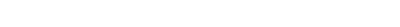Mass Transit Components and Services Sector M&A Transactions and Valuations
Mass Transit Components and Services Sector M&A Transactions and Valuations

Between 2020 and early 2025, buyers accelerated their activity in the mass transit components and services sector, responding to industry-wide shifts in fleet electrification, digital procurement, and lifecycle service integration. Strategic and financial acquirers targeted companies that provide aftermarket parts, mobile field services, fleet diagnostics, and component technologies supporting electric and hybrid transit systems. These acquirers pursued M&A opportunities to consolidate fragmented value chains, expand service footprints, and meet growing institutional demand for efficient, full-service transit solutions.
This report analyzes transaction activity and valuation dynamics in the sector from Q2 2020 to Q1 2025. It evaluates strategic trends, capital deployment, and valuation benchmarks, including EV/revenue and EV/EBITDA multiples. Key transactions-such as New Flyer’s acquisition of NABI, Model 1’s purchase of Alliance Bus Group, and Interstate Companies’ acquisition of Telin Transportation Group-highlight industry priorities including vertical integration, geographic expansion, and aftermarket monetization. The analysis presents investment themes and pricing patterns relevant to acquirers and buyers navigating this rapidly evolving mobility landscape.

Key Market Trends in the Mass Transit Components and Services Sector
This section outlines key trends driving consolidation, service integration, and value creation in the mass transit components sector. It highlights digital procurement, fleet modernization, and the shift toward full-service lifecycle models as core growth drivers.

- Consolidation and Vertical Integration: Companies in the sector are increasingly engaging in mergers and acquisitions to create end-to-end lifecycle platforms. These integrated models combine parts distribution, maintenance services, and technical support under one provider, enhancing operational efficiency and overall customer value.
- Digital Procurement and Inventory Solutions: Firms are investing in digital tools to streamline procurement, improve inventory visibility, and optimize fulfillment. Key advancements include automated reordering, real-time tracking, and integration with fleet management and ERP systems.
- Fleet Modernization Driving Component Complexity: The transition to electric and hybrid vehicles is driving demand for more varied component inventories. Suppliers must now support both legacy and next-generation fleets with an expanded range of parts, retrofit solutions, and engineering services.
- Diversification Beyond OEM Supply Chains: Transit agencies and fleet operators are increasingly sourcing components from non-OEM suppliers to reduce costs, minimize lead times, and avoid sole-source risks. This trend is fueling demand for flexible, multi-brand parts providers.
- Integrated Labor and Field Service Delivery: Suppliers are differentiating by delivering bundled solutions-such as mobile technician support, repair programs, custom kitting, and diagnostics-positioning themselves as full-service lifecycle partners rather than traditional parts vendors.

- Prior to 2020, the sector was largely fragmented, dominated by parts suppliers operating under transactional business models. Most companies focused exclusively on distribution, offering limited services and little integration with fleet operators.
- Between 2020 and 2023, the industry began consolidating through regional acquisitions. Companies expanded their offerings by bundling parts with field services, diagnostics, and support programs-marking a shift toward more integrated service models.
- In the latest phase, leading firms have evolved into full-service lifecycle partners. This transformation includes the adoption of digital procurement platforms, custom kitting, rebuild and retrofit services, and compatibility with electric and hybrid transit fleets-delivering end-to-end solutions for both public and private operators.

- Valuation multiples are based on a sample set of M&A transactions in the mass transit components and services sector using data collected on July 28, 2025.
- Transactions with EVs exceeding $100 million frequently show EV/revenue greater than 10x and EV/EBITDA greater than 100x, reflecting strategic acquisitions of integrated platforms with end-to-end service models. These targets typically combine multi-brand parts distribution with mobile technician programs, digital inventory systems, and long-term agency relationships—characteristics that drive pricing power, recurring revenue, and post-acquisition synergies.
- Most deals in the $25–150 million EV range trade around 2–3x EV/revenue and 10–15x EV/EBITDA. These targets often serve as regional service providers or second-tier integrators offering bundled parts and support services. Their valuations reflect balanced fundamentals: predictable cash flow, cost-efficient operations, and alignment with transit agency priorities such as reduced lead times and modernized fleet support.
- Numerous smaller deals with EVs under $25 million show valuation levels below 1x EV/revenue and 8x EV/EBITDA, highlighting a fragmented landscape of under-scaled distributors and niche service providers. These companies often lack digital procurement systems, embedded technician support, or multi-fleet compatibility, but represent attractive roll-up targets for buyers pursuing geographic expansion and integrated lifecycle service models.

Capital Markets Activities
M&A activity in the mass transit components and services sector is driven by fleet modernization, cost reduction, and service integration. Buyers target scalable providers offering parts distribution, field services, and digital procurement. Transactions focus on vertical integration and support for electric, hybrid, and legacy fleets, reflecting growing demand for full-service, cost-efficient lifecycle platforms.
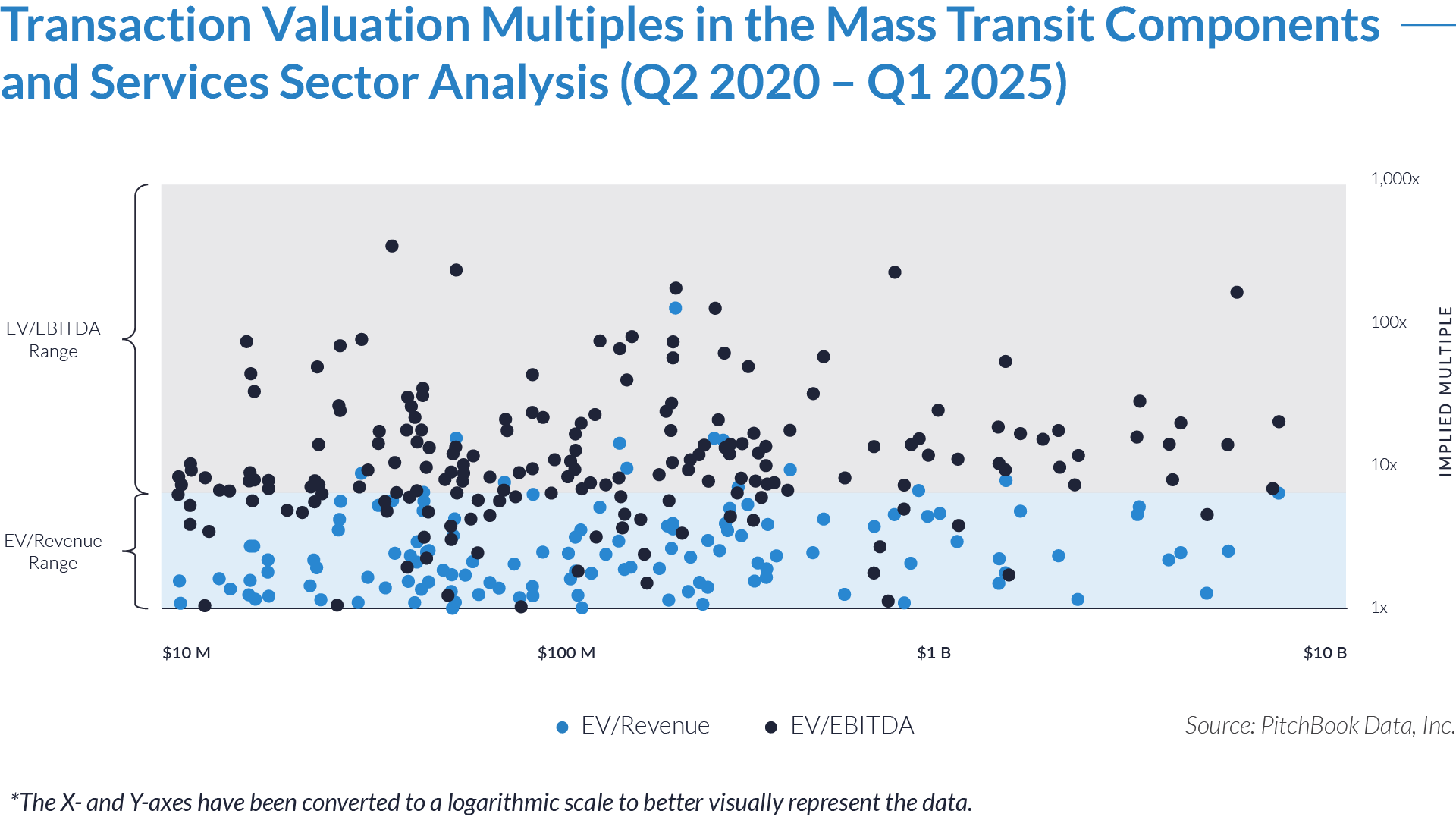
- Buyers committed a total of $255 billion across 1,362 deals over the 20-quarter period, reflecting sustained momentum and long-term confidence in the mass transit components and services sector.
- More than $64 billion was deployed between Q3 2021 and Q1 2022, with Q4 2021 marking the peak at $24 billion across 104 deals—the highest quarterly total by both value and volume. This spike was driven by stimulus-backed infrastructure spending and accelerated investment in transit modernization following pandemic-era disruptions.
- In 2023, acquirers closed over 300 deals, but capital deployment fluctuated. Investment dropped to $4 billion in Q2, then rebounded to $18 billion and $11 billion in subsequent quarters. The pattern reflects a shift toward more selective dealmaking amid tightening macroeconomic and financing conditions.
- Capital deployment gained renewed momentum in late 2024 and early 2025, with Q1 2025 totaling $21 billion across just 60 deals-a sign that buyers are prioritizing quality over quantity and shifting away from broad-based consolidation strategies.
The graphs below present the geographic distribution of transactions, providing additional detail on regional trends and investment dynamics.
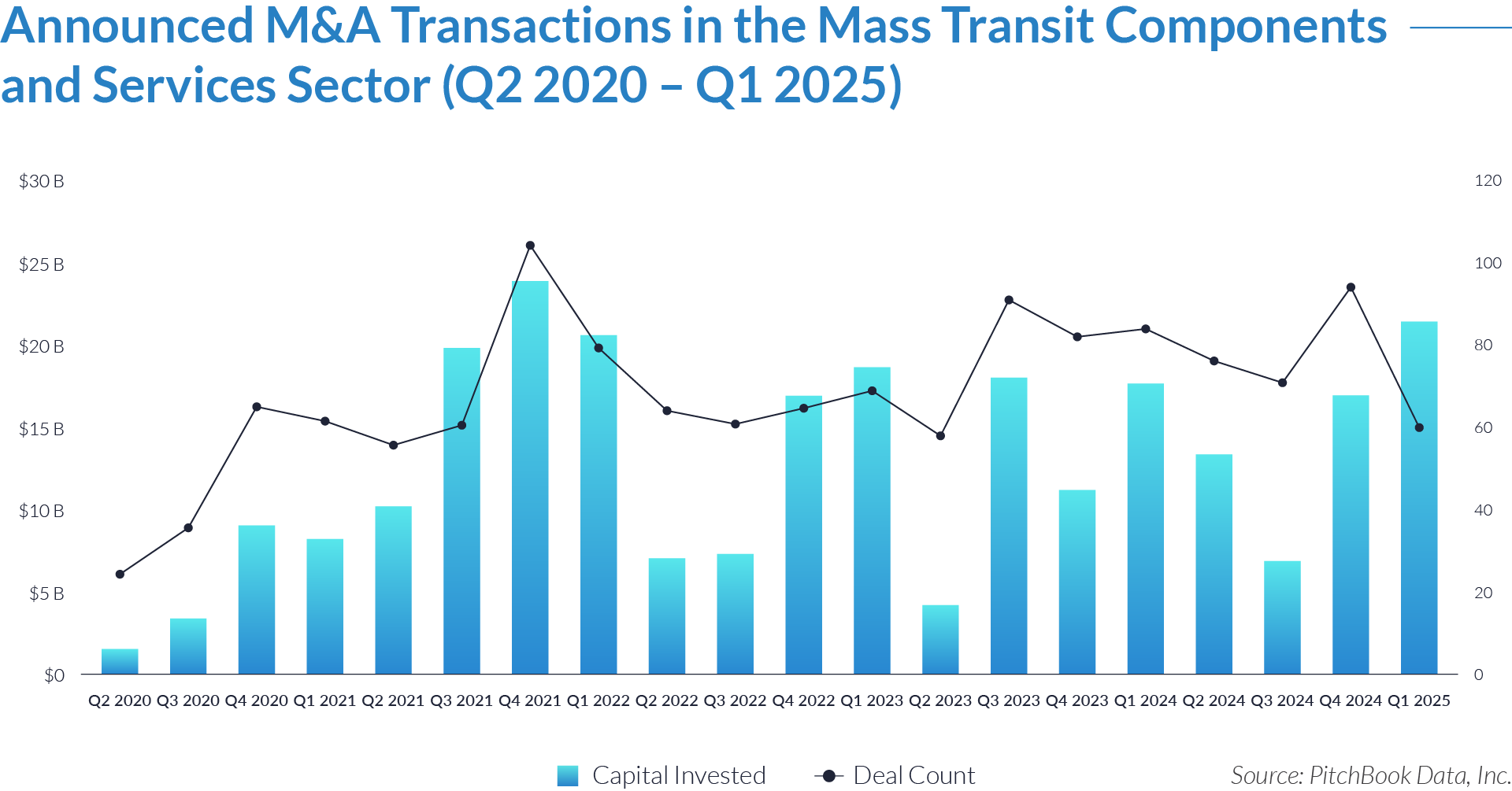
- US-based buyers accounted for 49% of total capital deployed, underscoring their leading role in shaping sector consolidation. This reflects the scale and strategic ambitions of North American firms seeking to expand vertically across parts distribution, mobile field services, and digital procurement. These buyers often target platform businesses with recurring revenue models and embedded service capabilities.
- While capital was concentrated among a few developed markets, over 50% of deal activity targeted companies in emerging and international regions beyond the US, UK, and China. This shift reflects growing demand for transit modernization, localized parts support, and service infrastructure in rapidly urbanizing regions-driving investment in multi-brand providers capable of serving diverse fleet configurations.
- China attracted 9% of deal activity, signaling buyers interest in domestic suppliers and aftermarket players amid restructuring trends and increased focus on electrification and localized production. In contrast, Germany and Canada contributed a combined 12% of total capital, consistent with their broader participation in global industrial and infrastructure investments, though with fewer transactions relative to US dealmakers.
The deal-type dynamics below set the stage for understanding how capital flows and strategic priorities shape the mass transit components and services sector growth and landscape.
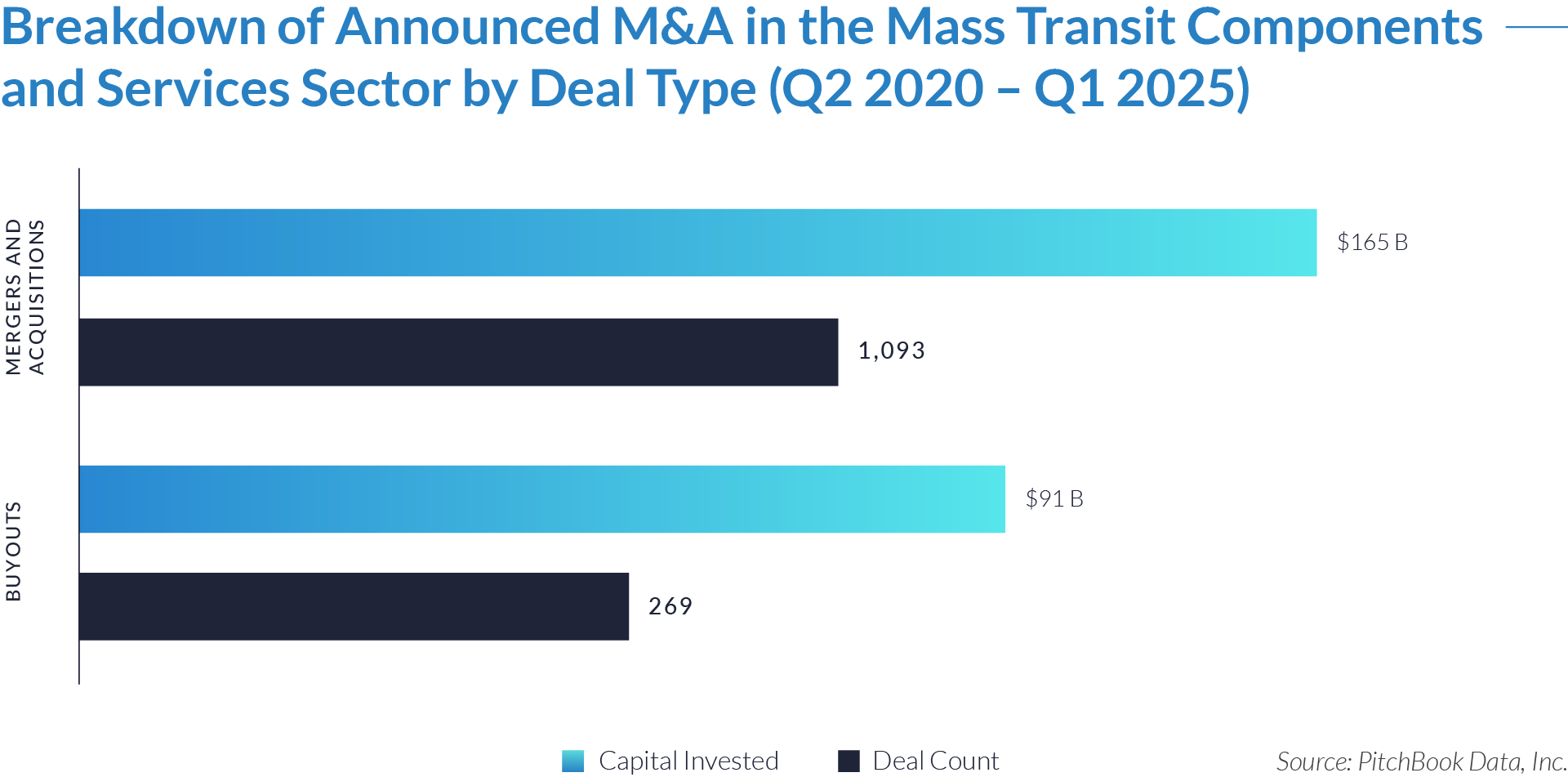
- Buyers completed 1,093 M&A transactions totaling $165 billion, representing over 60% of total capital deployed. This underscores a strong strategic focus on consolidation to gain market share, capture synergies, and build integrated service platforms within the evolving transit ecosystem.
- Buyout activity accounted for 269 deals and $91 billion, a smaller share by volume but marked by significantly higher average deal sizes. This reflects a more selective approach, with investors targeting scalable, high-margin businesses offering long-term value and operational leverage.
- M&A remained the primary growth driver, enabling rapid expansion into adjacent markets and service lines. These transactions supported vertical integration, product diversification, and geographic scale, reinforcing buyer efforts to build comprehensive, full-service transit solutions.
M&A Transactions Case Studies
Three strategic transactions in the mass transit components and services sector reflect growing consolidation among parts suppliers, service networks, and vehicle integrators aiming to deliver end-to-end lifecycle solutions. The acquired companies-each with strong regional footprints, institutional customer relationships, and aftermarket capabilities-enabled acquirers to expand geographic reach, deepen OEM alignment, and strengthen recurring revenue through service and parts. These transactions demonstrate a broader industry shift toward vertical integration, aftermarket monetization, and full-service platforms.

Case Study 01
TELIN TRANSPORTATION GROUP

Telin Transportation Group, based in Farmington, Minnesota, was a leading regional dealer and authorized Thomas Built Bus distributor. It provided new and used bus sales, parts distribution, warranty repairs, and full-service fleet maintenance to institutional and municipal clients-including K–12 school districts, transit agencies, and private shuttle operators. Telin also developed expertise in electric school bus deployment, offering grant advisory, fleet planning, and charging infrastructure support. Known for its strong service culture and long-standing customer relationships, Telin was a key partner in school transportation across the Upper Midwest.

Transaction Structure
Interstate Companies acquired Telin Transportation Group through an asset purchase. The purchase price was not disclosed.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The acquisition of Telin extended Interstate Companies’ footprint into Minnesota, complementing its existing presence in Montana, Wyoming, North Dakota, and South Dakota. Telin brought long-standing relationships with school transportation agencies, public fleet operators, and electrification-focused government clients. This added new customer segments and strengthened ties to Thomas Built Bus accounts, while enabling cross-selling across vehicle sales, parts, and service contracts. It also improved responsiveness to institutional customers through enhanced regional proximity.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
The transaction supported Interstate’s regional growth and reinforced its national presence under the I-State Truck Centers brand. It strengthened OEM alignment by deepening Interstate’s role as a certified Thomas Built Bus dealer and service provider. The deal also expanded aftermarket capabilities, adding inventory, an established customer base, and opportunities to grow recurring revenue through parts delivery, warranty work, and fleet maintenance. Notably, it advanced Interstate’s entry into the electric school bus market, leveraging Telin’s emerging expertise in EV consulting, infrastructure support, and grant advisory-positioning the combined entity to meet rising demand and government funding opportunities.

Case Study 02
ALLIANCE BUS GROUP

Alliance Bus Group was the second-largest bus dealership network in the US, operating approximately eight locations nationwide. The company offered a full suite of services spanning the entire vehicle lifecycle-including sales of new and used paratransit, school, transit, and shuttle buses, as well as parts distribution, maintenance, refurbishment, training, and financing-reflecting its “Along for the Whole Ride” philosophy. With over 100 employees, a large inventory of OEM and aftermarket parts, next-day shipping capabilities, in-house technical support, and warranty services, Alliance delivered comprehensive fleet solutions to transit and commercial vehicle operators.

Transaction Structure
Model 1 Commercial Vehicles (formerly Creative Bus Sales) acquired Alliance Bus Group through an asset purchase. The transaction value was not disclosed.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
The acquisition significantly expanded Model 1’s presence in the paratransit, shuttle, school transportation, and public fleet segments, particularly across the Southeast, Northeast, and Texas-regions where Alliance Bus Group had strong, long-standing relationships. Alliance’s customer base included municipal transit agencies, school systems, healthcare transport providers, and government fleet operators. These segments closely aligned with Model 1’s existing clientele, creating opportunities for cross-selling vehicles, parts, and services while lowering customer acquisition costs in overlapping markets.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
The transaction advanced several strategic goals for Model 1, including geographic growth through the addition of five regional hubs-bringing its total network to over 21 locations nationwide. Alliance’s established OEM partnerships enhanced Model 1’s brand portfolio and dealer coverage, improving its leverage in manufacturer negotiations. The deal also strengthened aftermarket capabilities by integrating parts inventories, warehousing infrastructure, and a sizable installed customer base, supporting logistics efficiency and recurring revenue growth. Most importantly, the acquisition accelerated Model 1’s transition toward a vertically integrated platform, expanding its offering beyond vehicle sales to include parts, technical services, leasing, and mobile field support-fully aligned with fleet lifecycle management strategies.

Case Study 03
NABI

North American Bus Industries (NABI) was a US-based manufacturer of heavy-duty transit buses that operated from 1992 to 2015. The company offered a broad portfolio of models-including high-floor, low-floor, articulated, and composite-bodied designs-available with various conventional and alternative powertrain configurations. In addition to manufacturing, NABI operated an aftermarket parts division in Delaware, Ohio, and maintained service support facilities in Mira Loma, California, providing ongoing support for its extensive installed fleet throughout North America.

Transaction Structure
New Flyer acquired NABI for $80 million in cash, funded through a combination of new equity from Marcopolo S.A. and a drawdown from its existing senior credit facility.
Market and Customer Segments Combination
NABI’s customer base consisted primarily of large municipal transit agencies and public transportation authorities across North America-segments that closely mirrored New Flyer’s existing clientele. The acquisition enabled New Flyer to increase market share in the US public fleet sector, gain access to transit agencies previously served by NABI, and capitalize on NABI’s legacy platforms to drive additional parts and service revenue.
Acquisition Strategic Rationale
The acquisition reinforced New Flyer’s position as North America’s leading transit bus manufacturer by removing a major competitor and integrating NABI’s manufacturing and service operations. It expanded New Flyer’s aftermarket capabilities through NABI’s established parts distribution and field service infrastructure, improving support for its growing installed base. The deal also allowed New Flyer to streamline its product lineup by phasing out NABI’s older bus models and focusing on its more advanced platform-enhancing production efficiency, reducing costs, and aligning operations with long-term goals for innovation and sustainability.

M&A activity in the mass transit components and services sector remained strong over the past five years, fueled by continued investment in fleet modernization, digital parts distribution, and integrated service platforms. Strategic buyers targeted companies with recurring aftermarket revenue, strong institutional relationships, and the ability to support electric and hybrid transit fleets. Financial sponsors pursued scalable operators with regional density, operational synergies, and potential for platform expansion. Valuation multiples varied widely, shaped by company size, service integration, and alignment with long-term infrastructure trends. Looking ahead, sustained demand for transit reliability, cost efficiency, and lifecycle support is expected to drive ongoing M&A as buyers seek differentiated assets to lead in an increasingly service-oriented and electrified mobility ecosystem.
Source: Model 1, Interstate Companies, TORYS, New Flyer, Pitchbook Data.