Electronics and Embedded Systems Sector M&A Transactions and Valuations
Electronics and Embedded Systems Sector M&A Transactions and Valuations

Investors increased activity in the electronics and embedded systems sector between 2020 and early 2025, targeting companies involved in PCB design, embedded firmware, custom hardware manufacturing, and system-level integration. Buyers pursued targets that offered engineering-led services, supported industrial automation, and delivered scalable embedded technologies across high-reliability sectors such as industrial, medical, automotive, and aerospace.
Between Q2 2020 and Q1 2025, strategic and financial acquirers completed transactions that expanded technical capabilities and reshaped competitive positioning across the sector. This report analyzes capital deployment, deal volume, and valuation multiples over the period. It includes key transactions such as H.I.G. Capital’s buyout of SMTC, USI’s acquisition of Asteelflash, and the merger of GPV and Enics, and evaluates each based on strategic alignment, valuation level, and market impact.
The report provides data on EV/revenue and EV/EBITDA multiples to outline pricing trends, investor priorities, and growth expectations. It identifies recurring deal drivers such as engineering capabilities, manufacturing footprint, product complexity, and embedded IP. The analysis also outlines operational themes and investment strategies relevant to acquirers and investors in the electronics and embedded systems sector, offering a structured overview of consolidation activity, valuation benchmarks, and strategic direction.
Growth and Trends in the Electronics and Embedded Systems Sector M&A
The following exhibits provide a snapshot of revenue growth and strategic trends influencing M&A in the sector. Exhibit 1 reports strong performance in connectivity and cloud markets along with steady gains in industrial and medical segments. Exhibit 2 outlines how companies use diversification, innovation, and operational efficiency through acquisitions to expand capabilities and address evolving customer requirements.
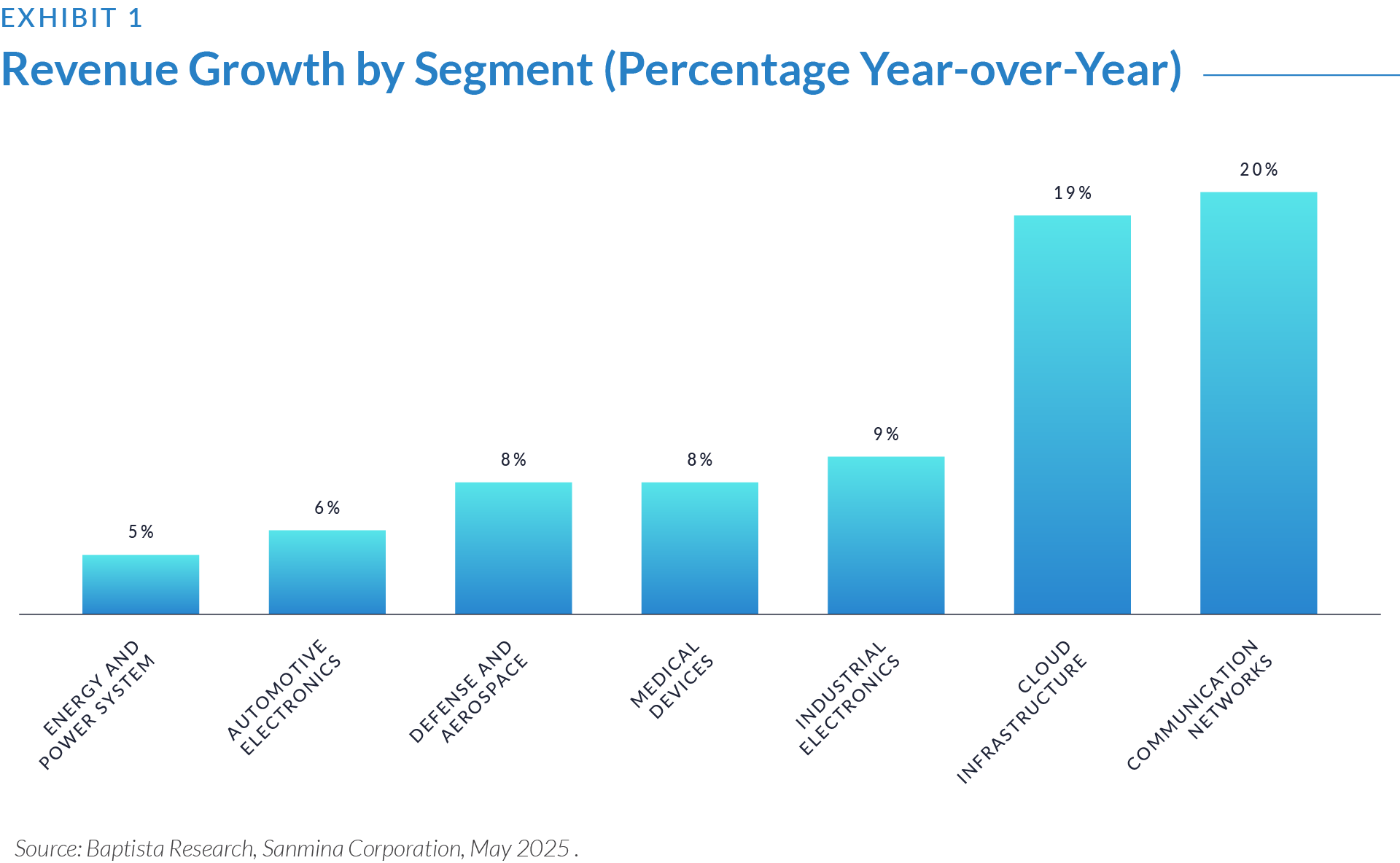
- Communication networks and cloud infrastructure drove revenue growth across the sector, achieving year-over-year (2024-2025) increases of approximately 18–20%. Major enterprises investing in next-generation connectivity and expanded data center capacity primarily fueled this growth.
- Industrial electronics demonstrated steady growth at approximately 9%, supported by strong demand for automation solutions and the necessity for companies to adopt advanced technologies to remain competitive.
- Medical devices sustained stable growth of around 8%, driven by continuous demand for innovations that improve patient outcomes, enhance healthcare delivery efficiency, and encourage ongoing technological advancement within the sector.
- Defense, aerospace, automotive, and energy segments experienced moderate growth between 5% and 7%, benefiting from ongoing modernization efforts, increased electrification, and technology-driven improvements in operational efficiency.
- Diversification: Companies are actively diversifying revenue streams across industrial, medical, automotive, aerospace, and cloud sectors to reduce reliance on a single market. This approach mirrors strategies seen in the Enics-GPV and Asteelflash-USI deals, where acquirers combined complementary customer bases and expanded geographic coverage to strengthen resilience against sector-specific volatility.
- Innovation: Continued investments in advanced technologies—including high-density printed circuit boards, optical interconnects, and AI-enabled systems—are driving product innovation and enabling firms to stay ahead of evolving customer needs. Transactions like H.I.G. Capital’s acquisition of SMTC demonstrate the importance of embedding engineering and design capabilities to support next-generation electronic systems.
- Profitability: Firms prioritize operational efficiency and financial resilience through lean inventory management and robust cash flow. The Enics-GPV merger illustrates this focus, as the combined entity sought greater scale and process optimization to improve profitability while maintaining quality across diverse end markets.
- Agility: Rapidly evolving customer demand—driven by cloud infrastructure, 5G networks, electric vehicles, and IoT adoption—is accelerating the need for more sophisticated and flexible electronic systems. Acquisitions such as USI’s purchase of Asteelflash highlight how companies are expanding engineering resources and regional manufacturing capacity to respond quickly to these trends and better serve global OEMs.
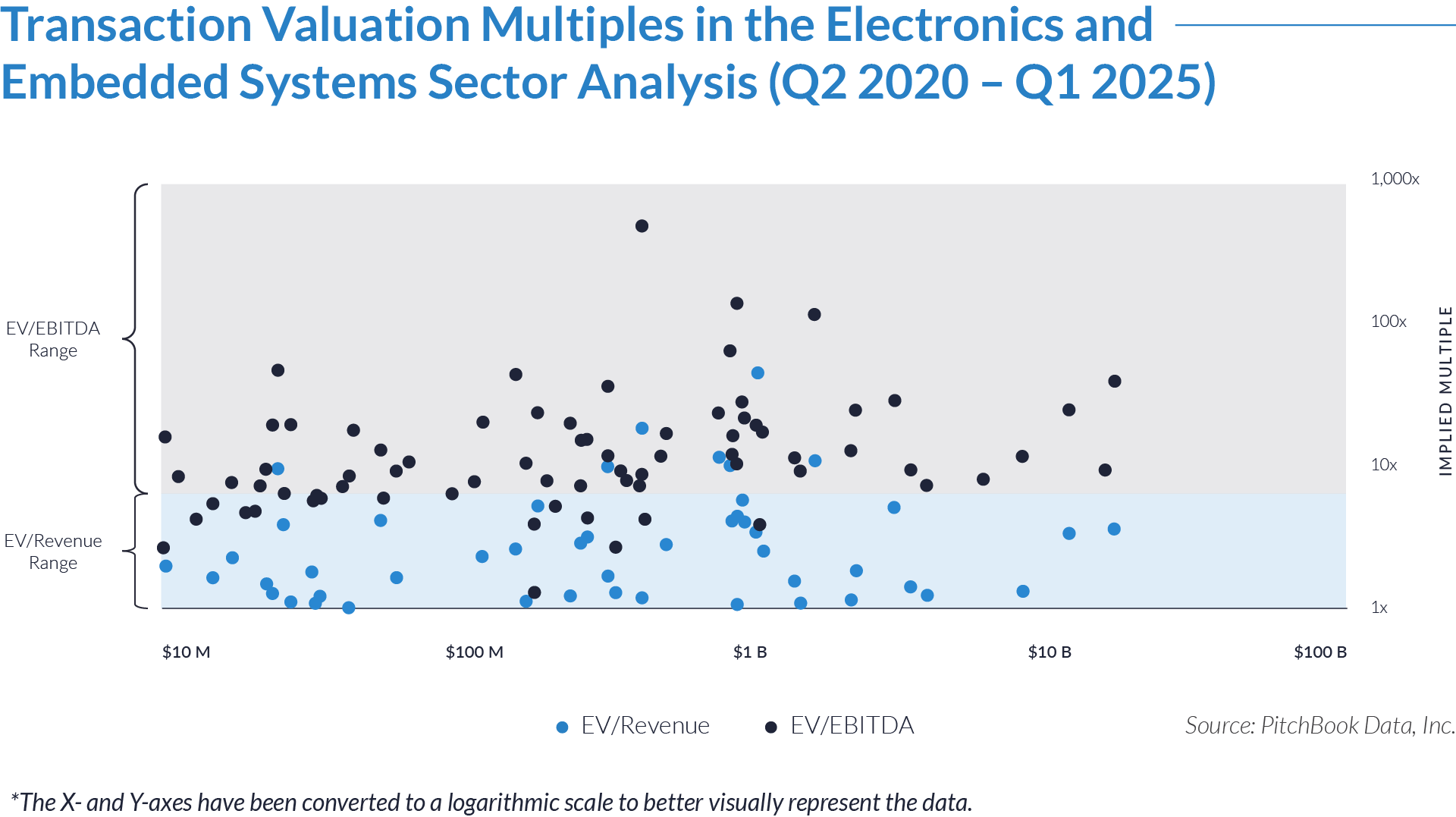

- Valuation multiples are based on a sample set of M&A transactions in the electronics and embedded systems sector using data collected on June 18, 2025.
- The data shows a wide dispersion in valuation multiples, with EV/revenue ranging from 1x to 47x and EV/EBITDA from 1x to 1,039x. This variation reflects the sector’s diverse composition, including both capital-intensive mature businesses and early-stage innovation-led firms. Companies at the higher end of these ranges typically offer proprietary technologies, embedded software capabilities, or IP-driven models that justify premium valuations due to scalability and recurring revenue potential.
- Most transactions occur within more moderate ranges—approximately 1x EV/revenue and 9x EV/EBITDA—indicating that many businesses in the sector pursue steady, incremental growth. These companies often operate in regulated industries such as aerospace, automotive, or industrial automation and rely on OEM partnerships, long-term contracts, or compliance-driven demand to maintain stable financial performance.
Capital Markets Activities
The data highlights transaction trends, valuation metrics, and investment activity in the electronics and embedded systems sector. Rising demand for intelligent devices and real-time control is driving M&A in embedded computing, SoC design, and edge processing. Buyers are targeting companies specializing in PCB design, embedded firmware, sensor integration, and industrial IoT solutions that enable automation and data-driven operations. These transactions support vertical integration across hardware, software, and connectivity, advancing smart manufacturing, automotive electrification, and high-reliability industrial systems. Investment is also growing in firms with modular architectures and secure embedded platforms.
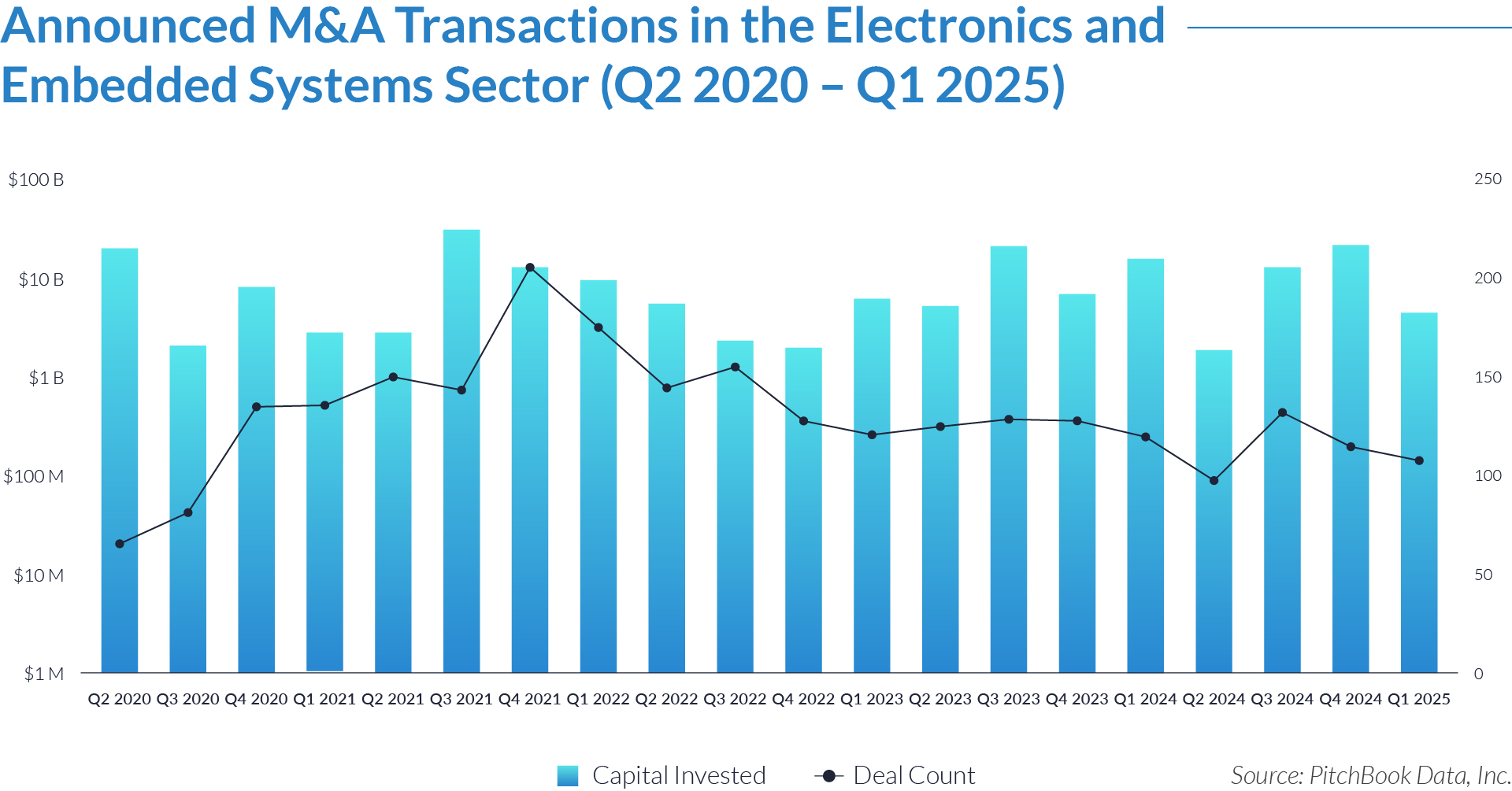
- Investors allocated approximately $179 billion across 2,577 deals in the electronics and embedded systems sector over the past 20 quarters. Strategic and financial acquirers consistently pursued targets involved in embedded technologies and advanced electronics manufacturing.
- Investors allocated approximately $28 billion in Q3 2021, the highest quarterly total across the 20-quarter period. The spike reflected intensified demand for embedded hardware, system design services, and scalable electronics platforms—driven by strategic buyers expanding their capabilities in advanced manufacturing and digital systems.
- Deal volume consistently ranged between 120 and 150 deals per quarter, even when capital investment varied significantly. This pattern indicates that investors prioritized smaller, strategic acquisitions—such as engineering consultancies, custom PCB providers, and embedded design houses—over large platform plays.
- After a low point of $2 billion in Q2 2024, capital investment recovered to $12 billion in Q3 and $20 billion in Q4. This rebound suggests that buyers renewed their focus on high-reliability manufacturing, edge computing platforms, and integration-ready embedded systems ahead of 2025.
The graphs below present the geographic distribution of transactions, providing additional detail on regional trends and investment dynamics.
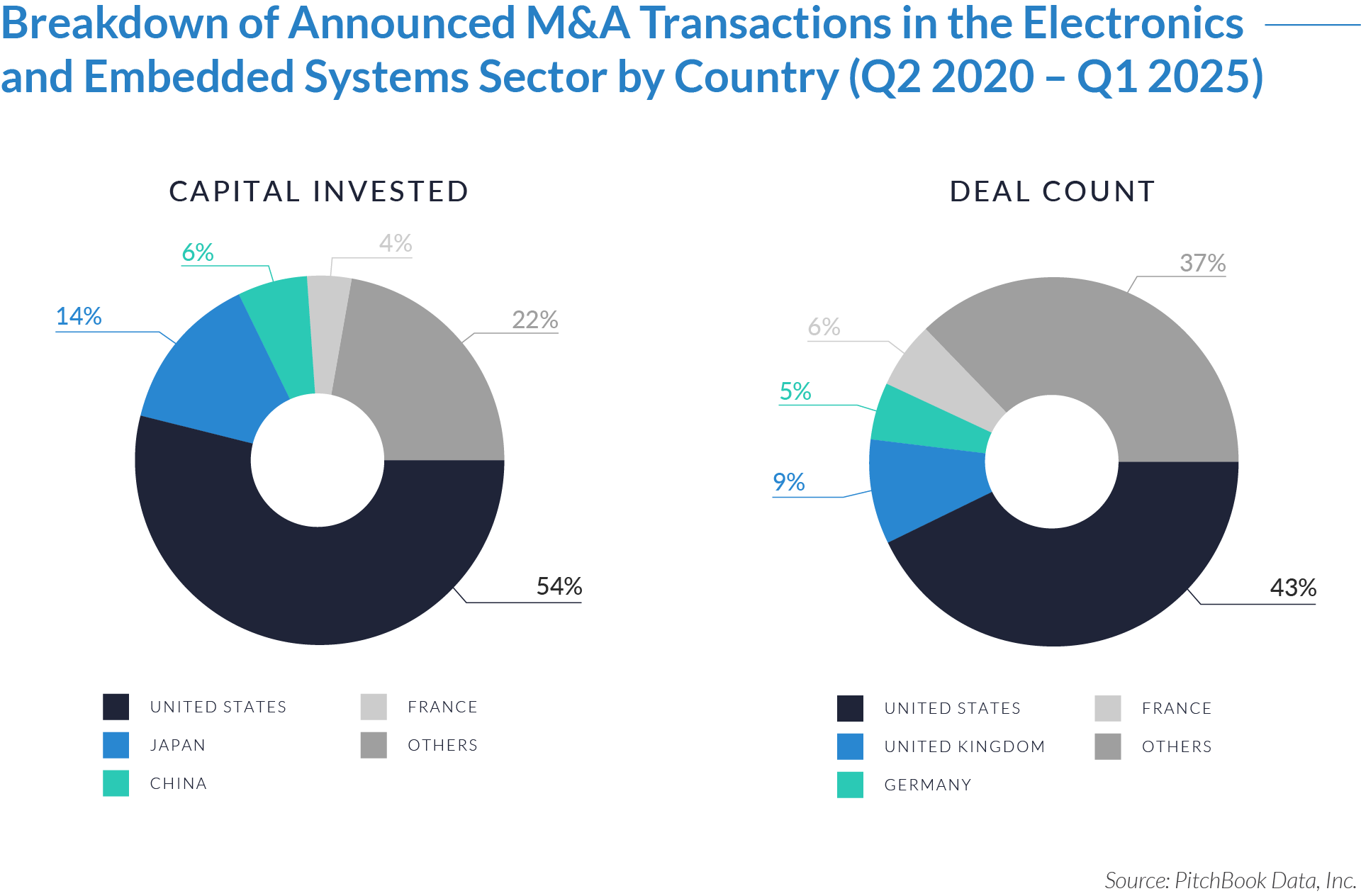
- US-based investors contributed 54% of total capital and executed 43% of the transactions, establishing the US as the most active and well-capitalized market in the electronics and embedded systems sector. This activity reflects the country’s concentration of private equity firms, institutional capital, and strategic acquirers driving both domestic and cross-border M&A.
- Buyers executed 37% of deals and allocated 22% of capital in international and emerging markets, indicating substantial transaction activity outside the top-tier investor countries. Acquirers focused on these regions for their cost efficiency, manufacturing capabilities, and regional specialization, reinforcing their growing importance in global M&A strategies.
- Japanese and Chinese investors deployed 14% and 6% of total capital, respectively. These capital flows supported cross-border expansion and sector exposure, particularly in advanced electronics and embedded systems. While these countries accounted for less deal volume, their financial contributions played a significant role in enabling international growth and supply chain integration.
The deal-type dynamics below set the stage for understanding how capital flows and strategic priorities shape the electronics and embedded systems sector growth and landscape.
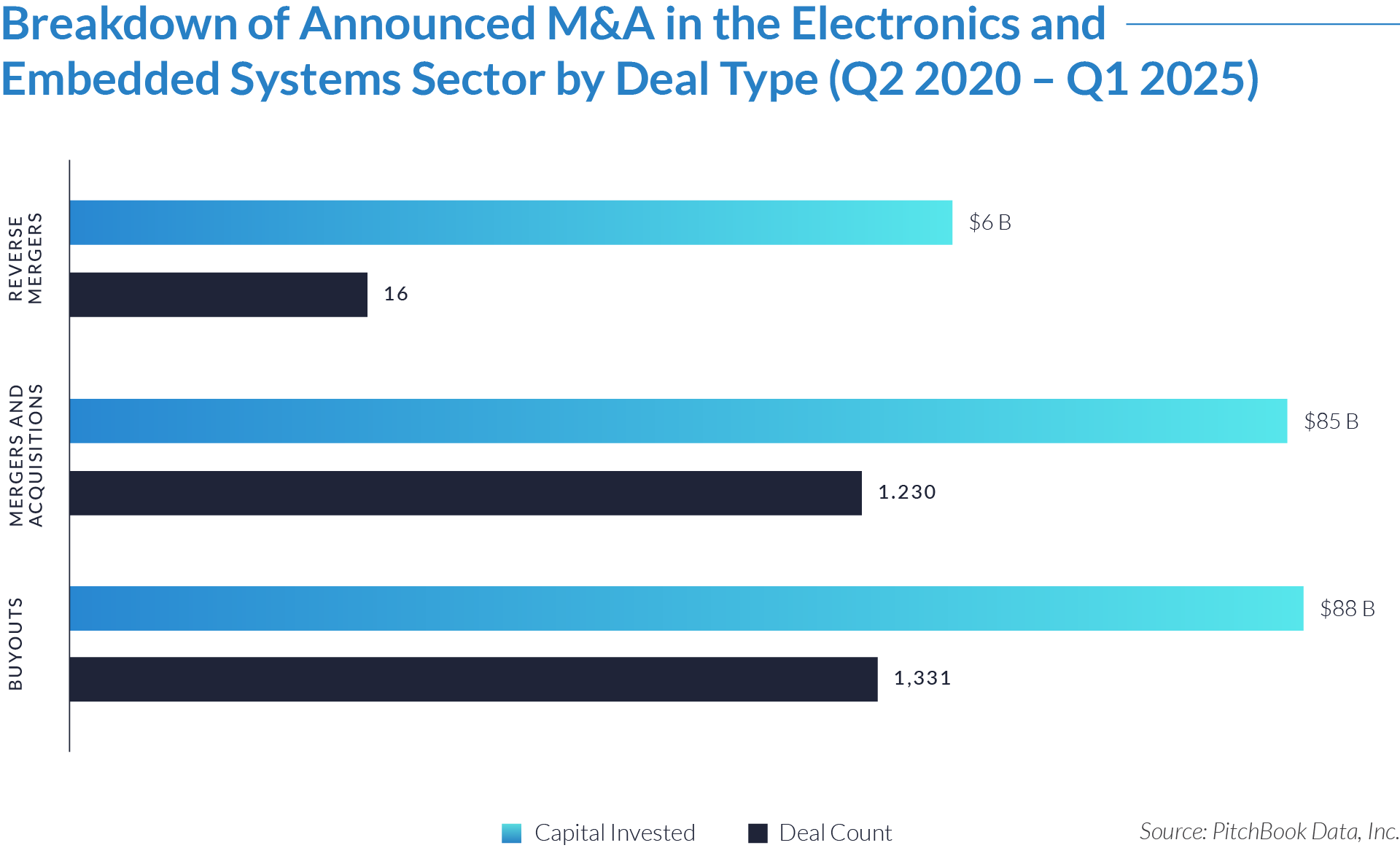
- Investors committed approximately $88 billion across 1,331 buyout transactions, making buyouts the most capital-intensive and widely used deal structure. Private equity and strategic acquirers primarily used this structure to gain control of platform assets in the electronics and embedded systems sector.
- Mergers and acquisitions generated roughly $85 billion across 1,230 deals, closely trailing buyouts. Strategic acquirers pursued these transactions to consolidate complementary technologies, expand customer bases, and enhance manufacturing capabilities.
- Reverse mergers accounted for only 16 transactions and approximately $6 billion in deal value. Sponsors and growth-stage companies likely used this structure to access public markets through non-traditional pathways.
M&A Transactions Case Studies
Three strategic transactions in the electronics and embedded systems sector reflect a shift toward vertical integration, embedded intelligence, and high-reliability design. The deals involved acquiring design firms, system integrators, and manufacturers to enable full-product lifecycle delivery. Targets offered expertise in PCB layout, firmware, and testing for complex, low-to-mid volume applications in industrial, medical, and aerospace markets. Acquirers expanded into embedded engineering to gain IP ownership, modular design capabilities, and long-term customer engagement. These moves support priorities around design control, innovation, and supply chain resilience amid growing demand for electrification, automation, and connectivity.

Case Study 01
ENICS

Enics, formerly headquartered in Switzerland, was a leading Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) provider specializing in industrial and medical electronics. Prior to its merger, the company offered end-to-end services including engineering support, PCB assembly, system integration, testing, and after-sales support. With operations across Europe and Asia, Enics served high-reliability sectors such as industrial automation, medical technology, energy, and transportation.

Transaction Structure
Enics merged with GPV International, a Danish EMS provider owned by Schouw & Co. As part of the deal, Schouw & Co. took an 80% stake in the combined company, while Ahlström Capital, Enics’s former majority owner, kept a 20% minority share. The transaction was completed in cash, but the financial details were not disclosed.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The merger formed one of Europe’s largest EMS providers by combining Enics’ expertise in industrial and medical electronics with GPV’s capabilities in high-mix, low- to medium-volume manufacturing across the industrial, cleantech, and instrumentation sectors. The combined group served a diversified customer base across Europe, Asia, and the Americas, operating 19 manufacturing sites with approximately 7,500 employees. This integration broadened the company’s end-market exposure and improved its ability to support OEMs seeking scalable, flexible manufacturing solutions.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
The merger aimed to create a globally positioned, mid-sized EMS company with a balanced portfolio across complementary markets. Enics and GPV shared a focus on quality, engineering-driven services, and long-term customer relationships, which positioned the combined business to benefit from trends such as nearshoring, supply chain diversification, and rising demand for intelligent industrial electronics. By merging operations, the companies achieved greater scale, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced competitiveness against larger global EMS providers. For Schouw & Co., the transaction supported its industrial investment strategy and reinforced its presence in the expanding electronics manufacturing sector.

Case Study 02
SMTC

SMTC Corporation, headquartered in Florida, is a global mid-sized Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) provider offering end-to-end solutions, including product design, PCB assembly, system integration, testing, and supply chain management. With facilities in the U.S., Canada, Mexico, and China, SMTC serves a diverse range of industries such as medical, industrial, aerospace, and telecommunications. The company holds certifications including ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and AS9100, enabling it to operate as a flexible, high-reliability manufacturing partner for complex electronic systems.

Transaction Structure
In April 2021, an affiliate of H.I.G. Capital acquired SMTC Corporation through a public-to-private leveraged buyout valued at $171 million. The deal was executed via an all-cash transaction, resulting in SMTC’s delisting from public markets.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
SMTC’s customer base spanned high-reliability and regulated sectors, including medical devices, industrial automation, aerospace, defense, and telecommunications. The acquisition strengthened H.I.G. Capital’s portfolio in these areas by expanding access to mission-critical electronic products and key OEM relationships. The combination enabled SMTC to scale its operations across North America and Asia and improved customer diversification across both established and emerging technology markets.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
The acquisition was driven by H.I.G. Capital’s objective to expand its presence in the growing EMS sector by leveraging SMTC’s operational strength, vertically integrated service offerings, and global footprint. The buyout aimed to accelerate SMTC’s growth through operational improvements, targeted investments, and increased responsiveness to customer needs. Transitioning to private ownership gave SMTC greater strategic flexibility to pursue long-term initiatives and innovation without the constraints of public market reporting.

Case Study 03
ASTEELFLASH
Asteelflash is a global Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) provider and a wholly owned subsidiary of USI Group. The company operates 18 manufacturing facilities across North America, Europe, North Africa, and Asia, delivering end-to-end solutions such as PCB assembly, box-build, system integration, testing, and post-production support. Asteelflash serves complex and regulated industries including aerospace, automotive, energy, medical, and IoT. Its operations specialize in high-mix, low- to mid-volume production and emphasize advanced engineering, supply chain agility, and smart manufacturing capabilities.

Transaction Structure
In August 2020, Universal Scientific Industrial (Shanghai) Company (SHG: 601231) acquired Asteelflash in a full cash transaction valued at $516 million.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The acquisition brought together Asteelflash’s established presence in Europe and North America with USI’s operational base in Asia, resulting in a more geographically balanced global manufacturing network. The integration expanded customer reach across key end markets, particularly in high-complexity, high-reliability segments such as automotive electronics, industrial IoT, and medical devices. This combination enabled stronger geographic coverage and deeper engagement with multinational OEMs seeking EMS partners that offer both local responsiveness and global scalability.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
USI acquired Asteelflash to expand its global footprint, strengthen its position in the European market, and diversify its customer portfolio. Asteelflash’s expertise in high-mix, low- to mid-volume production complemented USI’s strength in high-volume manufacturing, allowing the combined entity to address a broader range of product complexity. The acquisition also provided access to Asteelflash’s experienced engineering talent and flexible manufacturing capabilities, supporting USI’s strategic objective of becoming a more agile, regionally diversified, and technology-oriented EMS provider.
Buyers maintained consistent M&A activity in the electronics and embedded systems sector over the past five years, targeting businesses that deliver embedded intelligence, high-reliability design, and scalable manufacturing capabilities. Valuation multiples varied due to differences in company maturity, technical complexity, and revenue visibility. Acquirers prioritized targets with strong engineering capabilities, diversified customer bases, and regional manufacturing presence. Ongoing demand for automation, connectivity, and intelligent systems will likely sustain buyer interest and drive continued consolidation across the sector.
Source: H.I.G. Capital, LINCOLN International, GPV, AHLSTROM, PR Newswire, Pitchbook Data.