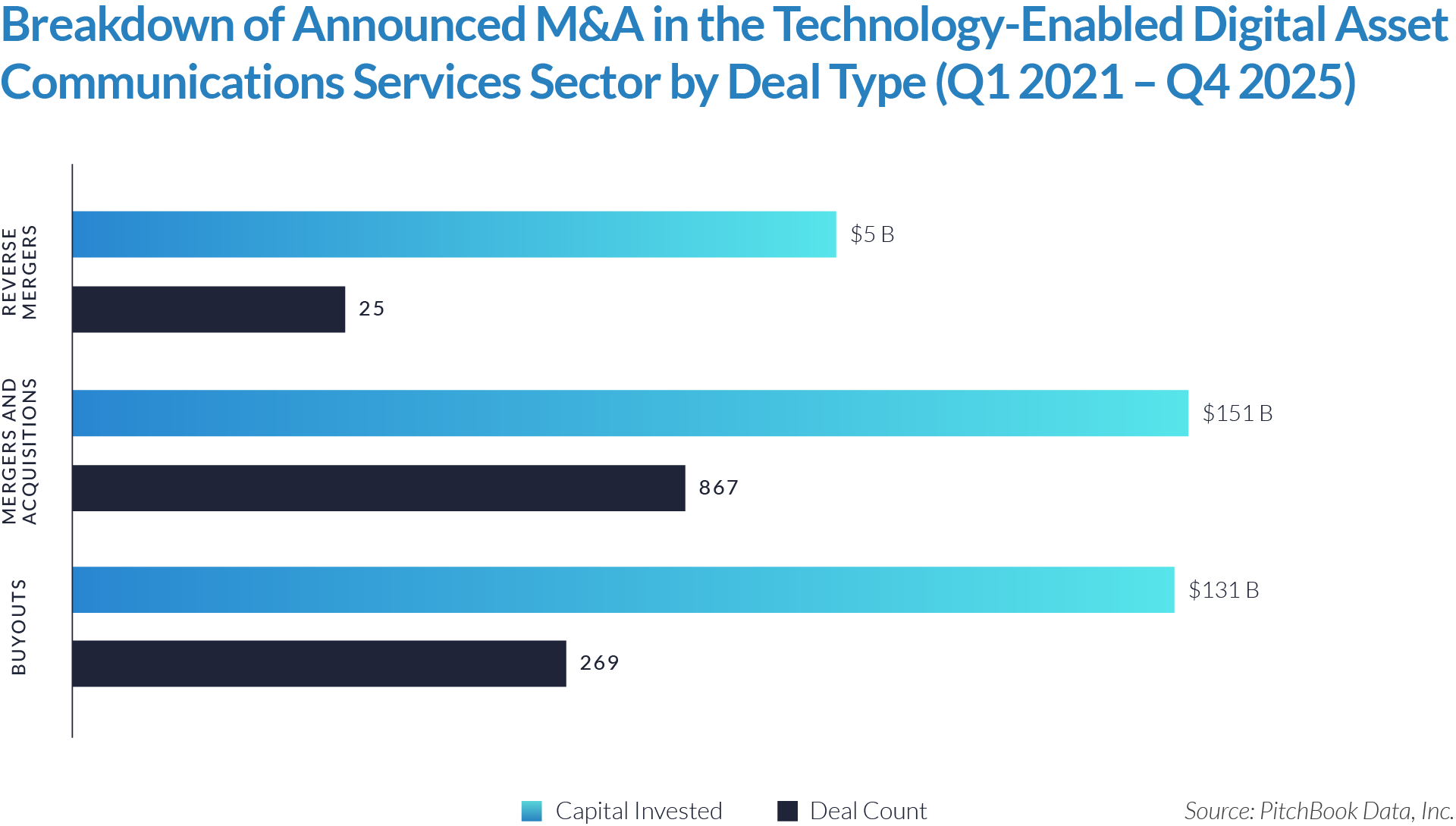
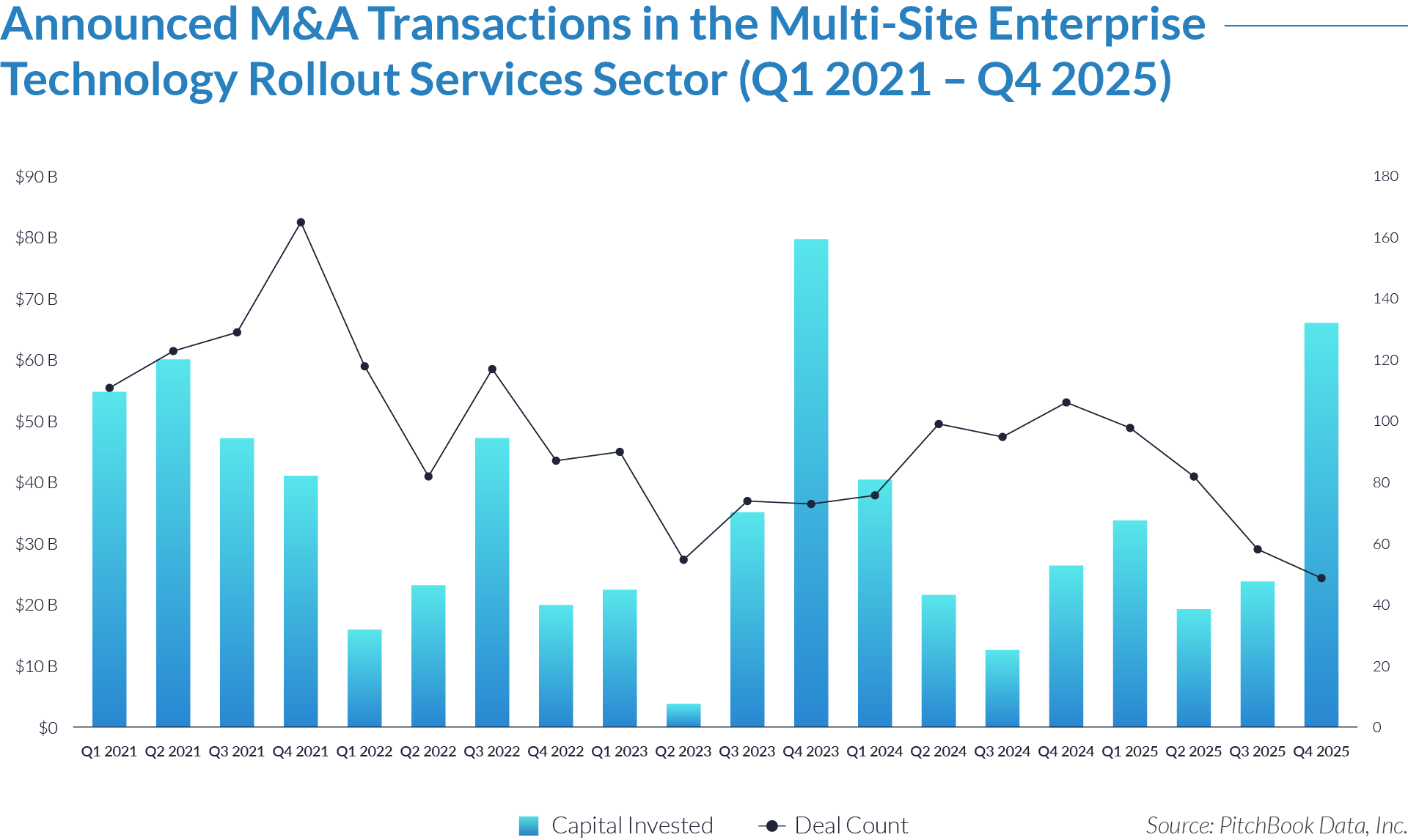
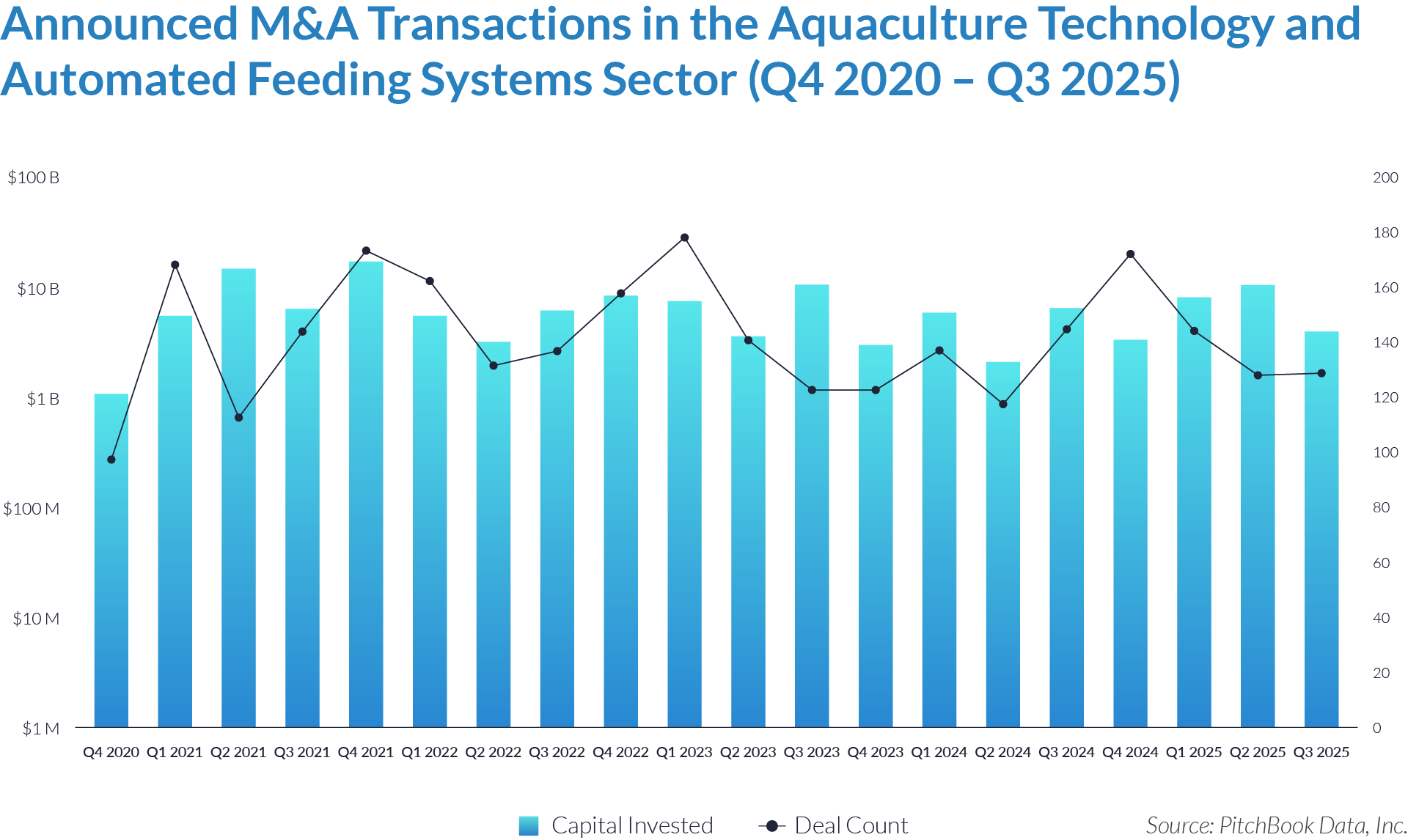
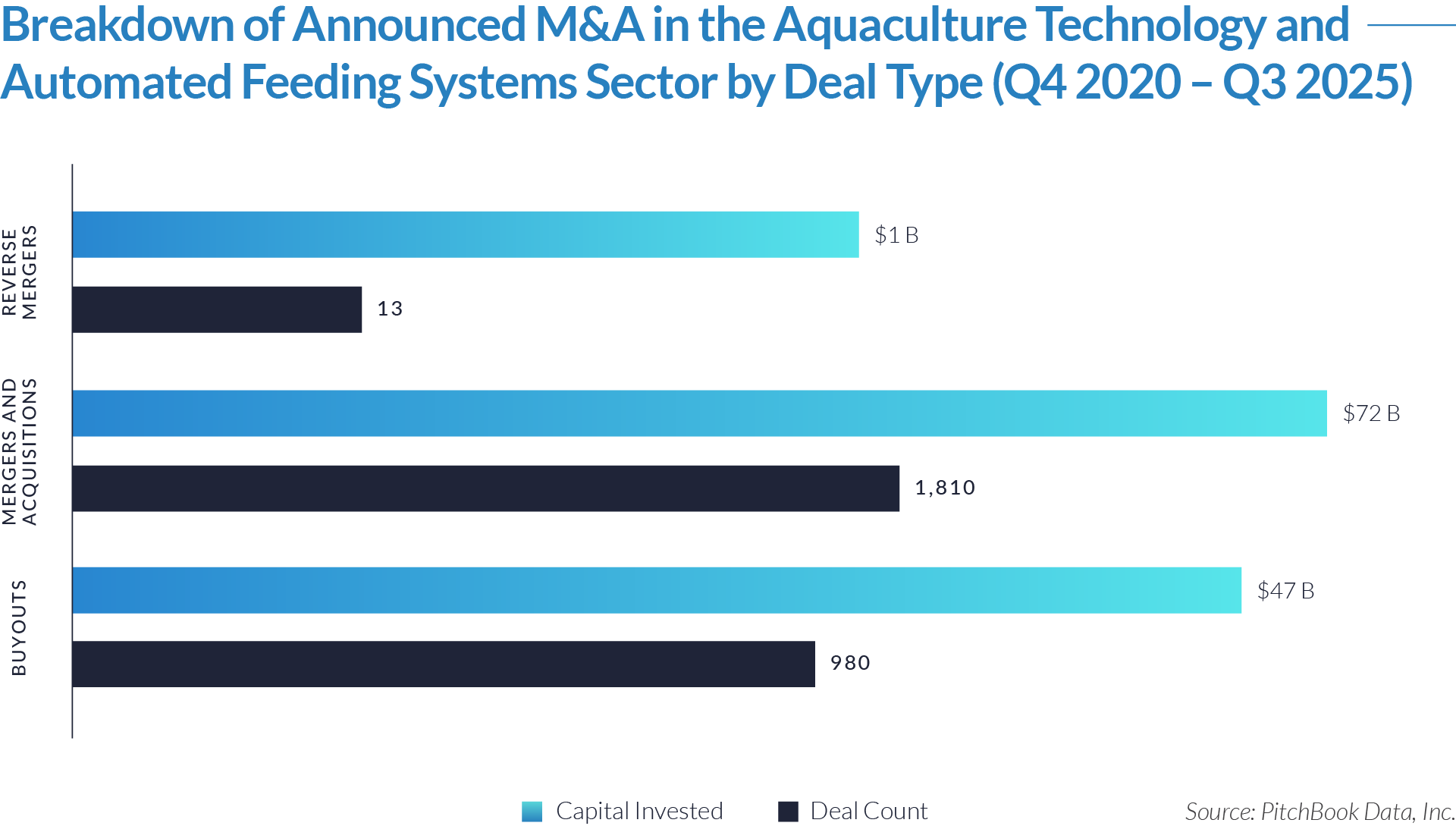
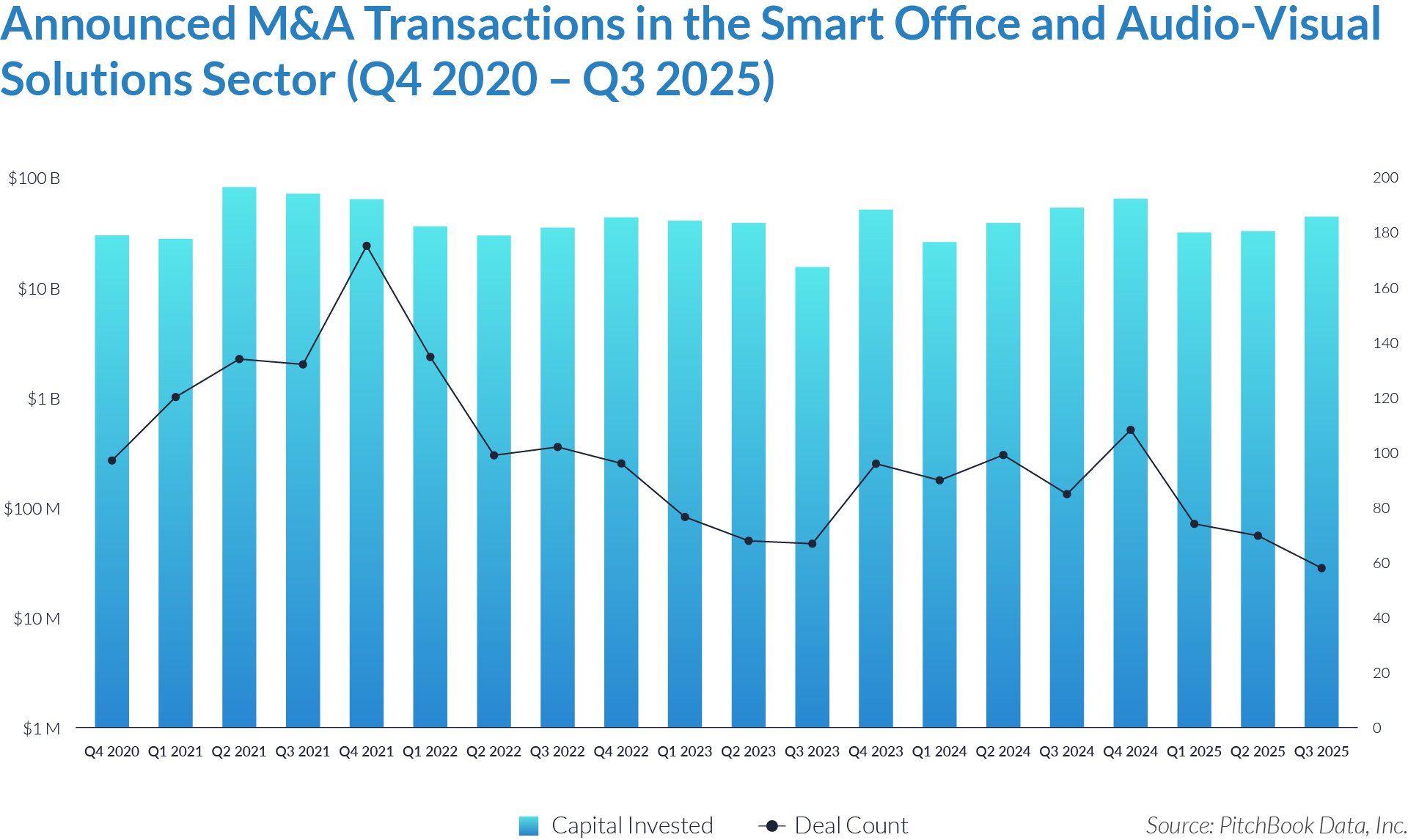
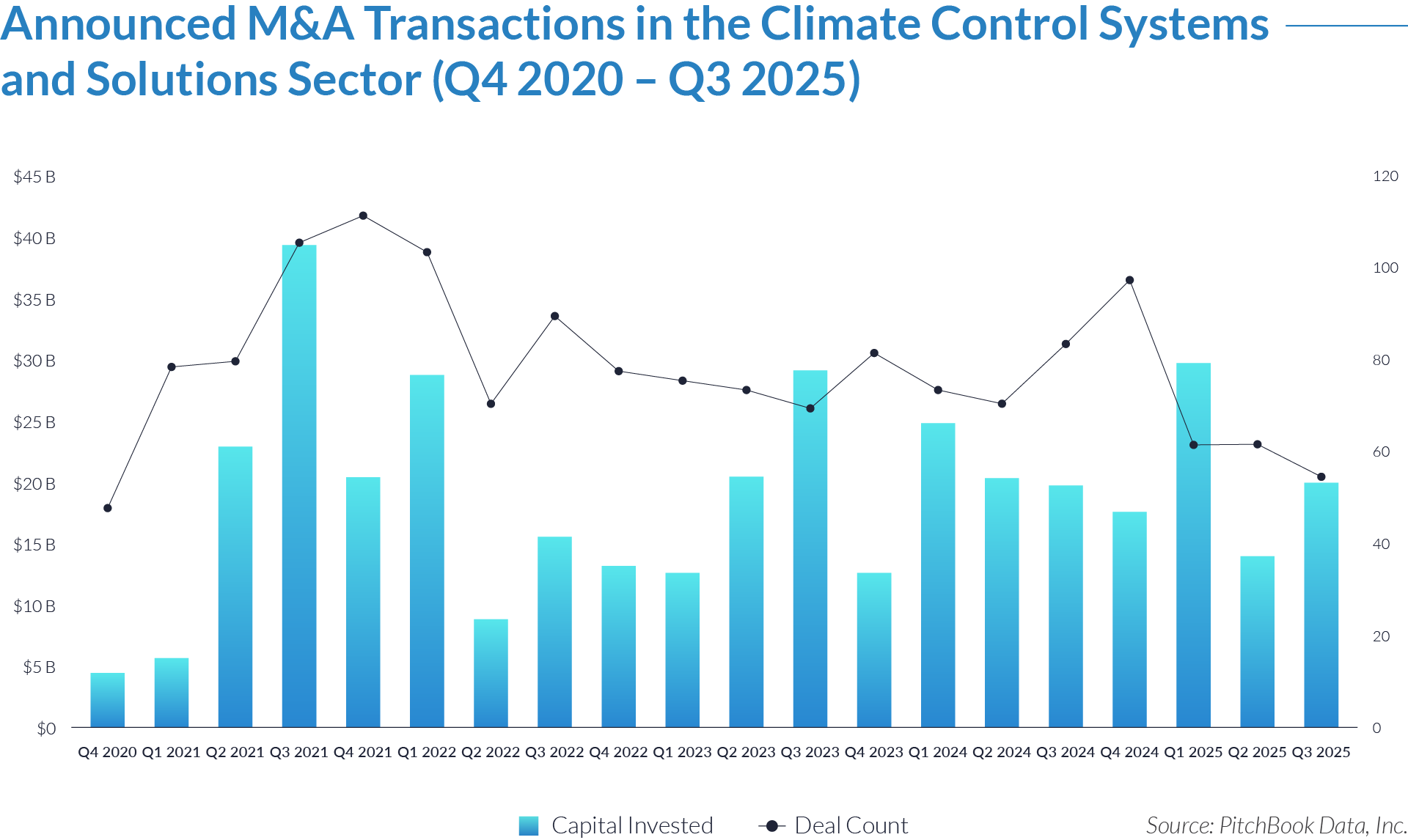
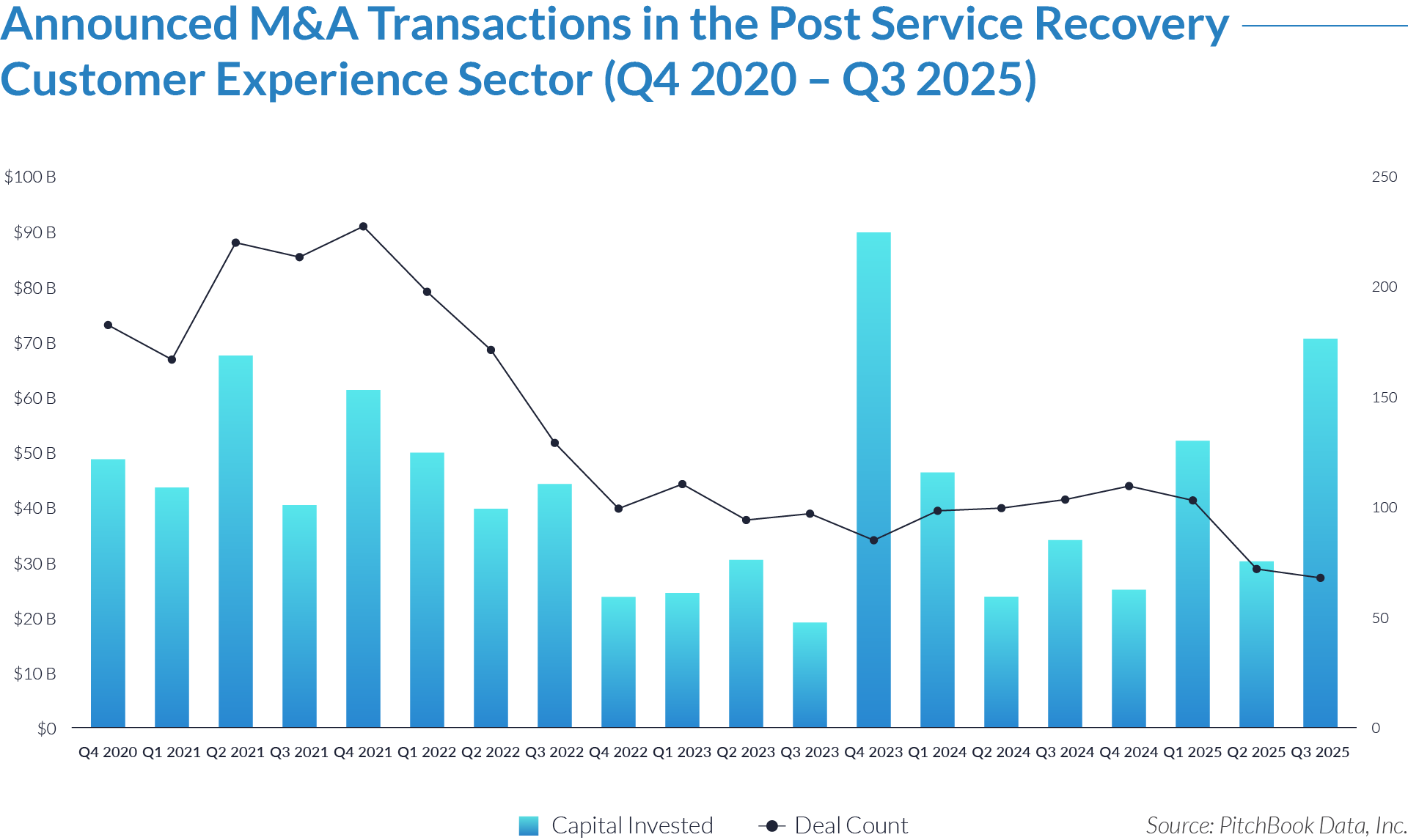
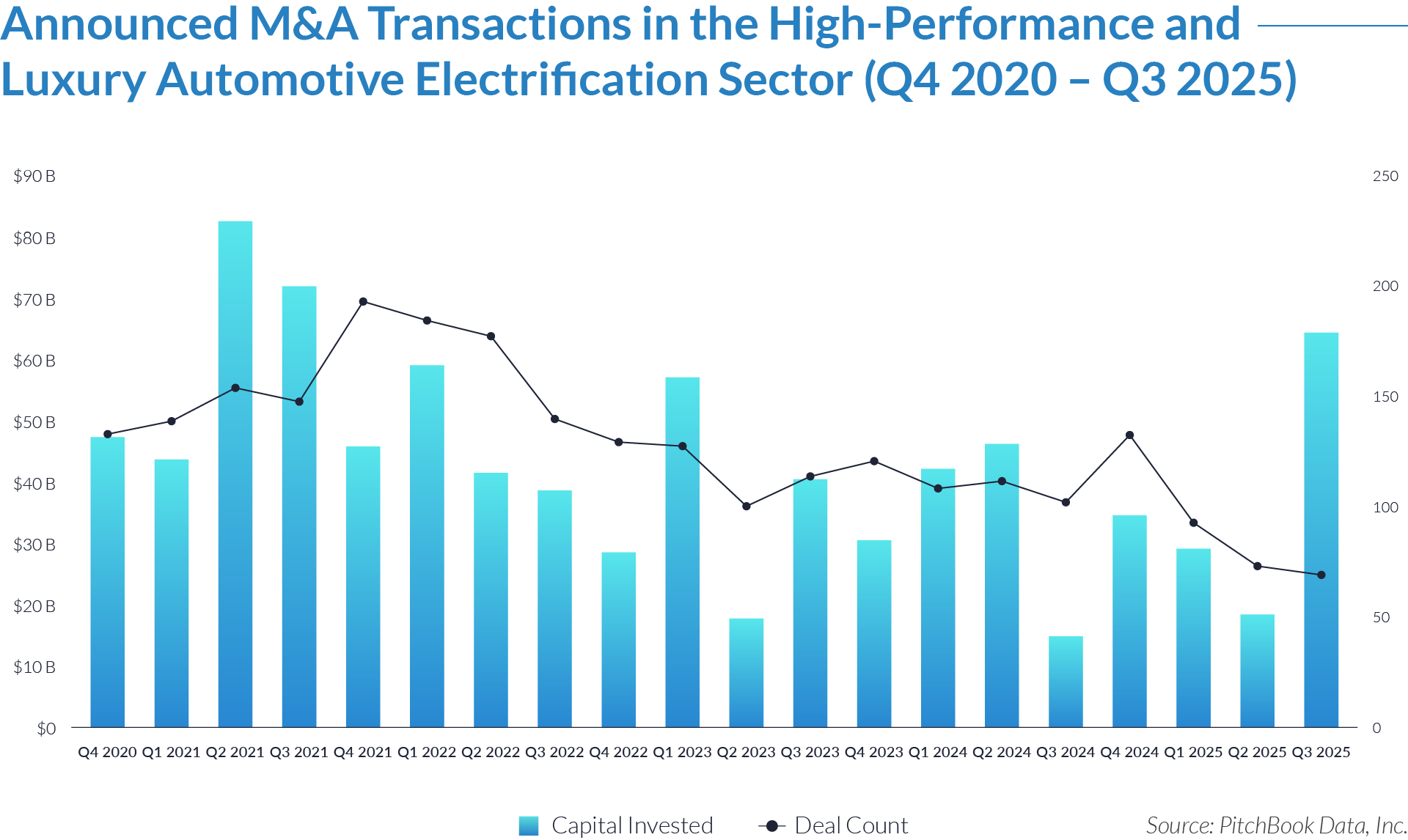
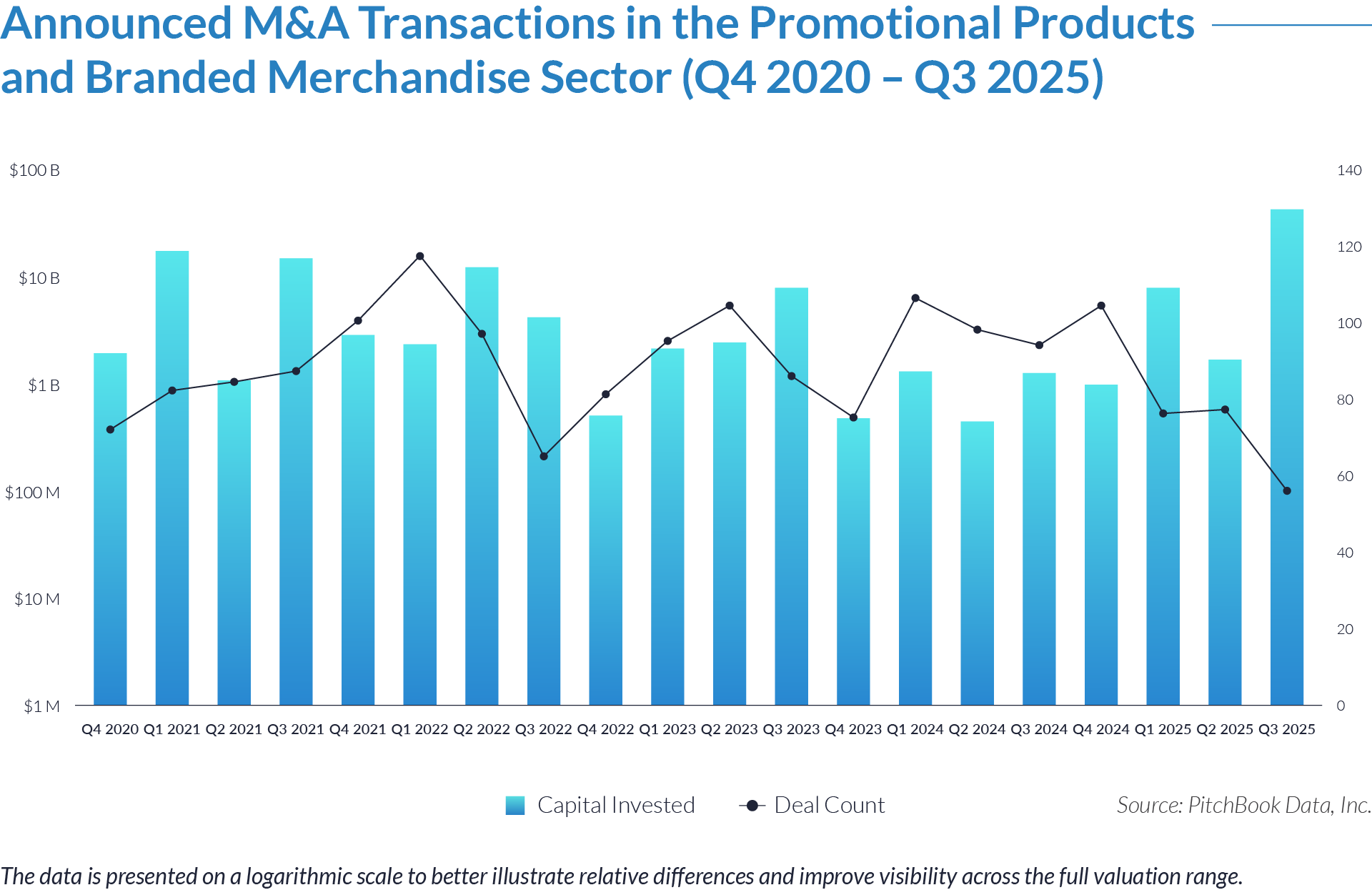
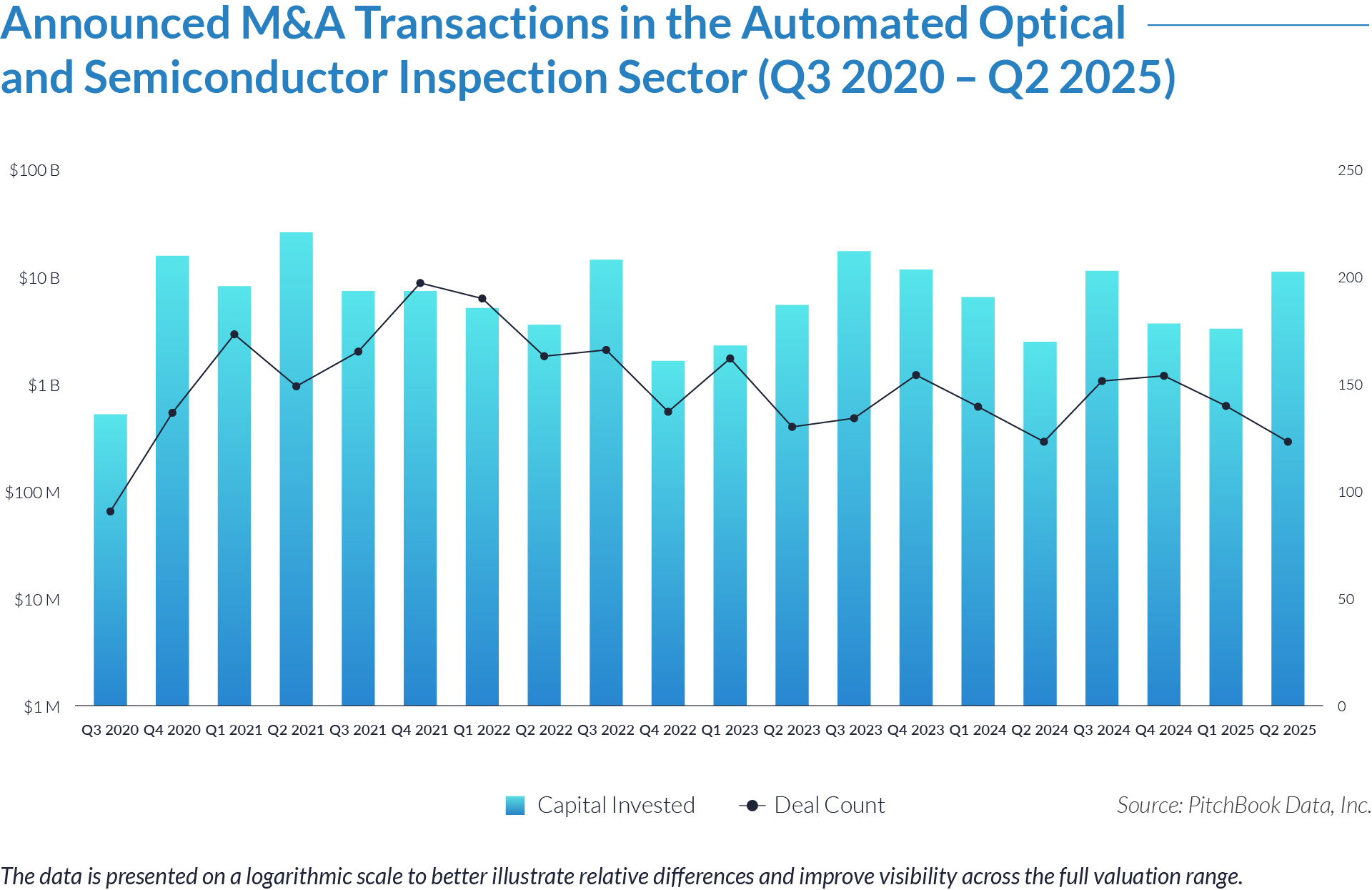
- Sustained transaction volume signals a structural shift toward software-defined front-office healthcare. The deployment of $484 billion across 1,445 transactions over 20 quarters demonstrates that capital is reallocating structurally toward workflow software that controls patient access, data capture, and operational efficiency, rather than reflecting a cyclical investment theme. Investors increasingly position intake platforms as long-term healthcare infrastructure rather than discretionary IT spend.
- High deal frequency relative to aggregate value highlights scarcity of scaled platforms. While deal volume remains elevated, a limited number of large transactions account for a disproportionate share of total value, indicating that scaled, workflow-critical platforms remain scarce and command outsized premiums. Meanwhile, a long tail of smaller assets continues to transact at lower multiples, reinforcing a two-tier market dynamic.
- Extreme multiple dispersion reflects acquirer underwriting of future control rather than current profitability. The widespread between low singledigit and greater than 25x EV/revenue multiples indicates that acquirers price assets based on future control of patient flow and clinical data rather than near-term EBITDA, particularly for platforms embedded at the digital front door of care delivery. This dynamic indicates that acquirers increasingly price assets based on strategic control points within care delivery rather than near-term financial performance.
- Persistent consolidation reflects the strategic imperative to assemble end-to-end workflow ownership. The volume and consistency of transactions show that acquirers actively pursue integrated intake to clinical workflow platforms rather than isolated point solutions, seeking to increase switching costs, expand monetization points, and secure long-term customer dependency.
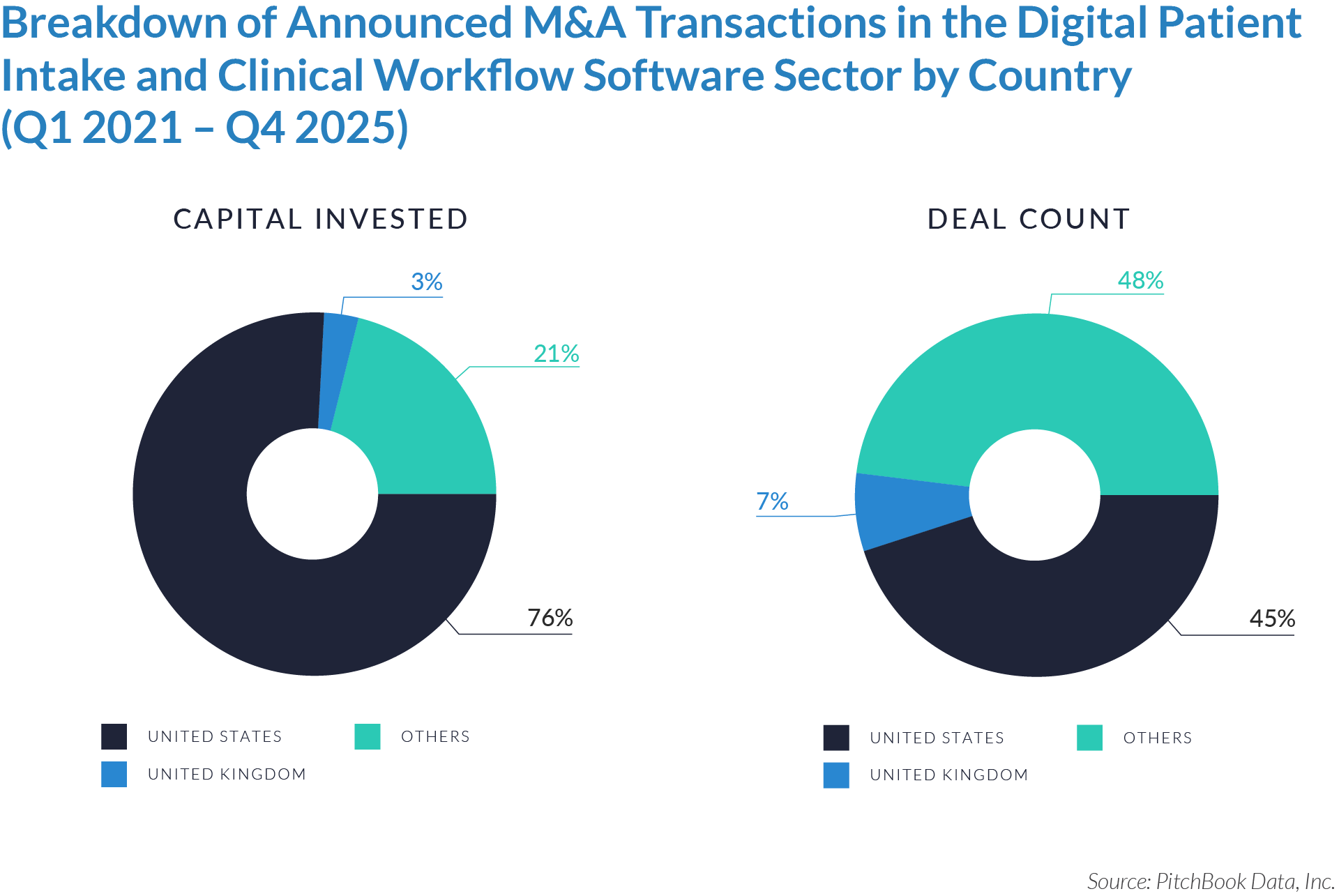
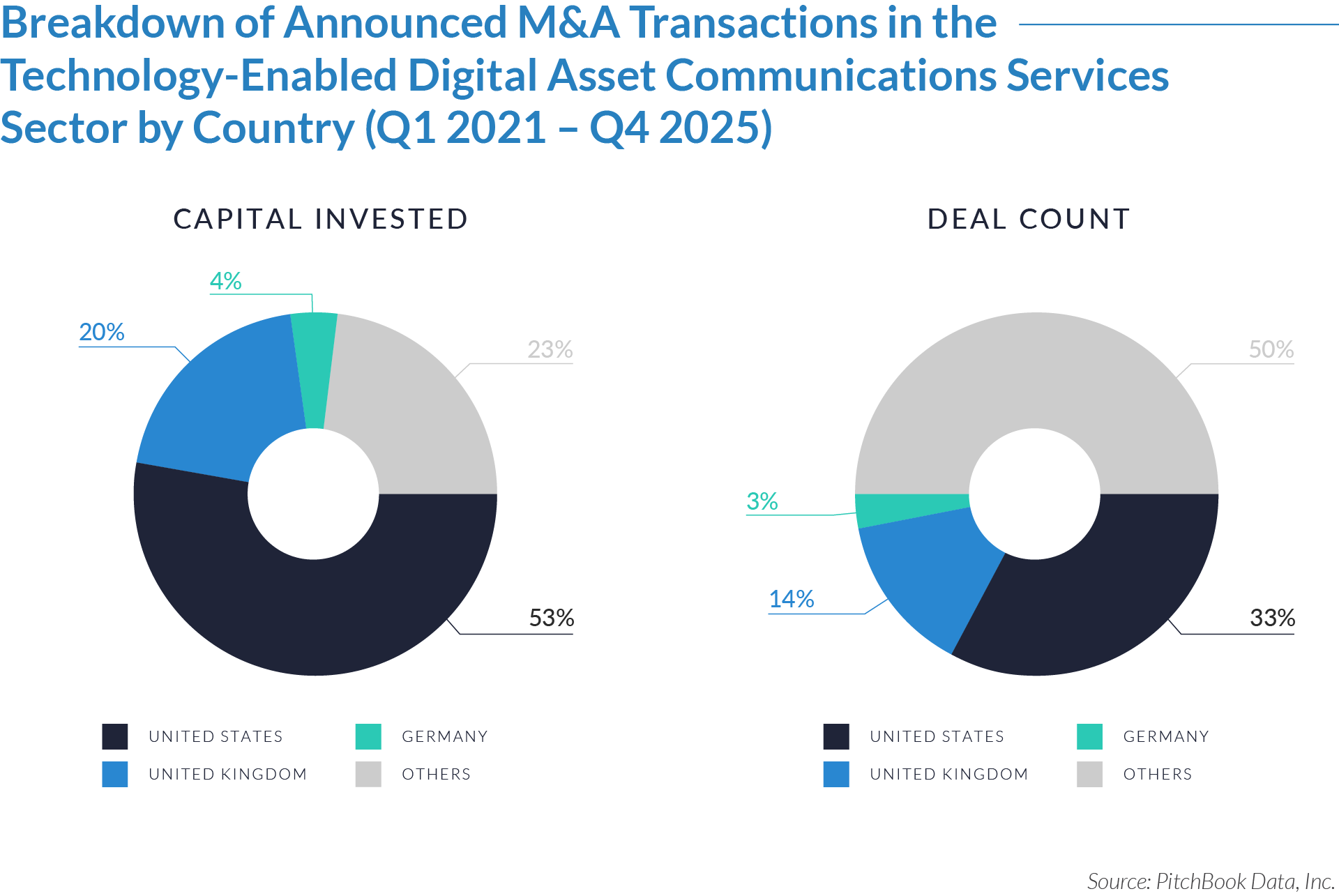
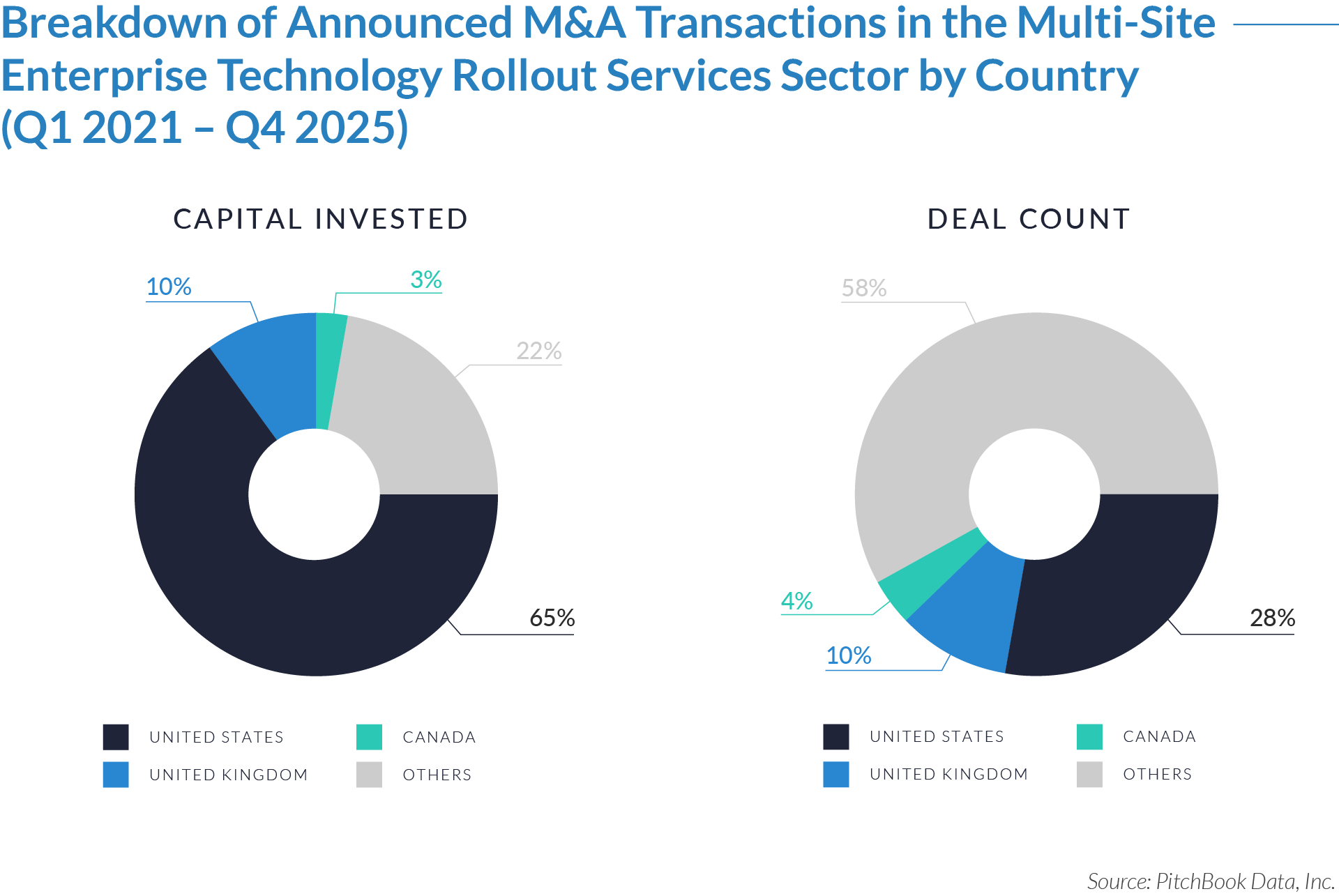
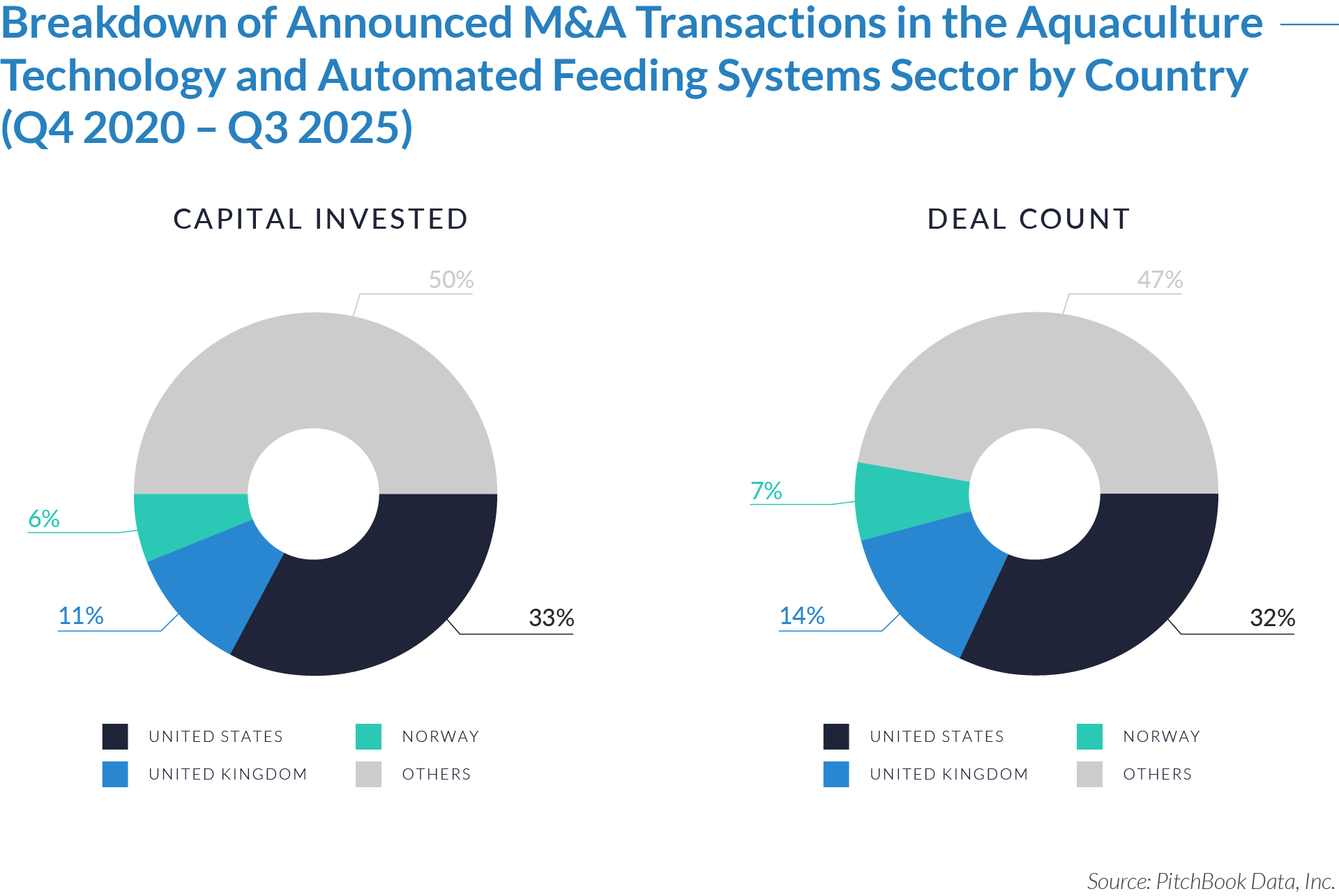
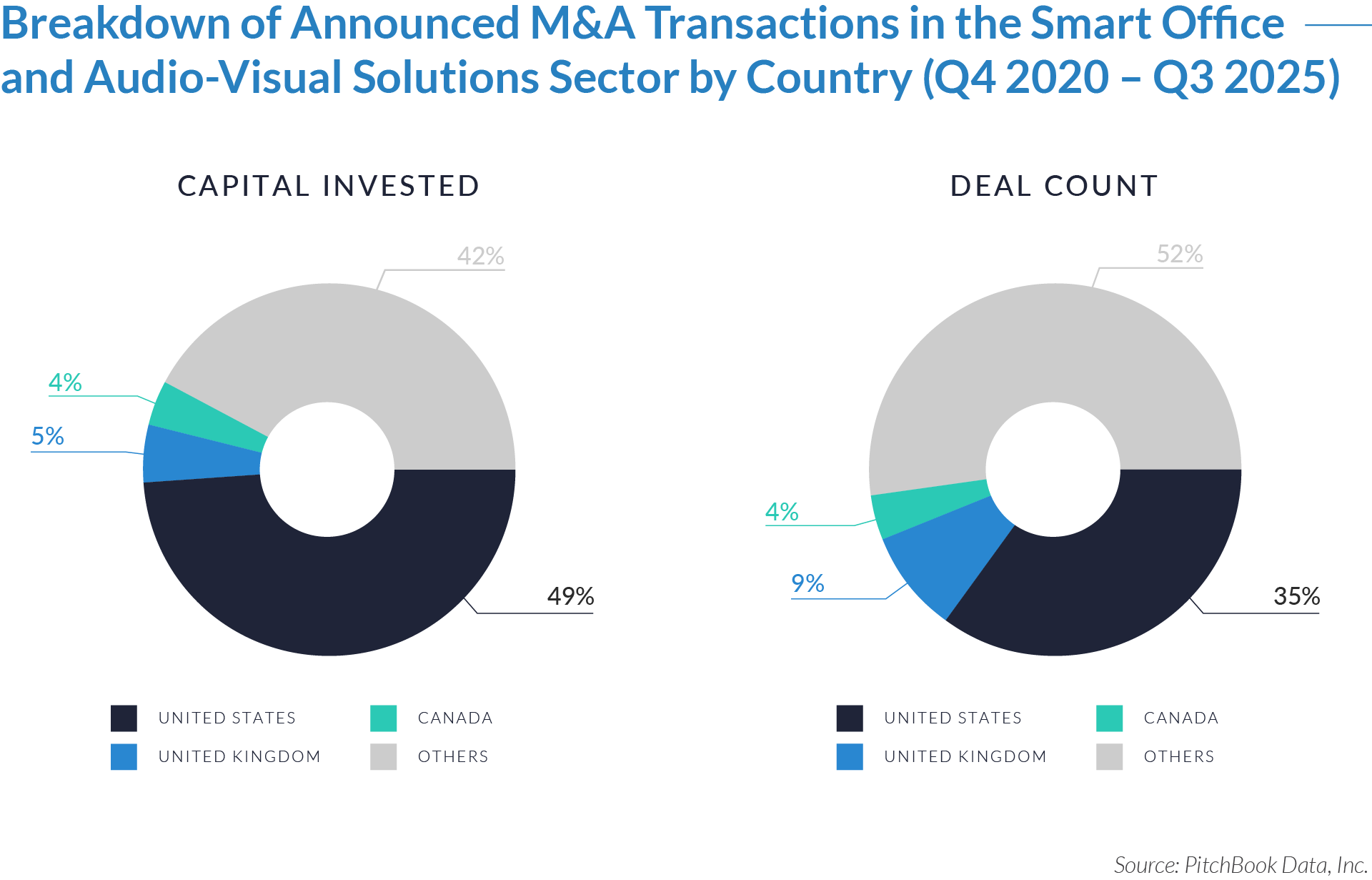
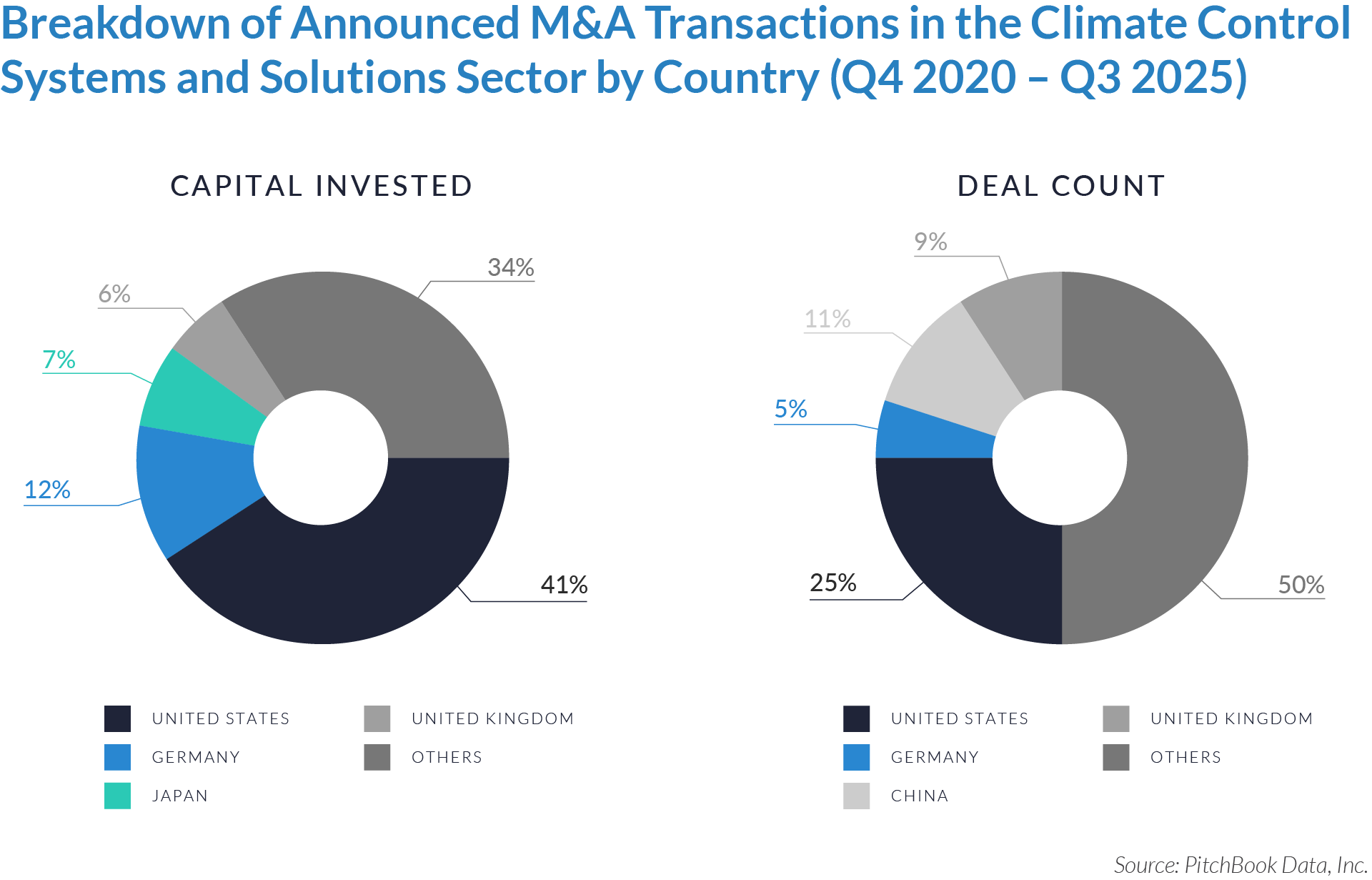
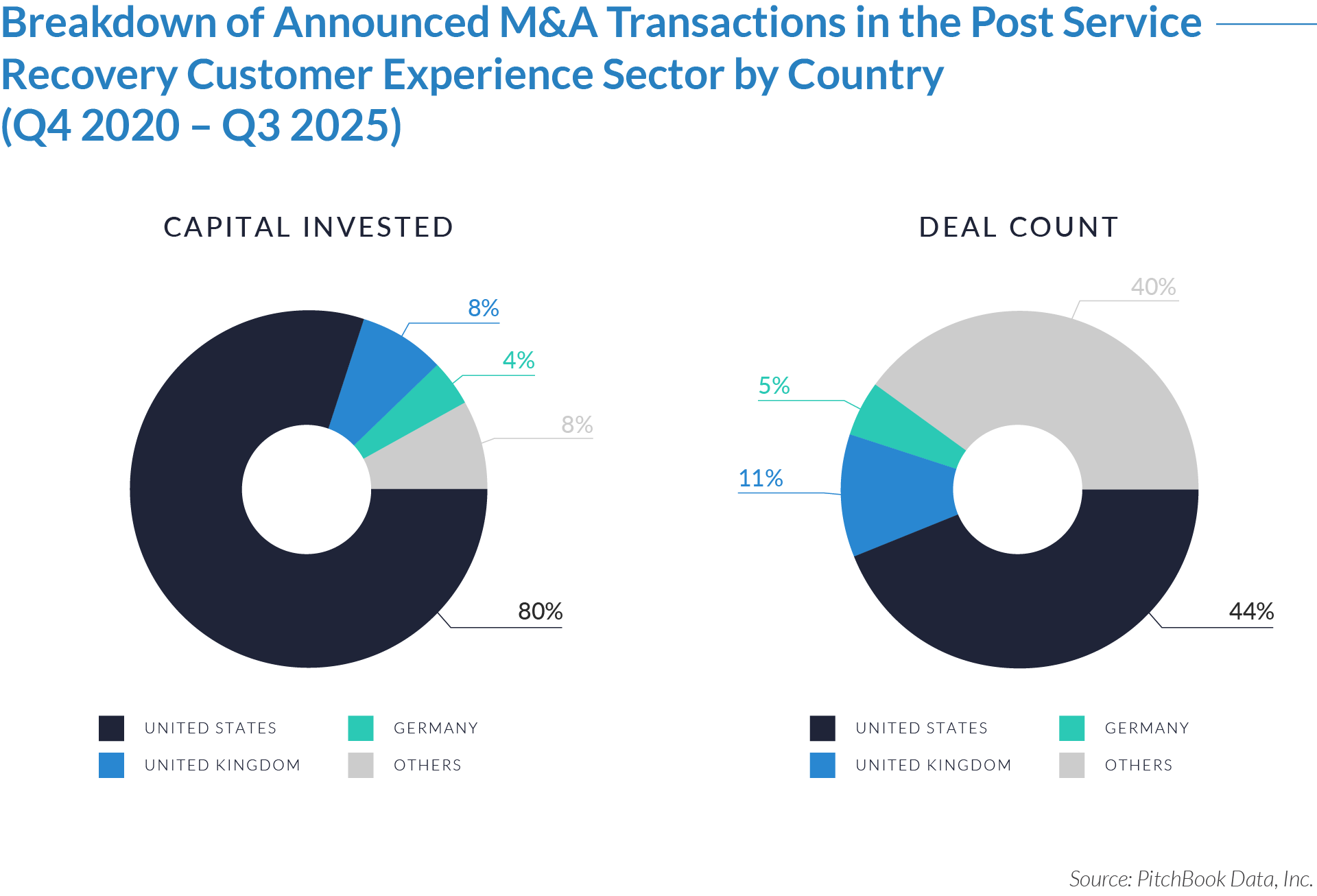
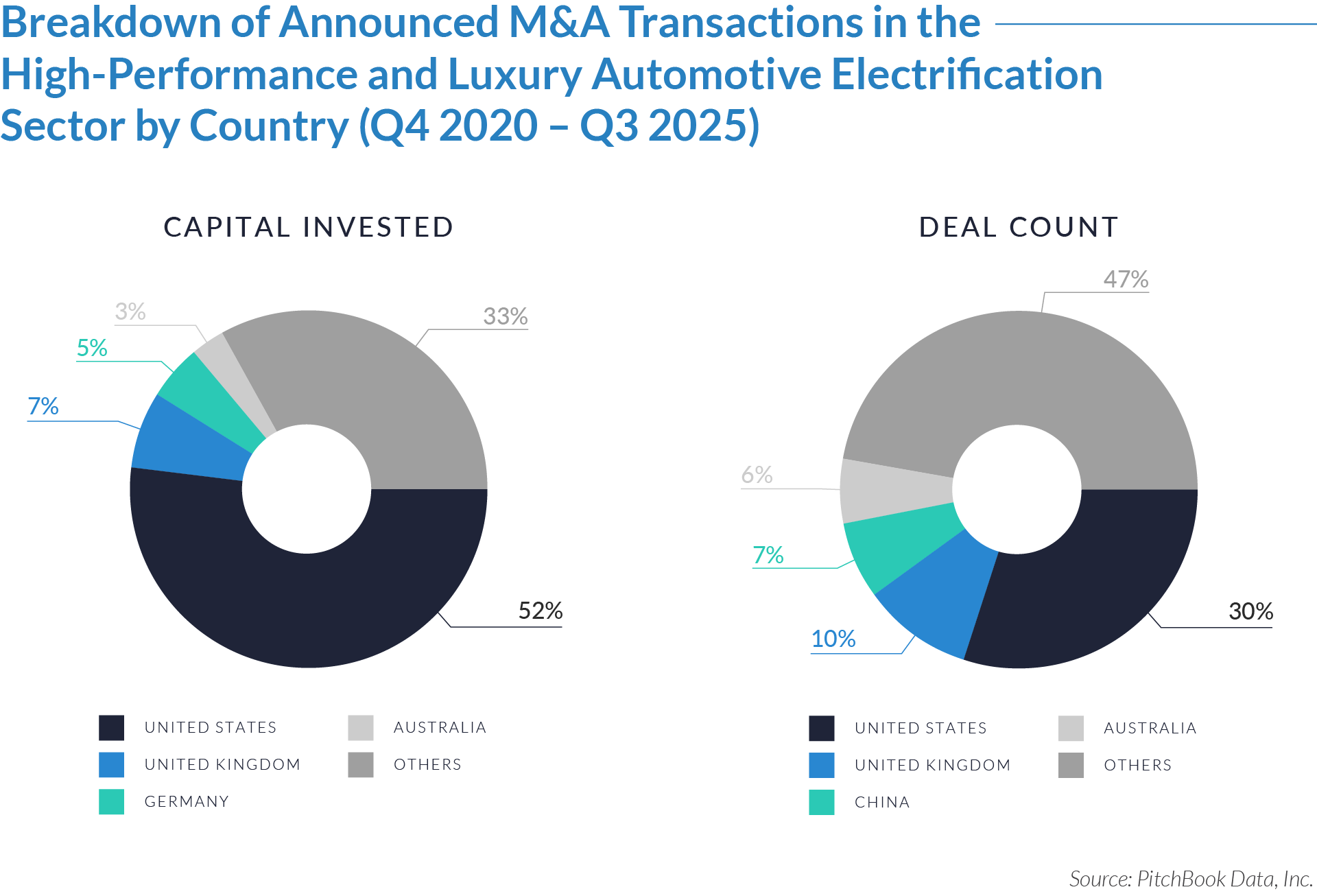
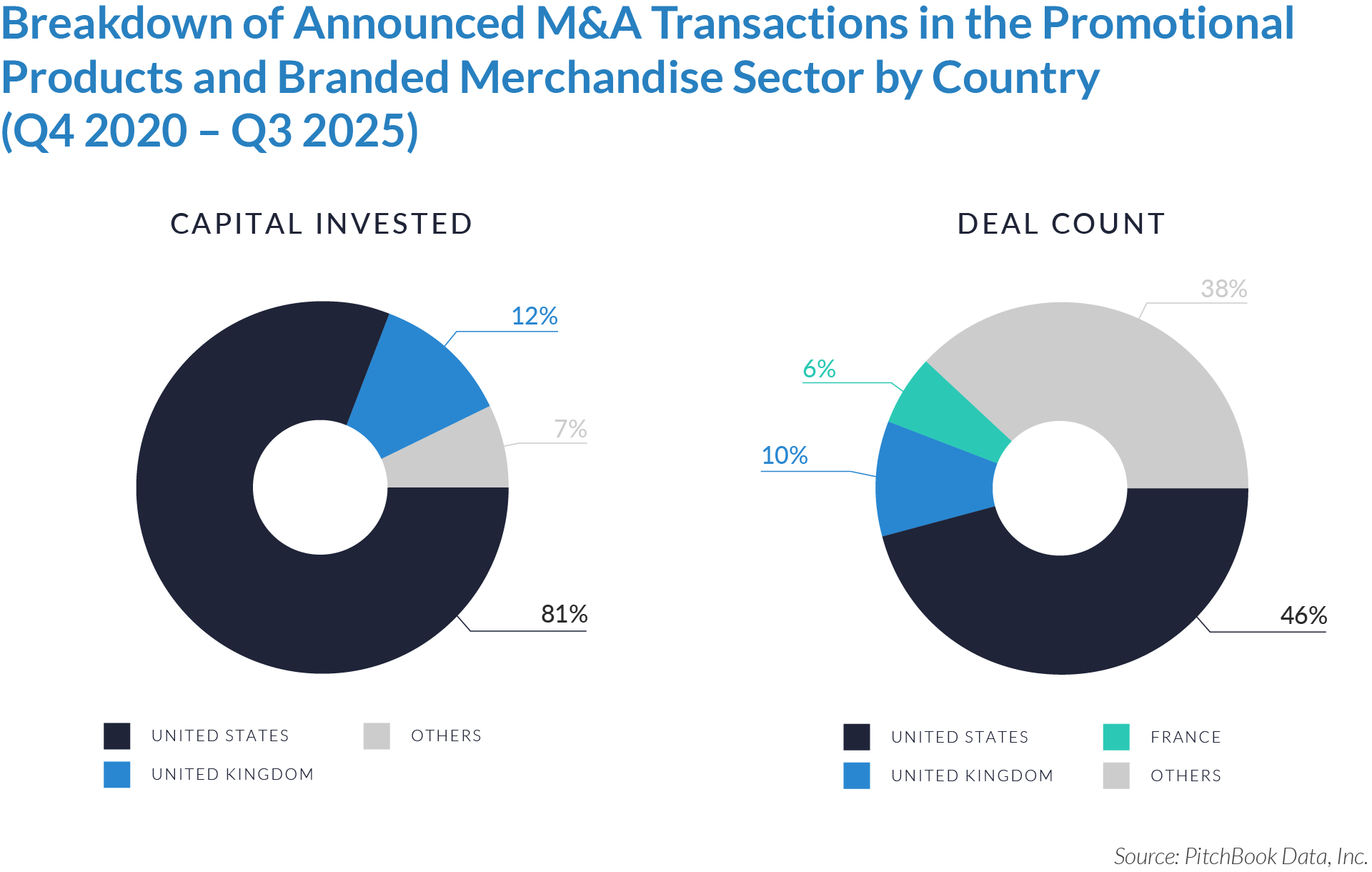
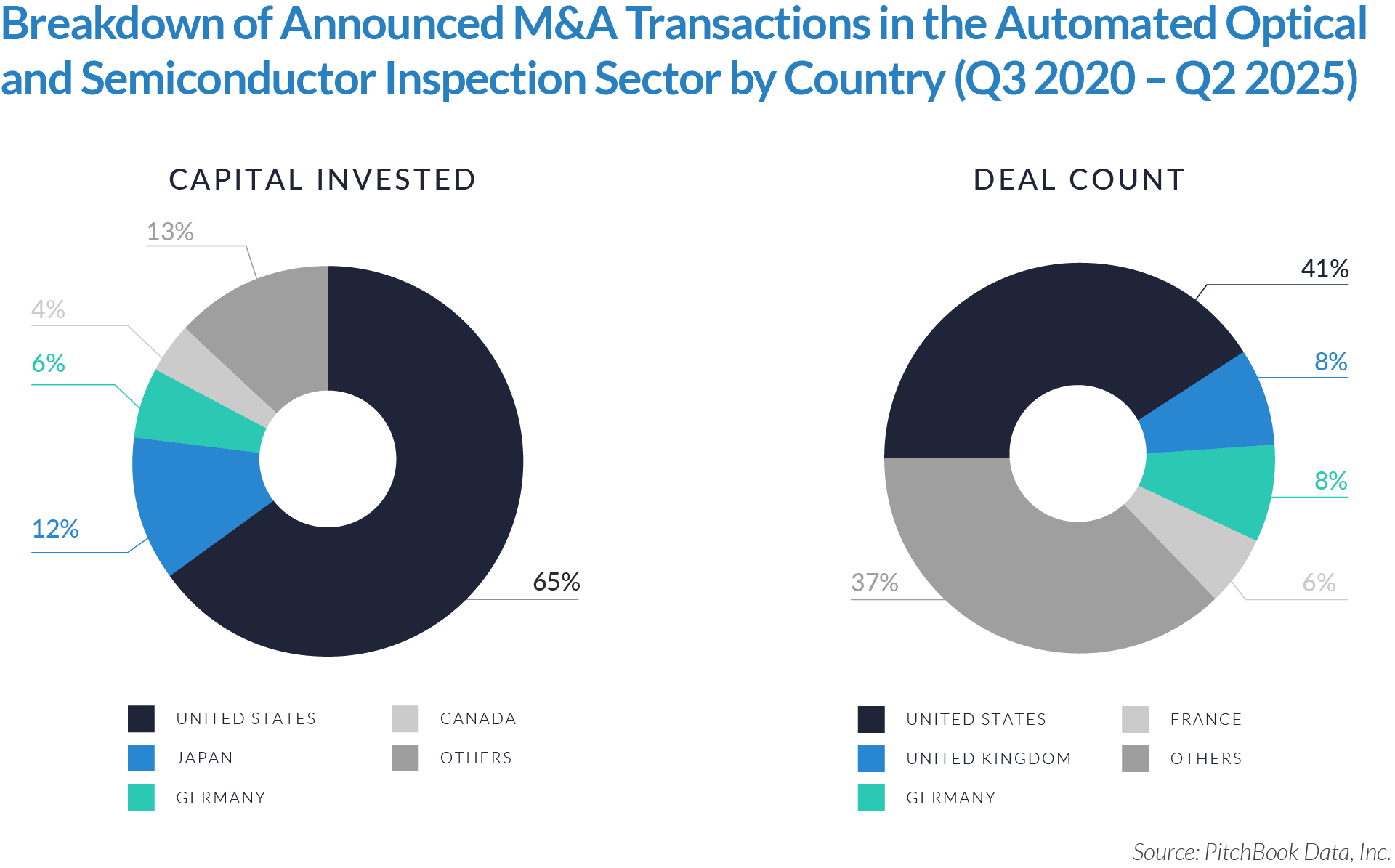
- The United States functions as the primary value engine and valuation benchmark for the sector, accounting for 45% of deal volume while originating 76% of total capital invested, reinforcing its position as the sector’s primary economic control point. Provider fragmentation, reimbursement complexity, and strong pricing power expand monetization opportunities for digital patient intake and clinical workflow software, enabling US-based platforms to scale more rapidly, command premium valuations, and anchor buyout and sponsor-to-sponsor transaction activity.
- The United Kingdom operates as an active adoption market with structurally constrained value creation, representing 7% of deal count but only 3% of capital invested, which reflects steady transaction activity but limited platform scale. Centralized healthcare delivery and budget-constrained buyers support product validation and consistent deal flow while constraining revenue expansion and enterprise value, positioning the UK primarily as a bolt-on or market-entry geography rather than a core value driver. As a result, UK-based assets more frequently serve as bolt-on acquisitions or strategic entry points rather than standalone value anchors.
- Emerging and international markets drive transaction volume without proportional value capture, accounting for 48% of deal volume but only 21% of invested capital, highlighting a fragmented long tail of smaller, localized assets. While these regions offer geographic expansion and incremental growth optionality, acquirers typically realize meaningful value only after integrating assets into scaled platforms with US-style operating leverage, commercial discipline, and expanded product breadth.
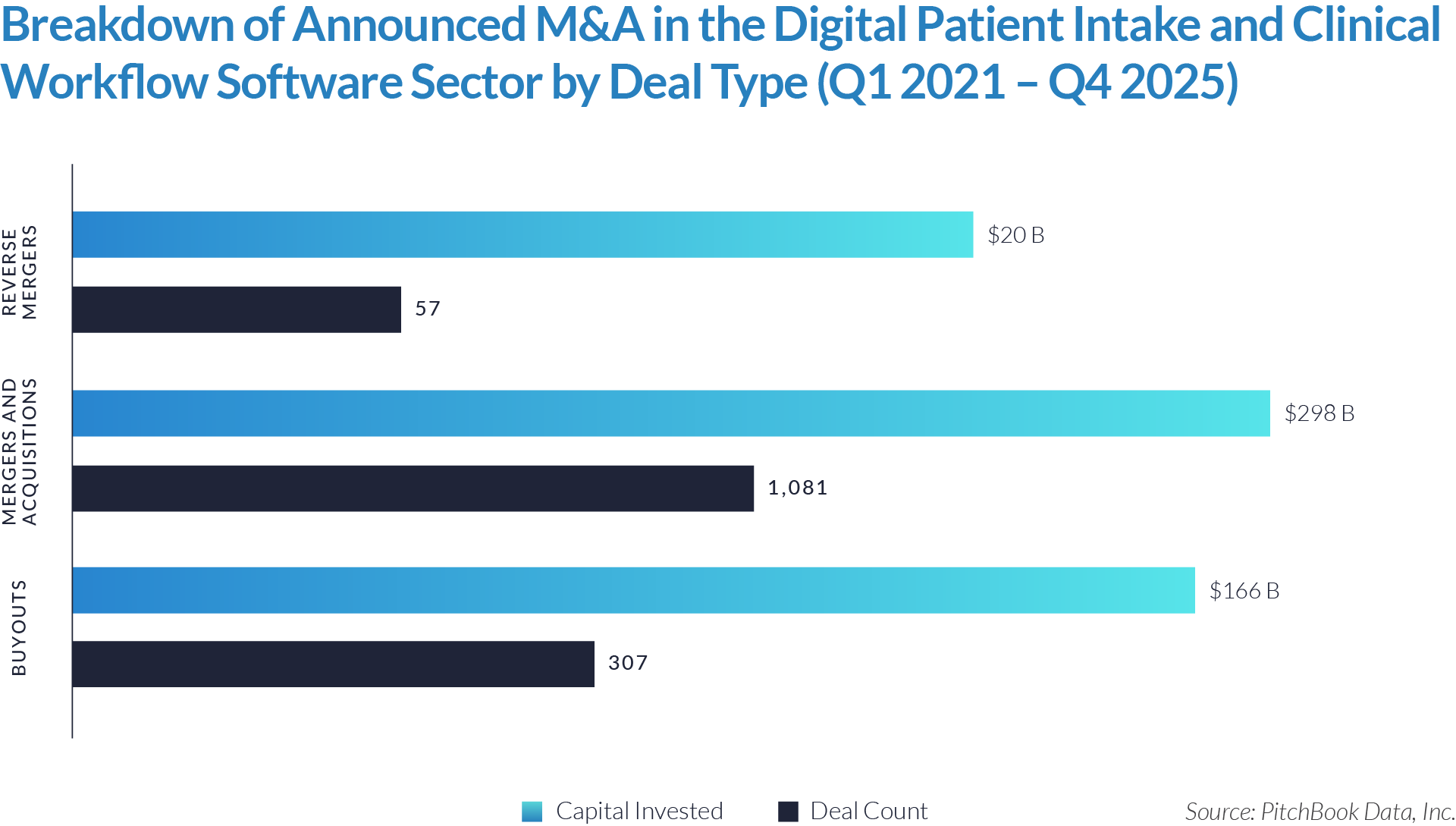
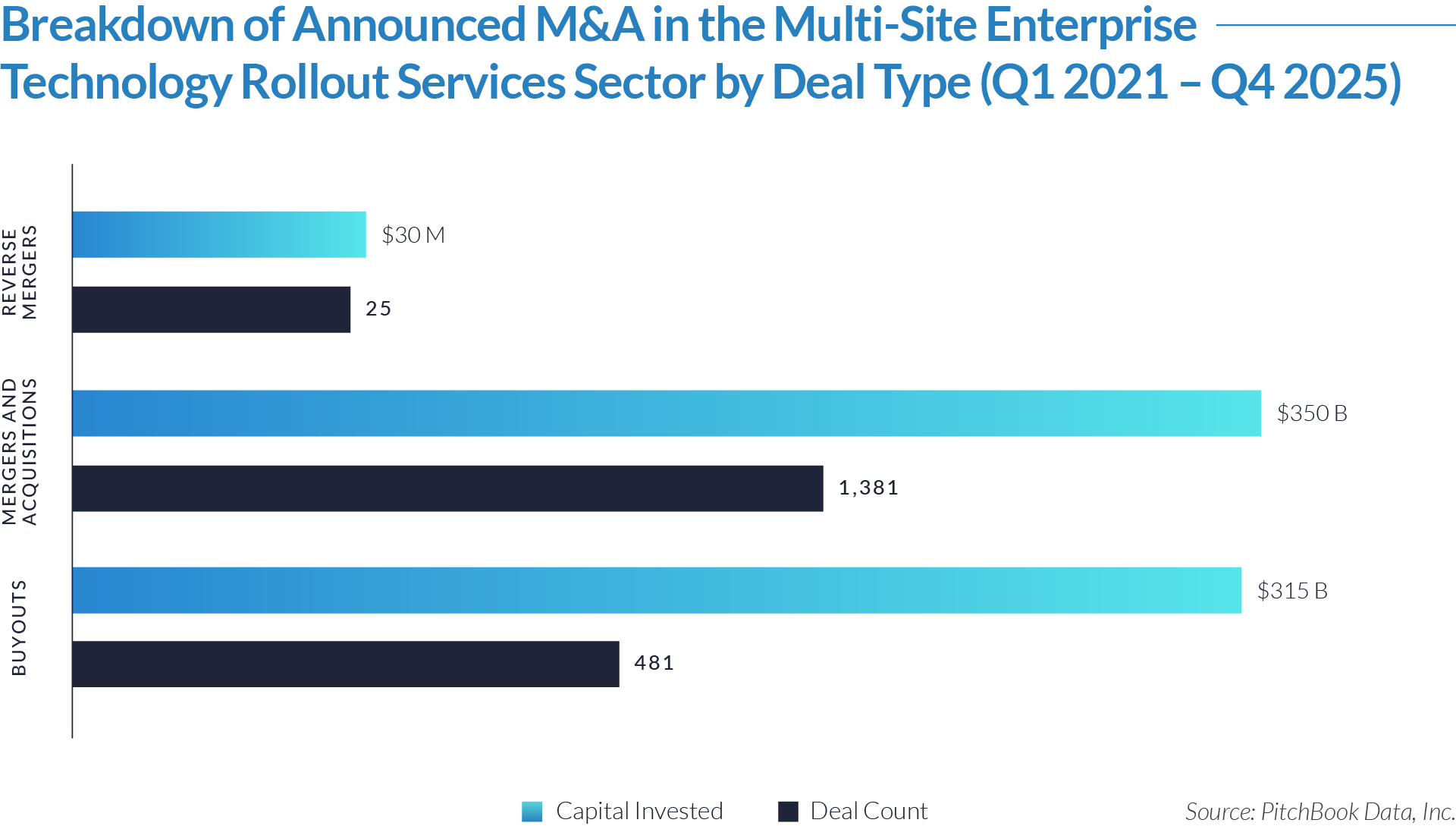
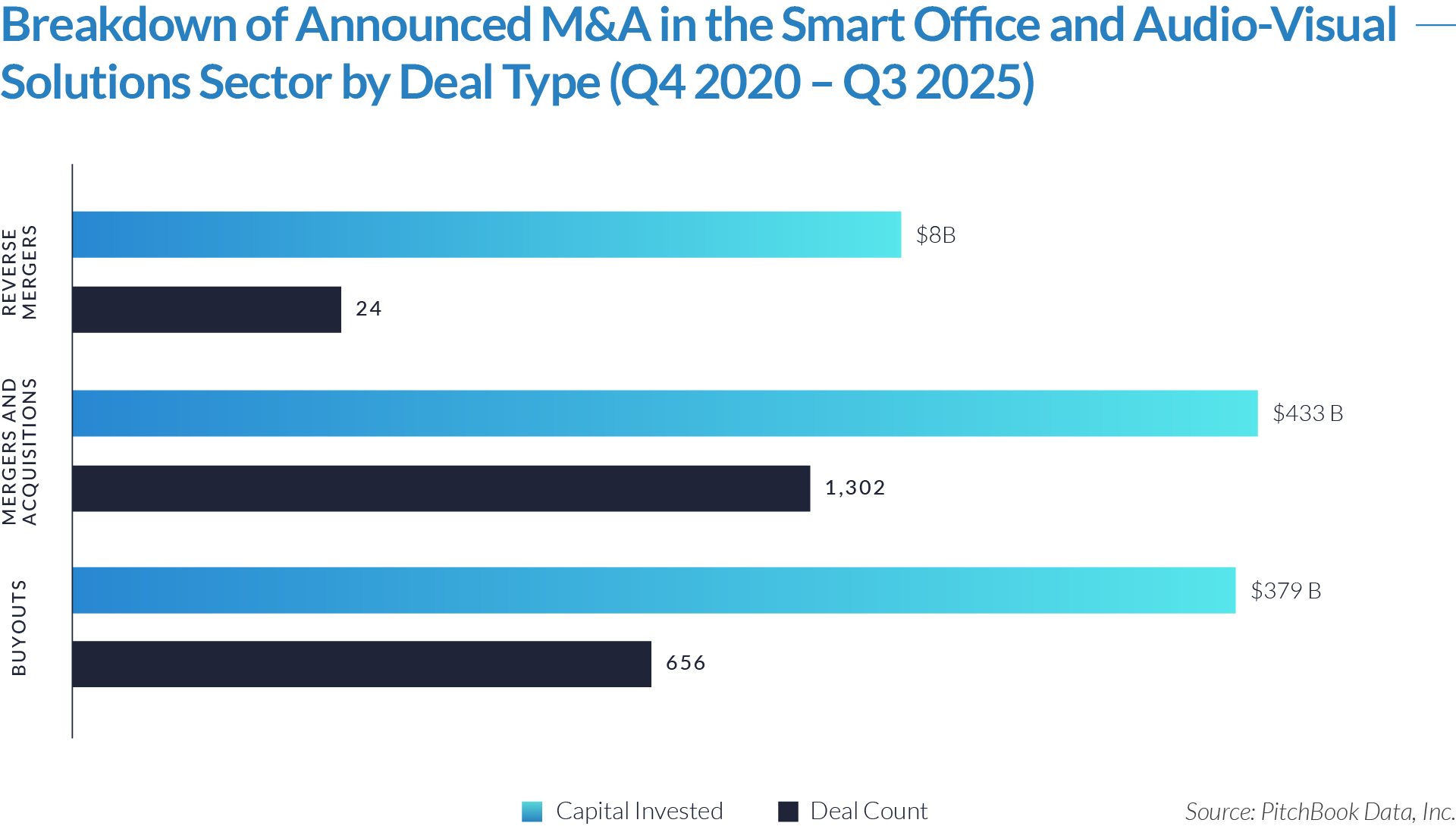
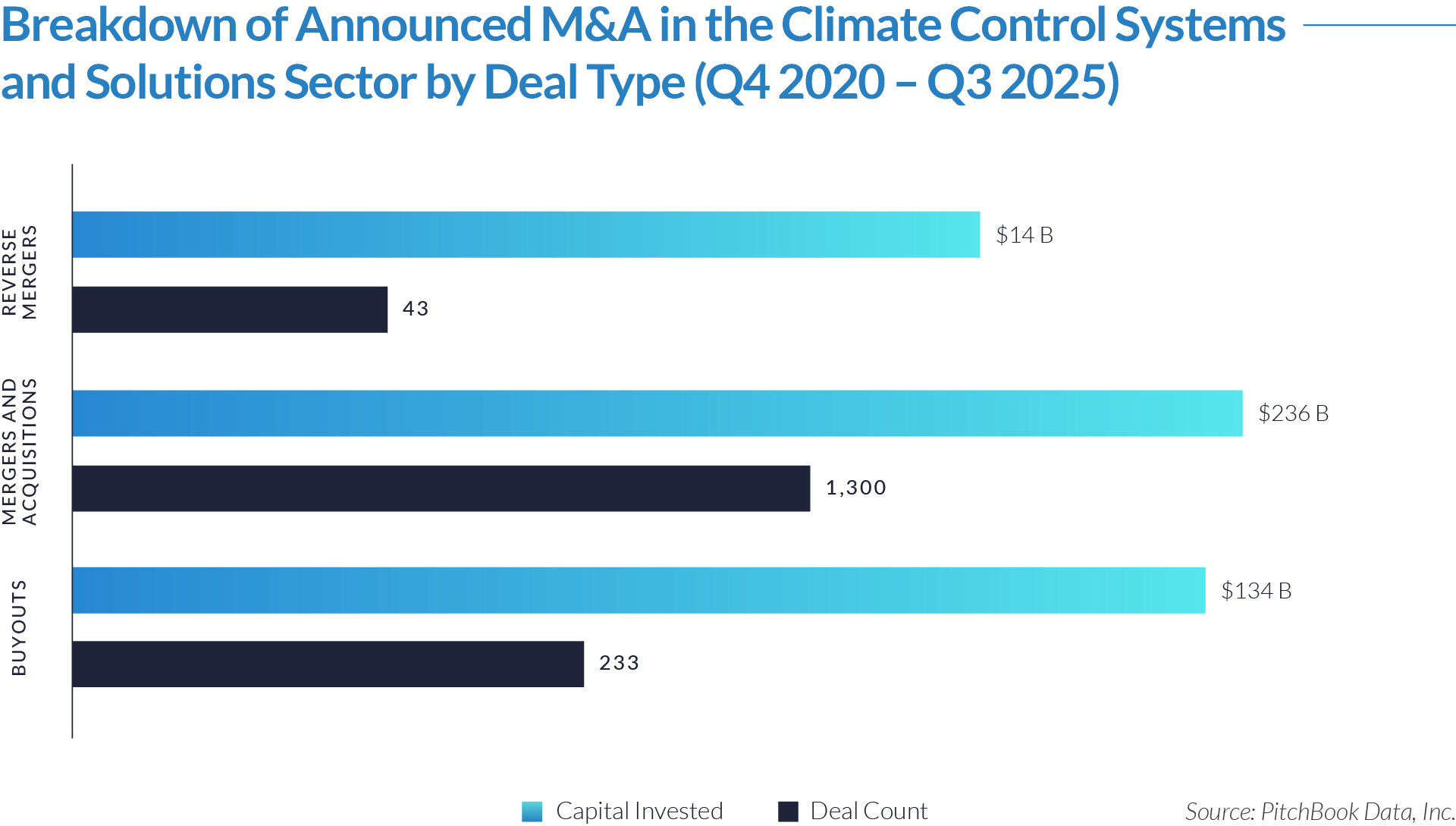
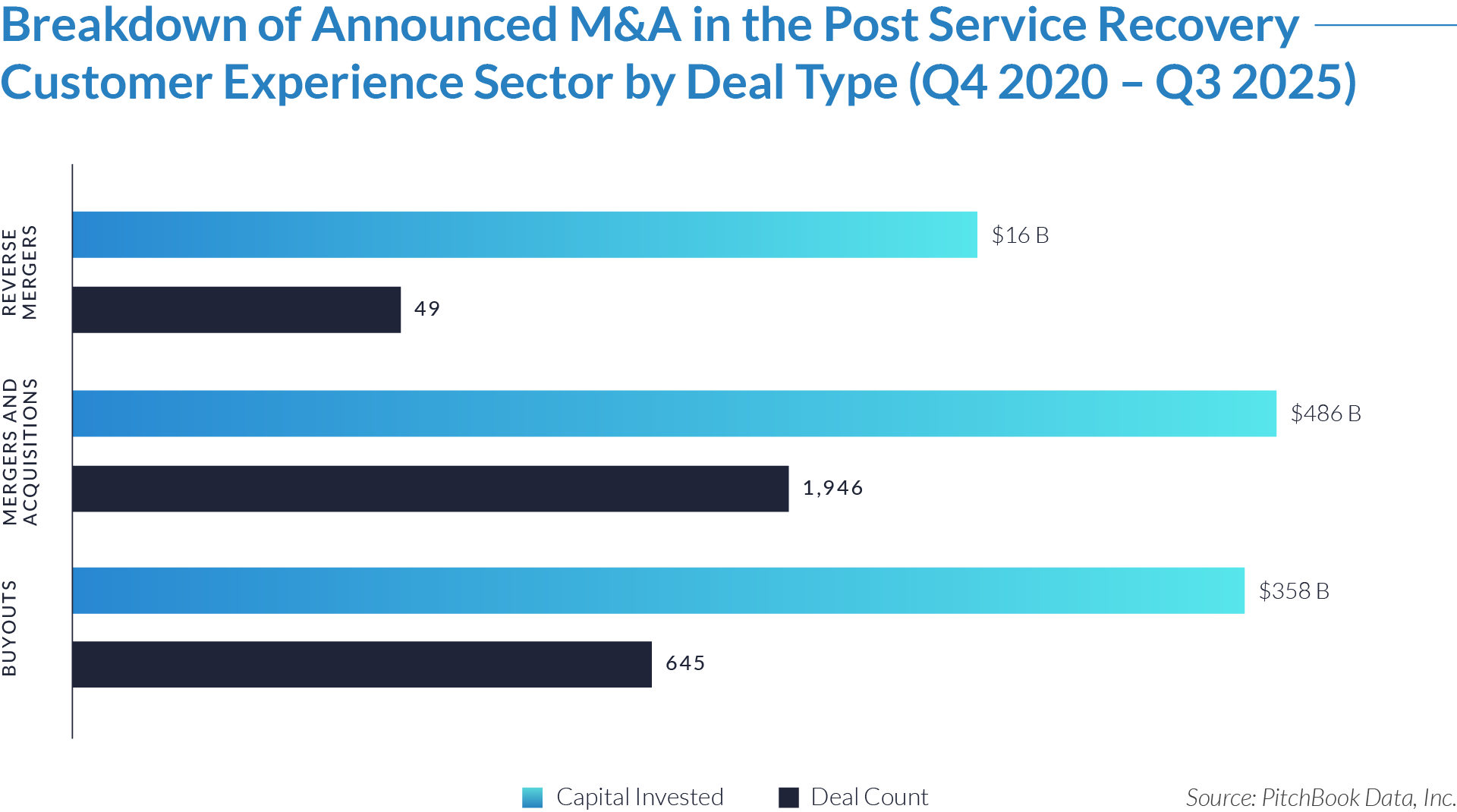
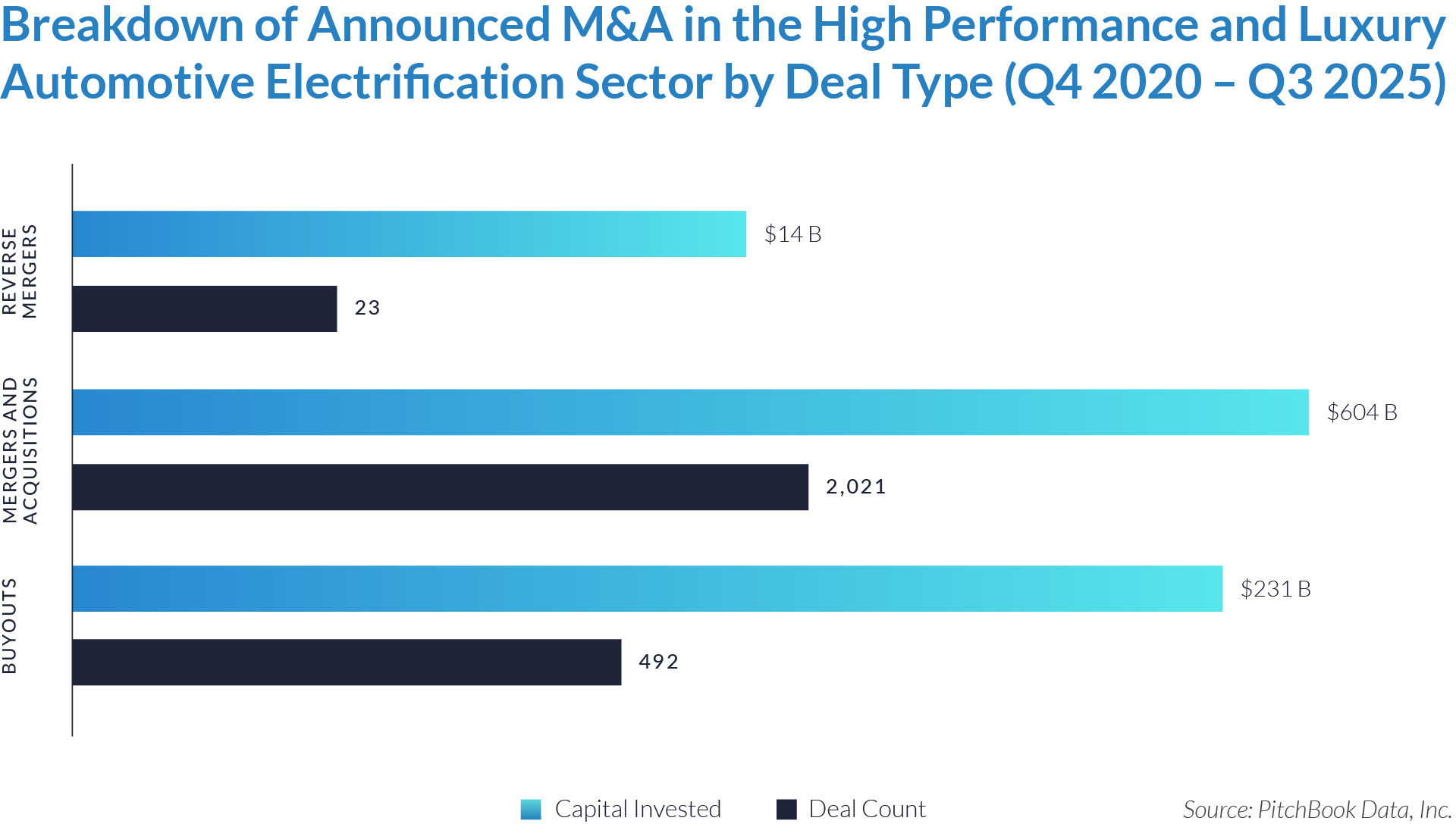
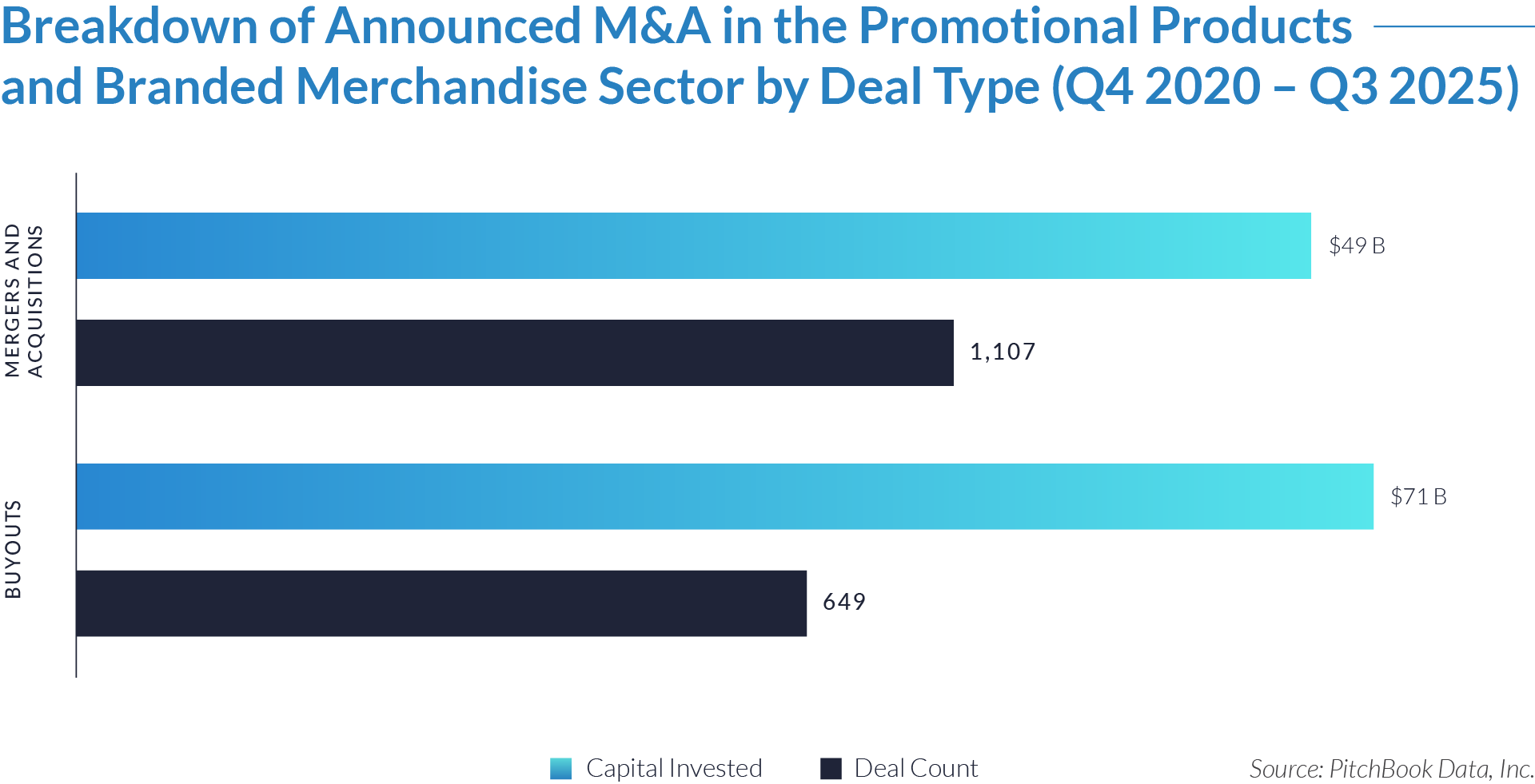
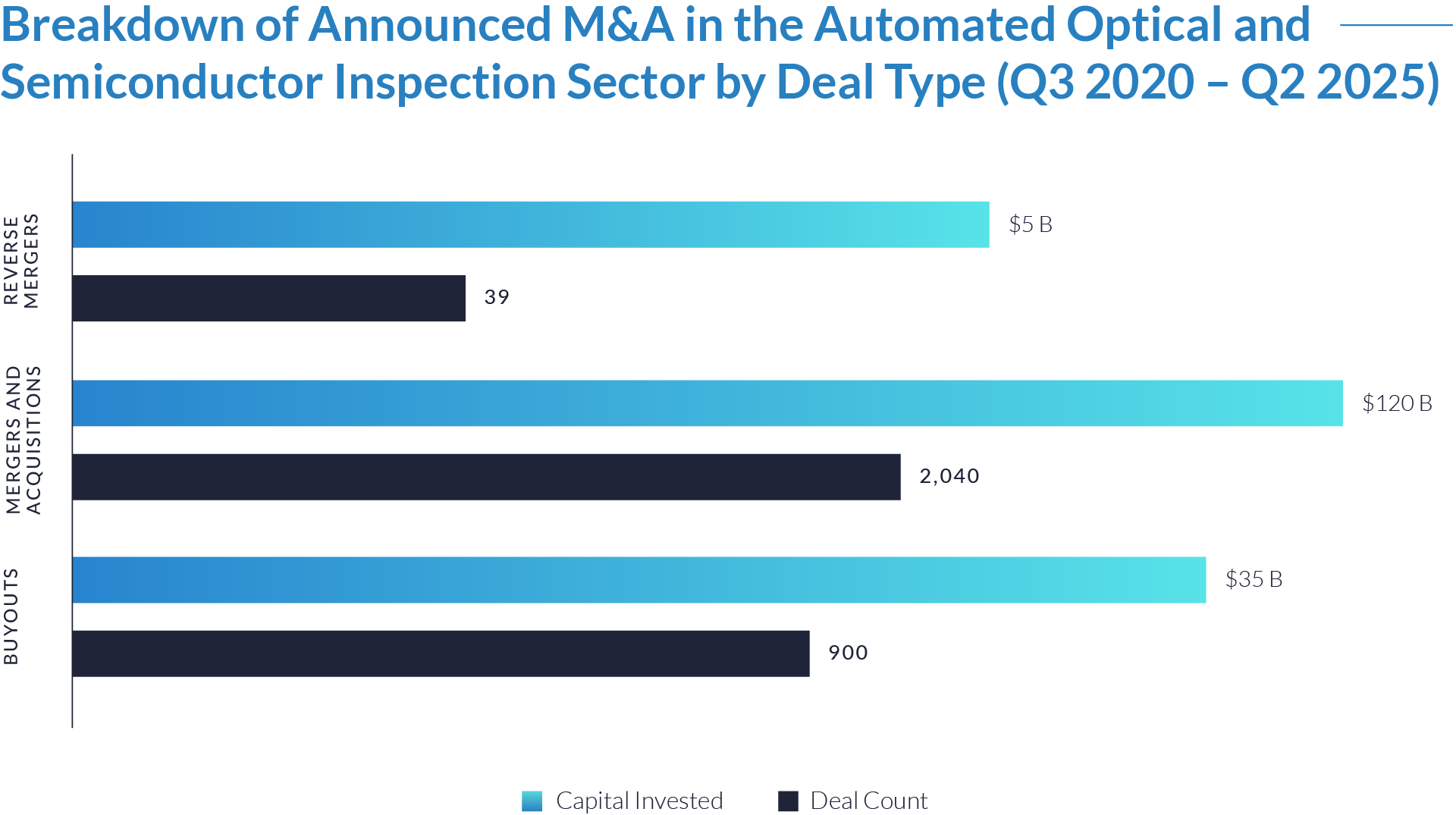
- M&A activity drives sector evolution, signaling capability aggregation rather than financial engineering. With 1,081 M&A transactions representing approximately $298 billion of invested capital, acquirers use M&A primarily to assemble broader patient intake and clinical workflow platforms. This activity indicates that both strategic buyers and financial sponsors prioritize functional expansion, workflow integration, and platform breadth over balance-sheet optimization.
- Buyouts capture a disproportionate share of invested capital, underscoring platform scarcity at scale. Although buyouts account for only 307 transactions, they represent approximately $166 billion of invested capital, implying that scaled, high-quality platforms remain limited in number and command materially larger transaction sizes. This dynamic reinforces the premium placed on market leadership, workflow criticality, and durable competitive positioning.
- Reverse mergers function as a marginal but opportunistic entry mechanism. The limited number of reverse mergers (57 transactions, approximately $20 billion invested) suggests acquirers deploy this structure selectively, primarily as an alternative listing or capital access pathway rather than a core consolidation strategy. These transactions typically reflect situations where speed to market or structural considerations outweigh deep operational integration.
- Capital allocation patterns reveal a two-track consolidation strategy. The coexistence of high-volume M&A activity alongside fewer, capital-intensive buyouts highlights a bifurcated market in which acquirers pursue bolt-on acquisitions to expand functionality and product breadth, while reserving buyouts for a small set of scaled platforms capable of anchoring long-term ecosystem control. This bifurcated approach suggests that future exits will concentrate among scaled platform assets rather than financially engineered roll-ups.
M&A Transactions Case Studies
Three transactions in the digital patient intake and clinical workflow software sector illustrate how private equity investors are acquiring and scaling software platforms embedded at the front end of outpatient and ambulatory care delivery. Acquirers are targeting solutions that digitize patient intake, scheduling, clinical documentation, and administrative workflows, enabling providers to improve operational efficiency, data accuracy, and patient experience. These transactions reflect strong investor demand for workflow-critical healthcare software characterized by recurring revenue, high switching costs, and deep integration into daily clinical operations, positioning these platforms as durable infrastructure within the broader healthcare services ecosystem.

Case Study 01
NEXTGEN HEALTHCARE

NextGen Healthcare, Inc. is a US-based healthcare software company that provides ambulatory electronic health record, practice management, and clinical workflow solutions to outpatient healthcare providers. The company’s platform supports physician practices, specialty clinics, and healthcare networks with core clinical documentation, patient scheduling, revenue cycle enablement, and administrative workflows. NextGen’s software is deeply embedded in day-to-day clinical operations, serving as a mission-critical system of record for outpatient providers and supporting long-term customer relationships through recurring, subscription-based revenue.

Acquirer
Madison Dearborn Partners is a Chicago-based private equity firm with a long track record of investing in scaled healthcare, technology, and business services platforms. The firm focuses on partnering with established, market-leading companies that exhibit durable cash flows, strong customer retention, and opportunities for operational improvement and long-term value creation.
Transaction Structure
NextGen Healthcare was acquired through a leveraged buyout transaction completed on June 6, 2025, in which Madison Dearborn Partners acquired a significant ownership stake alongside Thoma Bravo. The transaction represented a sponsor-to-sponsor ownership transition and recapitalization. Financial terms of the transaction were not publicly disclosed.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The transaction combines Madison Dearborn Partners’ experience scaling healthcare and software businesses with NextGen Healthcare’s established ambulatory healthcare software platform serving outpatient providers. Under sponsor ownership, NextGen continues to support physician groups, specialty clinics, and multi-site outpatient networks that rely on workflow-critical clinical and administrative systems. The partnership provides additional strategic and financial resources to deepen product capabilities, expand customer penetration, and support ongoing platform evolution across the ambulatory care market.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
The acquisition reflects sustained private equity demand for healthcare software platforms that are deeply embedded in clinical workflows and benefit from high switching costs, recurring revenue, and long-term customer relationships. NextGen’s position as a core system of record for outpatient providers, combined with its scale, predictable cash flows, and mission-critical role in care delivery, positions the company as a durable platform for continued operational optimization and product investment. The transaction aligns with Madison Dearborn Partners’ strategy of investing in established healthcare software platforms with clear opportunities for value creation through operational enhancement, disciplined product development, and long-term ownership.

Case Study 02
ADVANCEDMD

AdvancedMD is a US-based healthcare software company that provides cloud-based practice management, electronic health record, patient intake, billing, and clinical workflow solutions to ambulatory healthcare providers. The platform serves physician practices, specialty clinics, and outpatient care organizations, supporting front-office administration, clinical documentation, and revenue cycle workflows. AdvancedMD’s software is deeply embedded in daily clinical operations and generates recurring revenue through long-term customer relationships.

Acquirer
Francisco Partners is a global private equity firm specializing in technology and technology-enabled businesses, with a strong focus on software and healthcare IT platforms. The firm has extensive experience investing in scaled, mission-critical software assets and driving value creation through operational improvement, focused investment, and platform expansion.
Transaction Structure
AdvancedMD was acquired by Francisco Partners through a $1 billion leveraged buyout completed on December 16, 2024.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The transaction combines Francisco Partners’ deep expertise in scaling healthcare and enterprise software platforms with AdvancedMD’s established ambulatory healthcare software business serving outpatient clinics and physician groups. As a standalone entity, AdvancedMD is positioned to focus exclusively on ambulatory providers requiring integrated practice management, clinical workflow, and revenue cycle solutions, supported by increased investment flexibility and enhanced strategic focus.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
The acquisition reflects strong private equity demand for workflow-critical healthcare software platforms characterized by recurring revenue, high switching costs, and durable customer relationships. By separating AdvancedMD from Global Payments, Francisco Partners unlocked the opportunity to accelerate product development, sharpen strategic priorities, and pursue targeted growth initiatives. The transaction aligns with Francisco Partners’ strategy of acquiring established software platforms and enhancing long-term value through operational optimization, disciplined investment, and independent platform expansion.

Case Study 03
ATHENAHEALTH

Athenahealth, Inc. is a US-based healthcare software company that provides cloud-based electronic health record, practice management, patient engagement, and revenue cycle management solutions to ambulatory physician practices and outpatient healthcare providers. The company’s platform supports clinical documentation, scheduling, patient intake, billing, and administrative workflows and is deeply embedded in day-to-day provider operations. athenahealth generates recurring revenue through long-term customer relationships and subscription-based software offerings and is widely regarded as a mission-critical system of record within ambulatory care settings.

Acquirer
athenahealth was acquired by a consortium led by Hellman & Friedman, alongside Bain Capital, Bain Capital Tech Opportunities, GIC Private Limited, Ares Management, FS KKR Capital Corp, and Ergo Partners. The investor group comprises leading global private equity firms and institutional capital providers with extensive experience investing in large-scale, mission-critical healthcare and enterprise software platforms.
Transaction Structure
athenahealth was acquired through a leveraged buyout completed on November 26, 2021, valuing the company at approximately $17 billion.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The transaction combined the acquiring consortium’s expertise in scaling large, complex software platforms with athenahealth’s established ambulatory healthcare software business serving physician practices, specialty clinics, and multi-site outpatient care organizations. Under new ownership, athenahealth continued to support providers requiring reliable, workflow-integrated clinical and administrative systems, while benefiting from enhanced strategic flexibility and long-term investment capacity.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
The acquisition reflects sustained private equity demand for scaled healthcare software platforms characterized by recurring revenue, high switching costs, and deep integration into customer workflows. By completing a sponsor-to-sponsor LBO at significant scale, the acquiring consortium demonstrated confidence in athenahealth’s long-term growth profile, resilience, and strategic importance as a core clinical and administrative platform for ambulatory providers. The transaction positions athenahealth for continued product investment, operational optimization, and long-term value creation under institutional ownership.
As healthcare delivery shifts toward software-defined front-office and clinical operations, digital patient intake and clinical workflow platforms have transitioned from discretionary IT tools to core infrastructure supporting access, care coordination, and operational efficiency. Sustained transaction activity over the past five years reflects investor conviction that workflow-embedded software controlling patient entry points and clinical processes represents a durable, long-term asset class rather than a cyclical theme.
Looking ahead, acquirers are expected to remain selective, prioritizing scaled platforms with recurring revenue, deep workflow integration, and the ability to expand functionality across the patient and clinical lifecycle. Valuation dispersion is likely to persist, with premium outcomes concentrated among system-of-record and front-door platforms, while continued consolidation among smaller assets supports ongoing roll-up and platform-building opportunities. As regulatory, operational, and patient experience pressures intensify, well-integrated and execution-driven platforms are well positioned to anchor future consolidation and long-term value creation across the healthcare software landscape.
Source: Yahoo Finance, NextGen, Payments Dive, Advanced MD, athenahealth, HealthcareITNews , Pitchbook Data.