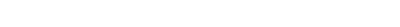Industrial Printing and Packaging Technology Sector M&A Transactions and Valuations
Industrial Printing and Packaging Technology Sector M&A Transactions and Valuations

The industrial printing and packaging technology sector comprises companies that develop inkjet printing systems, digital coders, marking equipment, workflow automation software, and integrated printing platforms. These systems enable high-speed printing, product serialization, labeling, and post-print processing across various production environments.
Investor activity in the sector rose significantly in response to growing demand for digital printing capabilities, on-demand customization, and automation. Acquirers focused on scalable inkjet platforms, integration-ready systems, and recurring revenue models. M&A activity concentrated on businesses that offered proprietary hardware, modular print engines, and digital workflow solutions.
From Q2 2020 to Q1 2025, buyers completed over 3,600 transactions, reshaping the sector’s competitive landscape and driving consolidation. This report analyzes deal volume, valuation multiples, and capital allocation. It examines key transactions, including Kyocera’s acquisition of NIXKA, Hitachi’s acquisition of Telesis Technologies, and Brother Industries’ acquisition of Domino Printing Sciences—each evaluated for strategic alignment, valuation metrics, and market impact.
The report includes EV/revenue and EV/EBITDA multiples to provide valuation benchmarks for software-enabled, automation-oriented, and high-margin businesses. It also identifies key deal drivers such as the adoption of inkjet technology, improvements in production efficiency, and demand for end-to-end system integration. Additionally, it highlights key trends shaping customer behaviors and end use market segmentation within the industry. The analysis concludes with an overview of how evolving technical capabilities and buyer strategies continue to influence investment decisions across the sector.

Key Trends Shaping the Industrial Printing and Packaging Technology Sector
This section analyzes the evolving customer demands, technology adoption drivers, and end-use market segmentation that collectively shape growth, competitive positioning, and consolidation trends across the industrial printing and packaging technology sector.
Adoption in the industrial printing and packaging technology sector is primarily driven by the need for digital transformation, automation, and traceability. Market data indicates that production efficiency (30%) and system integration (25%) are the leading investment drivers, as companies seek to reduce downtime, streamline operations, and enable end-to-end connectivity. Regulatory compliance and recurring revenue opportunities through software and service models each account for 15%, reflecting the growing importance of serialized labeling, uptime assurance, and maintenance contracts. Geographic diversification (10%) and on-demand customization (5%) are emerging factors, particularly as manufacturers look to scale across regions and tailor outputs to dynamic customer needs.
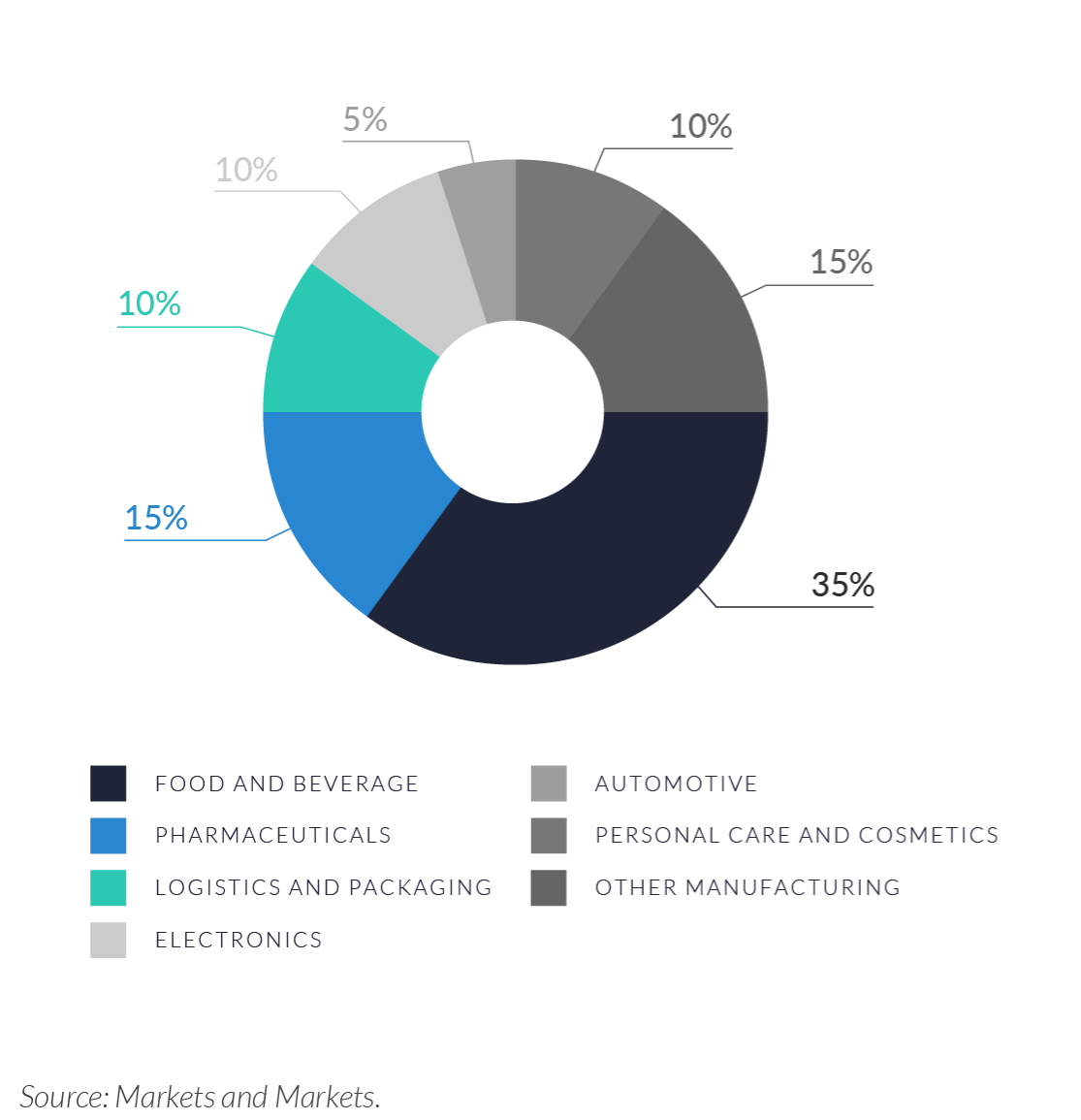
End-use demand in the industrial printing and packaging technology sector is highly segmented, with food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, logistics, and personal care representing the primary application areas. These industries require consistent, high-speed labeling, coding, and serialization, making them core drivers of technology adoption. In contrast, sectors like automotive, electronics, and general manufacturing adopt printing solutions more selectively, often favoring hybrid or legacy systems due to longer capital investment cycles and less frequent regulatory updates. This segmentation shapes both product development priorities and acquisition targeting across the sector.

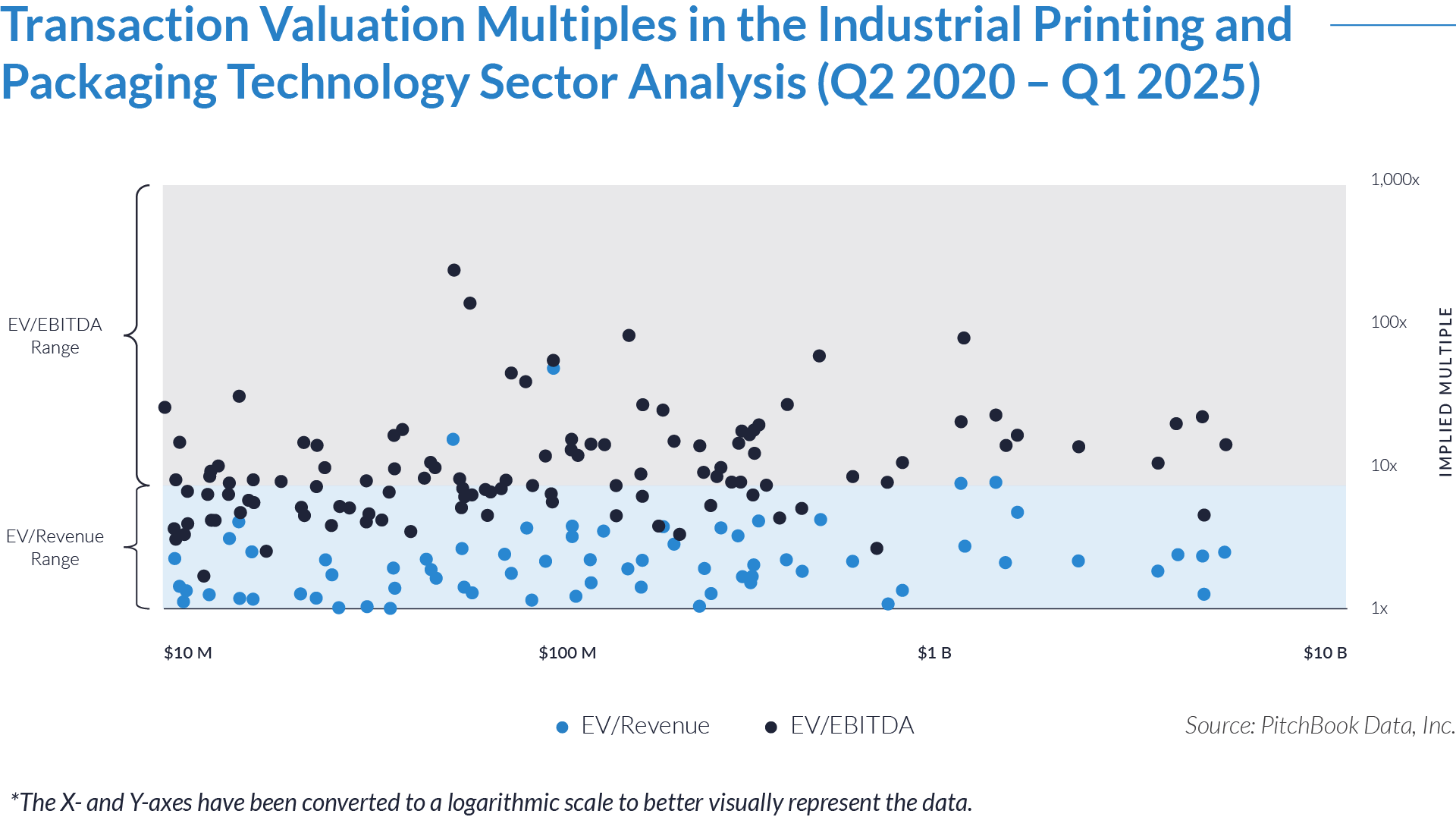
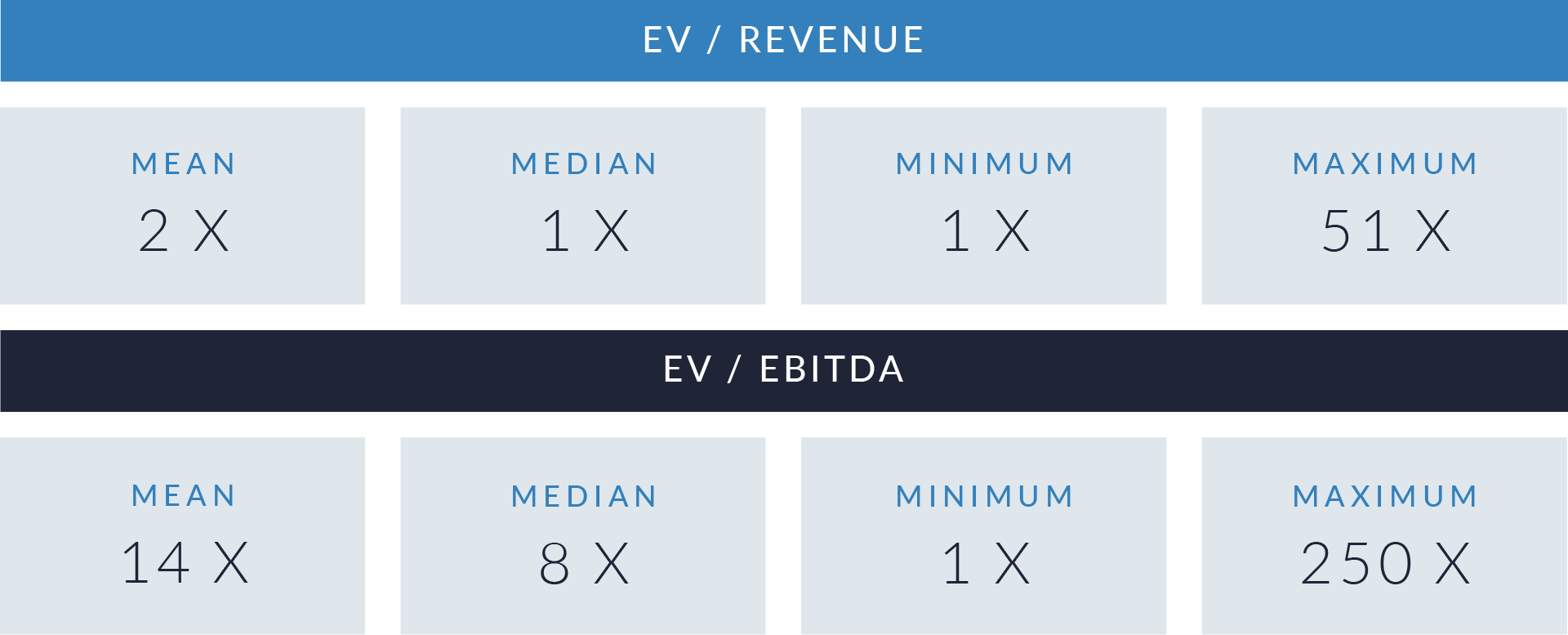
- Valuation multiples are based on a sample set of M&A transactions in the industrial printing and packaging technology sector using data collected on May 27, 2025.
- Valuation multiples based on EV/revenue vary significantly across the sector. Median values sit around 2x, while outliers exceed 50x. Acquirers apply higher multiples to businesses that supply modular inkjet platforms, integration-compatible systems, or variable data printing solutions—especially where regulatory or high-speed production requirements apply. Traditional equipment manufacturers and commodity packaging system providers typically trade between 1x and 3x.
- EV/EBITDA multiples typically fall within the 10x–15x range, though several transactions show values above 40x or even 100x. Buyers assign these premium valuations to businesses with proprietary inkjet components, recurring revenue streams from software or service contracts, or differentiated technology used in serialization, automation, or process control.
- Larger transactions with enterprise values above $1 billion usually reflect valuation ranges between 10x and 25x EV/EBITDA. These transactions show more pricing stability due to scale and diversified revenue. Smaller transactions display greater variation in multiples, often influenced by competitive sale processes, specialization, or growth potential linked to patented print modules or embedded workflow technologies.

Capital Markets Activities
The data highlights transaction trends, valuation metrics, and investment patterns in the industrial printing and packaging technology sector. Increased adoption of digital printing, modular inkjet systems, and automation platforms has contributed to higher M&A activity and growing private equity involvement. Acquirers are targeting providers of high-speed print engines, integration-ready hardware, and print workflow software that support variable data, real-time production control, and compliance-driven labeling. These transactions are driving consolidation across hardware and software layers, accelerating digital transformation, and expanding the use of value-added capabilities such as cloud-managed print infrastructure and end-to-end packaging integration.
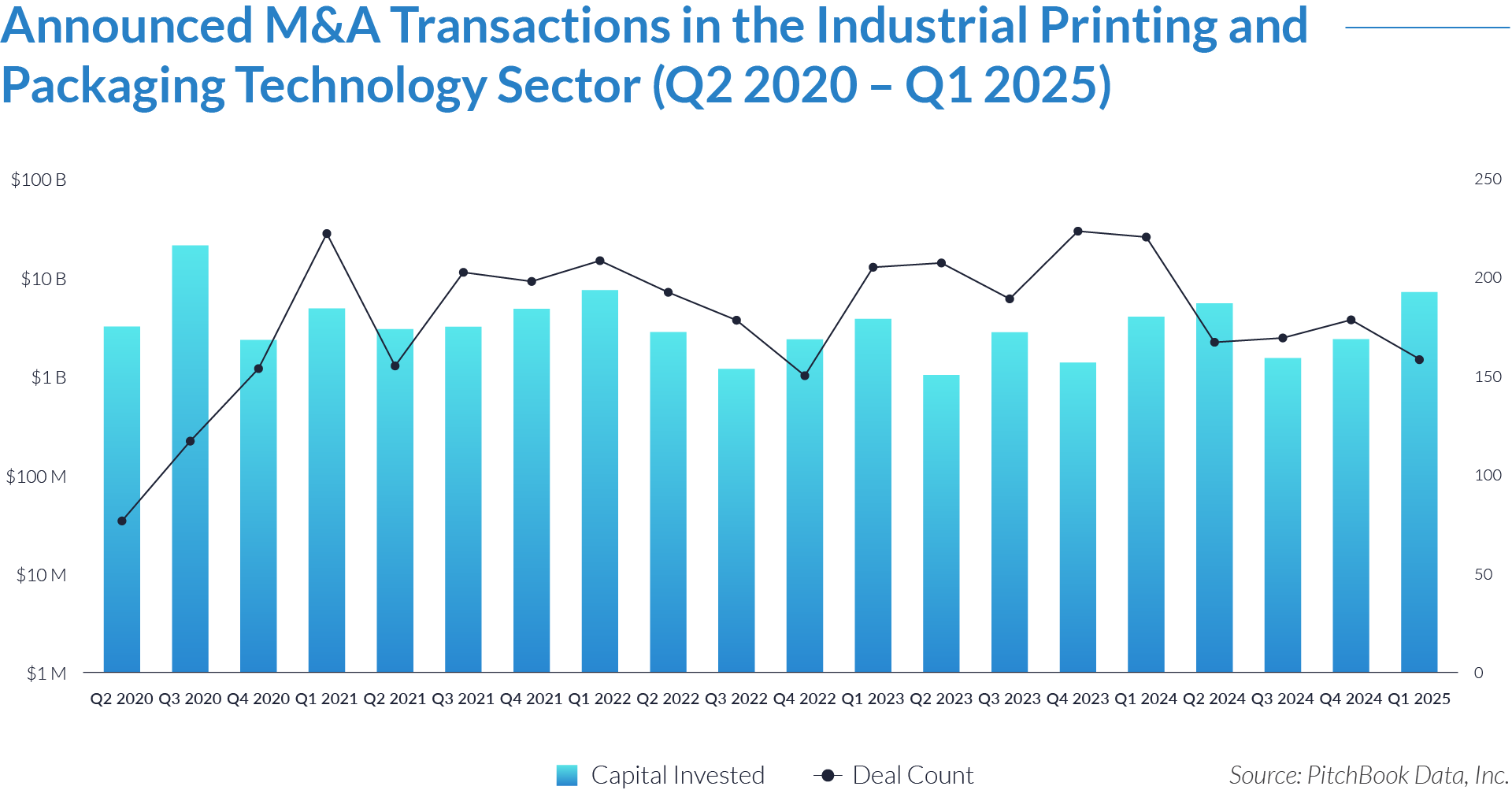
- Investors allocated $82 billion across 3,500 deals over a 20-quarter period, averaging $4 billion in capital and 179 transactions per quarter. This consistent activity reflects increased capital flow into industrial printing and packaging technology businesses with automation capabilities, supply chain integration features, and traceability solutions.
- Average deal size during the period reached approximately $23 million. In Q3 2020, the average rose to $172 million due to a concentration of large-scale transactions. These outlier periods involved consolidation of high-value assets or expansion into adjacent technologies, including digital printing and smart packaging systems. Overall, the sector primarily saw mid-market acquisitions and strategic add-ons.
- Capital deployment slowed after 2022, but deal volume remained steady. In 2023 and 2024, buyers completed an average of 190 transactions per quarter, while capital invested declined to $3 billion per quarter. This reduced the average deal size to $15 million. The shift reflects increased emphasis on bolt-on acquisitions, integration synergies, and targeted technology absorption rather than large-scale, high-cost transactions.
The graphs below present the geographic distribution of transactions, providing additional detail on regional trends and investment dynamics.
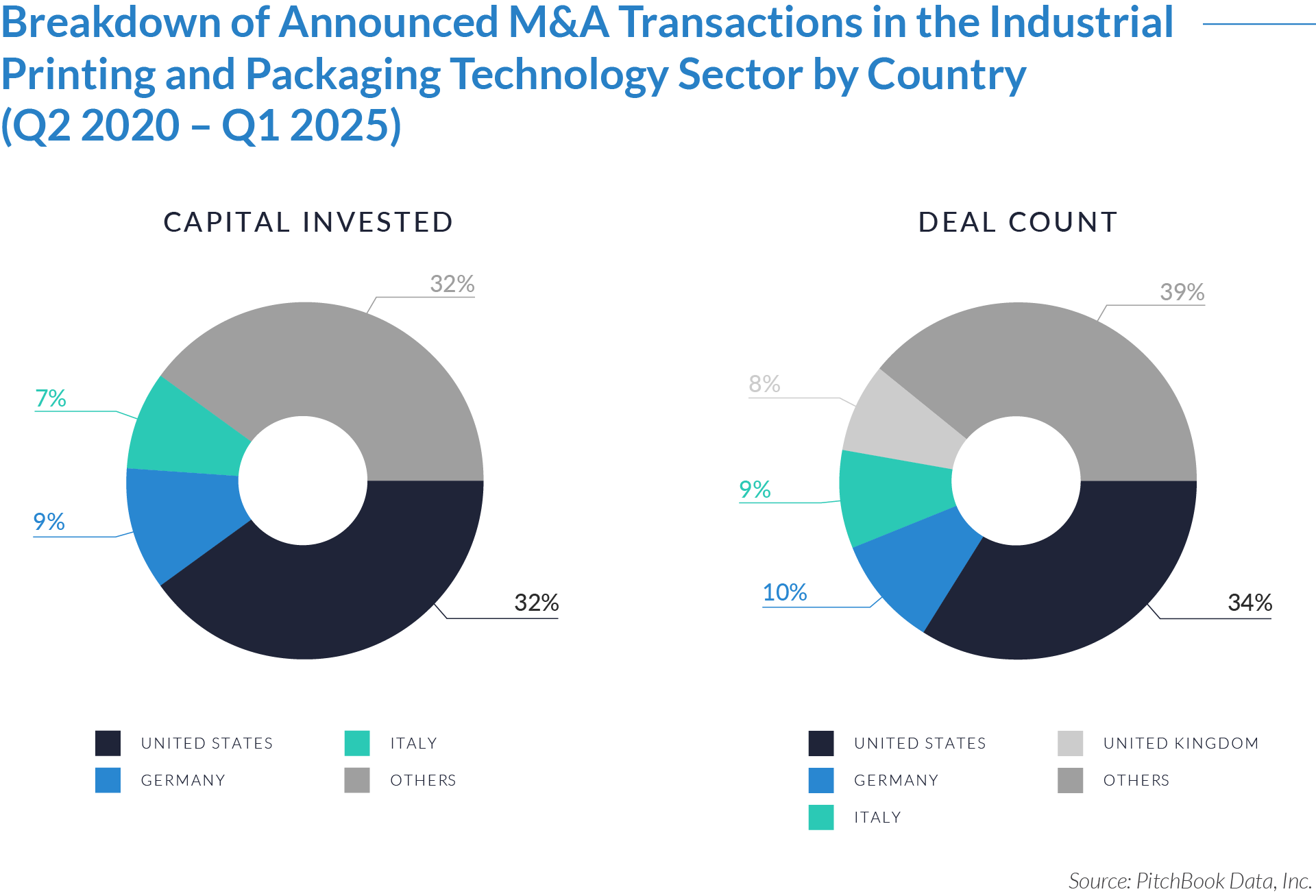
- US-based investors accounted for 32% of capital invested and completed 34% of deals, underscoring their dominant role in both domestic and international consolidation. Their activity focused on acquiring scalable platforms and automation-centric technologies to extend market leadership.
- German investors deployed 29% of capital while executing only 10% of deals, indicating a strategy centered on selective, high-value acquisitions—often targeting advanced production assets. Italy attracted 9% of deals with 7% of capital, reflecting its position as a source of specialized, mid-sized companies with integration potential.
- Investors executed 39% of deals and deployed 32% of capital across Asia, Eastern Europe, Latin America, and other international markets. These regions offered cost advantages, regional manufacturing hubs, and fragmented competitive landscapes—providing ample acquisition targets in digital coding, industrial inkjet, and automation technologies.
The deal-type dynamics below set the stage for understanding how capital flows and strategic priorities shape industrial printing and packaging technology sector’s growth and landscape.
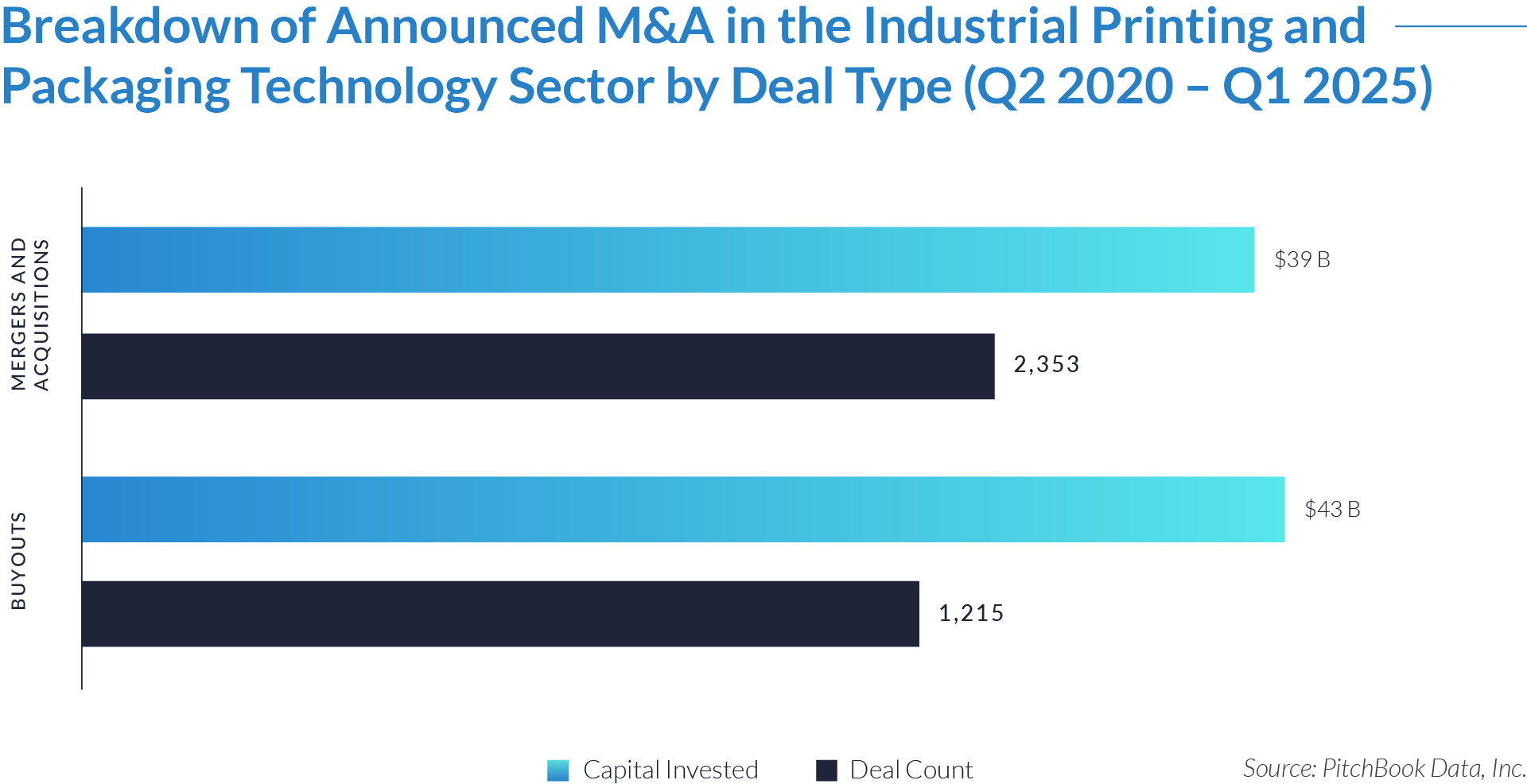
- Private equity firms completed 1,215 buyout transactions totaling $43 billion, accounting for 52% of total capital deployed while representing only 33% of deal volume. These firms targeted larger, high-value businesses, often selecting platform companies with scalable technologies, recurring revenue, or bolt-on acquisition potential.
- Strategic acquirers executed 2,353 mergers and acquisitions, representing 66% of deal volume and $39 billion in total capital. These transactions advanced sector consolidation by enabling vertical integration, technology expansion, and operational efficiencies—particularly in automation, labeling, and digital printing systems.
- The average buyout deal size reached approximately $35 million, nearly double the $17 million average for M&A transactions. This difference reflects a preference to use buyouts for acquiring mature, asset-intensive businesses, while M&A transactions more commonly target mid-sized companies or specialized technologies that complement existing operations.
M&A Transactions Case Studies
Three strategic acquisitions in the industrial printing and packaging technology sector highlight a broader shift toward platform integration, digital capability expansion, and scalable inkjet solutions. These transactions involve the consolidation of print engine manufacturers, marking system providers, and digital coding specialists to enable end-to-end system delivery. Each target brought modular architecture, application-specific technologies, and recurring revenue potential through software, services, and consumables. The acquirers strengthened their positions by moving up the value chain, combining component expertise with full-system capabilities to support labeling, product marking, and variable data printing. These deals reflect strategic priorities around technology control, integration, and differentiation in a precision-driven, compliance-focused market.

Case Study 01
NIXKA

NIXKA SAS, based in France, develops high-performance industrial inkjet print engines and systems. The company focuses on modular, easy-to-integrate solutions designed for precision, reliability, and user accessibility—even for operators without prior inkjet experience. Built on a strong foundation of inkjet innovation, NIXKA delivers scalable, plug-and-play platforms tailored to a broad spectrum of industrial applications.

Transaction Structure
Kyocera Corporation acquired full ownership of NIXKA SAS through an all-cash transaction. The purchase price was not disclosed.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The acquisition brought together NIXKA’s advanced inkjet engine technology and application-specific integration capabilities with Kyocera’s established expertise in high-speed inkjet printheads. This combination expanded Kyocera’s reach into full-system solutions and enabled it to serve a wider range of industrial printing customers seeking end-to-end platforms for packaging, labeling, and product marking.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
Kyocera pursued the acquisition to strengthen its position in the global digital printing market by advancing from a component supplier to a full-system provider. NIXKA’s technologies and customer relationships supported Kyocera in accelerating the development of turnkey inkjet solutions, broadening application capabilities, and entering high-growth industrial segments such as packaging and on-demand product customization.

Case Study 02
TELESIS TECHNOLOGIES

Telesis Technologies, based in the United States, manufactures permanent marking equipment and industrial coding systems. Its product range includes laser markers, dot-peen machines, scribe marking systems, and thermal inkjet printers, all engineered for high precision, traceability, and durability in demanding industrial settings. Telesis’s programmable and rugged marking solutions are widely used in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and metal fabrication. The company is known for delivering reliable direct part marking (DPM) and compliance-driven identification, supported by an extensive global service network.

Transaction Structure
Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems, a subsidiary of Hitachi Ltd. (TKS: 6501), acquired 100% of Telesis Technologies. The transaction value and payment structure were not disclosed, though it was likely completed as a cash deal in line with Hitachi’s standard acquisition practices.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The acquisition combined Telesis’s established presence in high-precision marking for aerospace, automotive, and industrial manufacturing with Hitachi’s existing inkjet printer operations. Telesis’s expertise in durable part marking and its global service network complemented Hitachi’s broader industrial equipment portfolio. This combination enabled cross-selling and expanded the joint offering for customers requiring integrated coding, marking, and traceability solutions.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
Hitachi completed the acquisition to strengthen its position in the global product identification market, with a focus on permanent part marking. By integrating Telesis’s technologies and service capabilities—particularly in dot-peen and laser systems—Hitachi enhanced its recurring revenue through expanded maintenance and aftermarket services. The deal aligned with Hitachi’s strategy to grow its industrial equipment division and improve competitiveness in sectors requiring robust, compliance-driven marking solutions.

Case Study 03
DOMINO PRINTING SCIENCES

Domino Printing Sciences is a global supplier of industrial printing and coding systems, with expertise in inkjet, laser, and thermal transfer technologies. The company delivers high-performance solutions for product identification, traceability, and regulatory compliance, supporting applications across food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and packaging. Its systems are engineered for seamless integration into production lines, enabling variable data printing, serialization, and marking on a wide range of materials. Headquartered in the United Kingdom, Domino operates in more than 120 countries as a subsidiary of Brother Industries.

Transaction Structure
Brother Industries (TKS: 6448) acquired Domino Printing Sciences (PINX: DMIPY) for approximately $2 billion in an all-cash transaction.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The acquisition integrated Domino’s strong position in industrial product identification and traceability with Brother’s background in consumer and office printing technologies. Domino’s established customer base in regulated and high-throughput sectors—such as food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics—enabled Brother to extend its reach into mission-critical industrial markets. The transaction allowed both companies to apply their combined expertise in inkjet and printing technologies to serve a broader range of enterprise and industrial clients.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
Brother Industries completed the acquisition to diversify beyond consumer electronics and strengthen its presence in the global industrial printing market. Domino’s advanced coding and marking systems, global operations, and reputation for engineering excellence aligned with Brother’s strategy to enter high-growth markets with recurring revenue potential. The deal also gave Brother direct access to Domino’s industrial customer relationships and accelerated its move into compliance-driven, high-margin printing applications.

The industrial printing and packaging technology sector demonstrated consistent M&A momentum from 2020 to 2025. Buyers prioritized targets with proprietary technology, automation capability, and resilient end-market exposure. As demand shifts toward digital integration, traceability, and efficiency, M&A will remain a central lever for achieving scale, differentiation, and long-term value creation.
Source: Domino, Brother.com PDF, Telesis – Press Release, LINCOLN International, GMI, Mordor Intelligence, Markets and Markets, Packaging Tech Today, Printing Watch, Pitchbook Data.